Mapreduce实例——最高温度排序
实验目的
1.了解Mapreduce排序的实验原理
2.熟练掌握Mapreduce排序的程序代码编写
3.培养编写MapReduce排序代码解决问题的能力
实验原理
Hadoop中Map、Reduce任务中Shuffle和排序的过程图如下:
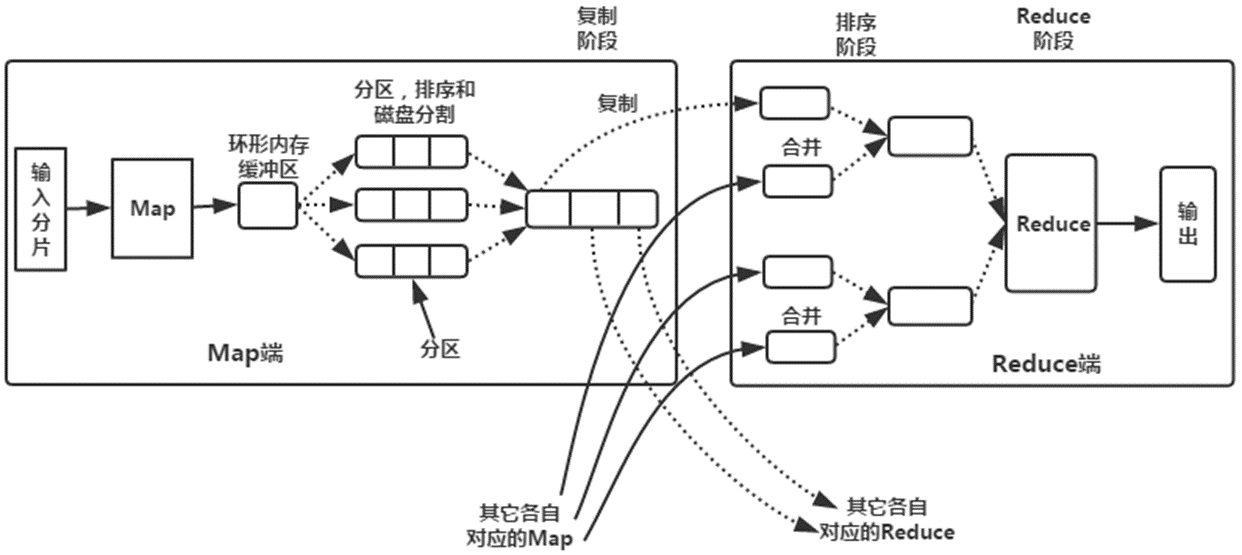
流程分析:
1.Map端
(1)每个输入分片会让一个map任务来处理,默认情况下,以HDFS的一个块的大小(默认为64M)为一个分片,当然我们也可以设置块的大小。map输出的结果会暂且放在一个环形内存缓冲区中(该缓冲区的大小默认为100M,由io.sort.mb属性控制),当该缓冲区快要溢出时(默认为缓冲区大小的80%,由io.sort.spill.percent属性控制),会在本地文件系统中创建一个溢出文件,将该缓冲区中的数据写入这个文件。
(2)在写入磁盘之前,线程首先根据reduce任务的数目将数据划分为相同数目的分区,也就是一个reduce任务对应一个分区的数据。这样做是为了避免有些reduce任务分配到大量数据,而有些reduce任务却分到很少数据,甚至没有分到数据的尴尬局面。其实分区就是对数据进行hash的过程。然后对每个分区中的数据进行排序,如果此时设置了Combiner,将排序后的结果进行Combia操作,这样做的目的是让尽可能少的数据写入到磁盘。
(3)当map任务输出最后一个记录时,可能会有很多的溢出文件,这时需要将这些文件合并。合并的过程中会不断地进行排序和combia操作,目的有两个:①尽量减少每次写入磁盘的数据量。②尽量减少下一复制阶段网络传输的数据量。最后合并成了一个已分区且已排序的文件。为了减少网络传输的数据量,这里可以将数据压缩,只要将mapred.compress.map.out设置为true就可以了。
(4)将分区中的数据拷贝给相对应的reduce任务。有人可能会问:分区中的数据怎么知道它对应的reduce是哪个呢?其实map任务一直和其父TaskTracker保持联系,而TaskTracker又一直和JobTracker保持心跳。所以JobTracker中保存了整个集群中的宏观信息。只要reduce任务向JobTracker获取对应的map输出位置就ok了哦。
到这里,map端就分析完了。那到底什么是Shuffle呢?Shuffle的中文意思是“洗牌”,如果我们这样看:一个map产生的数据,结果通过hash过程分区却分配给了不同的reduce任务,是不是一个对数据洗牌的过程呢?
