文件和目录:stat fstat lstat函数
#include <sys/stat.h> int stat( const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf ); int fstat( int filedes, struct stat *buf ); int lstat( const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf );文件 三个函数的返回值:若成功则返回0,若出错则返回-1
一旦给出pathname,stat函数就返回与此命名文件有关的信息结构。
fstat函数获取已在描述符filedes上打开的有关信息。
lstat函数类似于stat,但是当命名的文件是一个符号链接时,lstat返回该符号链接的有关信息,而不是由该符号链接引用文件的信息。
第二个参数buf是指针,它指向一个我们必须提供的结构。这些函数填写由buf指向的结构。该结构的实际定义可能随实现有所不同,但其基本形式是:
struct stat { mode_t st_mode; /* file type & mode (permissions) */ ino_t st_ino; /* i-node number (serial number) */ dev_t st_dev; /* device number (file system) */ dev_t st_rdev; /* device number for special files */ nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of links */ uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */ gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */ off_t st_size; /* size in bytes, for regular files */ time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */ time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */ time_t st_ctime; /* time of last file status change */ blksize_t st_blksize; /* best I/O block size */ blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of disk blocks allocated */ };
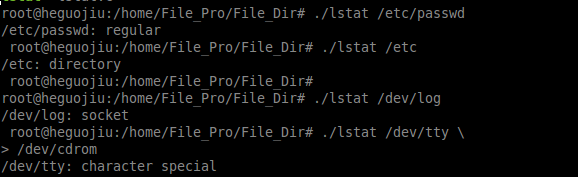
lstat参数打印文件类型实例:
#include "apue.h"
int main (int argc ,char *argv[])
{
int i;
struct stat buf;
char *ptr;
for(i=1;i<argc;i++)
{
printf("%s: ",argv[i]);
if (lstat(argv[i],&buf)<0)
{
err_ret("lstat error");
continue;
}
if (S_ISREG(buf.st_mode)) ptr="regular";
else if(S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode)) ptr="directory";
else if (S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode)) ptr="character special";
else if(S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode)) ptr="block special";
else if(S_ISFIFO(buf.st_mode)) ptr="fifo";
else if(S_ISLNK(buf.st_mode)) ptr="symbolic link";
else if(S_ISSOCK(buf.st_mode)) ptr="socket";
else ptr="** unknown mode **";
printf("%s
",ptr);
}
exit(0);
}
运行结果