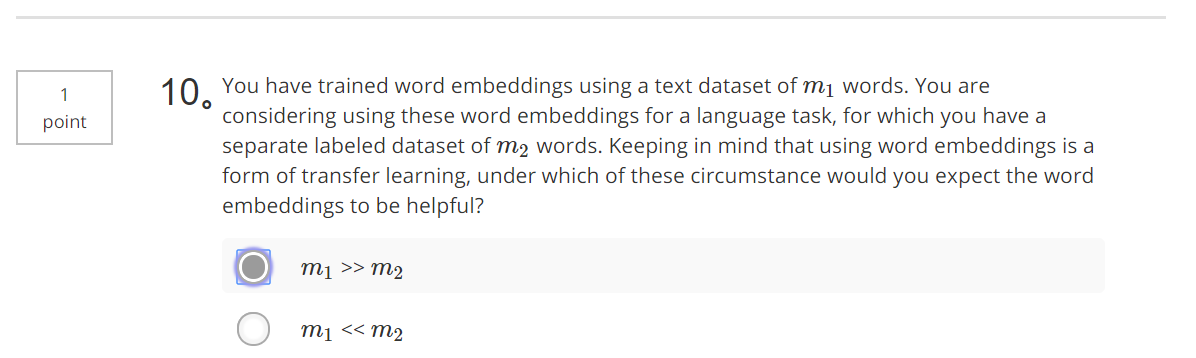
【解释】
The dimension of word vectors is usually smaller than the size of the vocabulary. Most common sizes for word vectors ranges between 50 and 400.

【解释】
过用t-SNE算法来将单词可视化。t-SNE算法所做的就是把这些n维的数据用一种非线性的方式映射到2维平面上,可以得知t-SNE中这种映射很复杂而且很非线性。
 【解释】
【解释】
Yes, word vectors empower your model with an incredible ability to generalize. The vector for "ecstatic would contain a positive/happy connotation which will probably make your model classified the sentence as a "1".


【解释】
Yes, the element-wise multiplication will be extremely inefficient.


【解释】
在skip-gram模型中,我们要做的是抽取上下文和目标词配对,来构造一个监督学习问题。上下文不一定总是目标单词之前离得最近的四个单词,或最近的n个单词。我们要的做的是随机选一个词作为上下文词,比如选orange这个词,然后我们要做的是随机在一定词距内选另一个词,比如在上下文词前后5个词内或者前后10个词内,我们就在这个范围内选择目标词。