2.Reduce端
(1)Reduce会接收到不同map任务传来的数据,并且每个map传来的数据都是有序的。如果reduce端接受的数据量相当小,则直接存储在内存中(缓冲区大小由mapred.job.shuffle.input.buffer.percent属性控制,表示用作此用途的堆空间的百分比),如果数据量超过了该缓冲区大小的一定比例(由mapred.job.shuffle.merge.percent决定),则对数据合并后溢写到磁盘中。
(2)随着溢写文件的增多,后台线程会将它们合并成一个更大的有序的文件,这样做是为了给后面的合并节省时间。其实不管在map端还是reduce端,MapReduce都是反复地执行排序,合并操作,现在终于明白了有些人为什么会说:排序是hadoop的灵魂。
(3)合并的过程中会产生许多的中间文件(写入磁盘了),但MapReduce会让写入磁盘的数据尽可能地少,并且最后一次合并的结果并没有写入磁盘,而是直接输入到reduce函数。
熟悉MapReduce的人都知道:排序是MapReduce的天然特性!在数据达到reducer之前,MapReduce框架已经对这些数据按键排序了。但是在使用之前,首先需要了解它的默认排序规则。它是按照key值进行排序的,如果key为封装的int为IntWritable类型,那么MapReduce按照数字大小对key排序,如果Key为封装String的Text类型,那么MapReduce将按照数据字典顺序对字符排序。
了解了这个细节,我们就知道应该使用封装int的Intwritable型数据结构了,也就是在map这里,将读入的数据中要排序的字段转化为Intwritable型,然后作为key值输出(不排序的字段作为value)。reduce阶段拿到<key,value-list>之后,将输入的key作为的输出key,并根据value-list中的元素的个数决定输出的次数。
实验环境
Linux Ubuntu 14.04
jdk-7u75-linux-x64
hadoop-2.6.0-cdh5.4.5
hadoop-2.6.0-eclipse-cdh5.4.5.jar
eclipse-java-juno-SR2-linux-gtk-x86_64
实验内容
经过清洗我们得到2017年7月的部分温度数据,数据存储到temperature_tb表中,包含(日期 ,温度)两个字段,内容以“\t”分割,样例数据内容如下:
1. date temperature
2. 2017-07-01 26
3. 2017-07-02 25
4. 2017-07-03 19
5. 2017-07-04 18
6. 2017-07-05 21
7. 2017-07-06 24
8. 2017-07-07 22
9. 2017-07-08 25
10. 2017-07-09 25
11. 2017-07-10 26
12. 2017-07-11 22
13. 2017-07-12 28
14. 2017-07-13 29
15. 2017-07-14 26
16. 2017-07-15 23
17. 2017-07-16 28
18. 2017-07-17 29
19. 2017-07-18 27
20. 2017-07-19 25
21. 2017-07-20 26
要求编写mapreduce程序来对温度由低到高进行排序,从而找出最高温度的日期。
实验结果数据如下:
1. temperature date
- 2.
3. 18 2017-07-04
4. 19 2017-07-03
5. 21 2017-07-05
6. 22 2017-07-07
7. 22 2017-07-11
8. 23 2017-07-15
9. 24 2017-07-06
10. 25 2017-07-09
11. 25 2017-07-08
12. 25 2017-07-19
13. 25 2017-07-02
14. 26 2017-07-20
15. 26 2017-07-14
16. 26 2017-07-10
17. 26 2017-07-01
18. 27 2017-07-18
19. 28 2017-07-16
20. 28 2017-07-12
21. 29 2017-07-13
22. 29 2017-07-17
实验步骤
1.切换到/apps/hadoop/sbin目录下,启动hadoop。
1. cd /apps/hadoop/sbin
- 2.
3. ./start-all.sh
2.在Linux本地新建/data/mapreduce13目录。
1. mkdir -p /data/mapreduce13
3.将命令行切换到/data/mapreduce13目录下,用wget命令从http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce13网址上下载数据文件data.txt。
1. cd /data/mapreduce13
2. wget http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce13/data.txt
然后在当前目录下用wget命令从http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce13/hadoop2lib.tar.gz网址上下载项目用到的依赖包。
1. wget http://192.168.1.100:60000/allfiles/mapreduce13/hadoop2lib.tar.gz
将hadoop2lib.tar.gz解压到当前目录下。
1. tar zxvf hadoop2lib.tar.gz
4.首先在hdfs上新建/mymapreduce13/in目录,然后将Linux本地/data/mapreduce13目录下的data.txt文件导入到hdfs的/mymapreduce13/in目录中。
1. hadoop fs -mkdir -p /mymapreduce13/in
2. hadoop fs -put /data/mapreduce13/data.txt /mymapreduce13/in
5.新建Java Project项目,项目名为mapreduce13。
在mapreduce13项目下新建包,包名为mapreduce。
在mapreduce包下新建类,类名为Temperature。
6.添加项目所需依赖的jar包,右键单击项目新建一个文件夹,名为libs,用于存放项目所需的jar包。
将/data/mapreduce13目录下hadoop2lib文件夹中的所有jar包,拷贝到eclipse中mapreduce13项目的libs目录下。
选中libs目录下所有jar包,单击右键,选择Build Path→Add to Build Path。
7.编写Java代码
在MapReduce过程中默认就有对数据的排序。它是按照key值进行排序的,如果key为封装int的IntWritable类型,那么MapReduce会按照数字大小对key排序,如果Key为封装String的Text类型,那么MapReduce将按照数据字典顺序对字符排序。在本例中我们用到第一种,key设置为IntWritable类型,其中MapReduce程序主要分为Map部分和Reduce部分。
Map部分代码:
1. public static class Map extends Mapper<Object , Text , IntWritable,Text >{
- 2. private static Text date=new Text();
- 3. private static IntWritable temperature=new IntWritable();
- 4. public void map(Object key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
- 5. String line=value.toString();
- 6. String arr[]=line.split("\t");
- 7. temperature.set(Integer.parseInt(arr[1]));
- 8. date.set(arr[0]);
- 9. context.write(temperature,date);
- 10. }
- 11. }
在map端采用Hadoop默认的输入方式之后,将输入的value值用split()方法截取,把要排序的温度字段转化为IntWritable类型并设置为key,日期字段设置为value,然后直接输出<key,value>。map输出的<key,value>先要经过shuffle过程把相同key值的所有value聚集起来形成后交给reduce端。
Reduce部分代码:
1. public static class Reduce extends Reducer<IntWritable,Text,IntWritable,Text>{
- 2. private static IntWritable result= new IntWritable();
- 3. //声明对象result
- 4. public void reduce(IntWritable key,Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
- 5. for(Text val:values){
- 6. context.write(key,val);
- 7. }
- 8. }
- 9. }
reduce端接收到<key,value-list>之后,将输入的key直接复制给输出的key,用for循环遍历value-list并将里面的元素设置为输出的value,然后将<key,value>逐一输出,根据value-list中元素的个数决定输出的次数。
完整代码:
1. package mapreduce;
2. import java.io.IOException;
3. import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
4. import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
5. import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
6. import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
7. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
8. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
9. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
10. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
11. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.TextInputFormat;
12. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
13. import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat;
- 14.
15. public class Temperature {
- 16. public static class Map extends Mapper<Object , Text , IntWritable,Text >{
- 17. private static Text goods=new Text();
- 18. private static IntWritable num=new IntWritable();
- 19. public void map(Object key,Text value,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
- 20. String line=value.toString();
- 21. String arr[]=line.split("\t");
- 22. num.set(Integer.parseInt(arr[1]));
- 23. goods.set(arr[0]);
- 24. context.write(num,goods);
- 25. }
- 26. }
- 27. public static class Reduce extends Reducer< IntWritable, Text, IntWritable, Text>{
- 28. private static IntWritable result= new IntWritable();
- 29. public void reduce(IntWritable key,Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException{
- 30. for(Text val:values){
- 31. context.write(key,val);
- 32. }
- 33. }
- 34. }
- 35. public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException{
- 36. Configuration conf=new Configuration();
- 37. Job job =new Job(conf,"Temperature");
- 38. job.setJarByClass(Temperature.class);
- 39. job.setMapperClass(Map.class);
- 40. job.setReducerClass(Reduce.class);
- 41. job.setOutputKeyClass(IntWritable.class);
- 42. job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
- 43. job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
- 44. job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
- 45. Path in=new Path("hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce13/in/data.txt");
- 46. Path out=new Path("hdfs://localhost:9000/mymapreduce13/out");
- 47. FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,in);
- 48. FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,out);
- 49. System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
- 50.
- 51. }
- 52. }
8.在Temperature类文件中,右键并点击=>Run As=>Run on Hadoop选项,将MapReduce任务提交到Hadoop中。
9.待执行完毕后,进入命令模式下,在HDFS上/mymapreduce13/out中查看实验结果。
1. hadoop fs -ls /mymapreduce13/out
2. hadoop fs -cat /mymapreduce13/out/part-r-00000

通过分析可以看到2017-07-13和2017-07-17两天温度最高,为29度。