A. Nastya and Strange Generator
题意好绕,读懂了之后还是比较简单的。
我们从(1)到(n),每次只能连续地放数直到放不了为止,否则就是不合法的情况。
详见代码:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/23 22:50:52
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e5 + 5;
int n ;
int p[N];
bool chk[N];
void run() {
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int x; cin >> x;
p[x] = i;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) chk[i] = false;
int now = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if(now == -1 || now + 1 > n || chk[now + 1] == true || now + 1 == p[i]) {
now = p[i];
chk[p[i]] = true;
} else {
cout << "NO" << '
';
return;
}
}
cout << "YES" << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
int T; cin >> T; while(T--)
run();
return 0;
}
B. Nastya and Scoreboard
题意:
每个数可以用(7)根电子管表示,类似于下图:
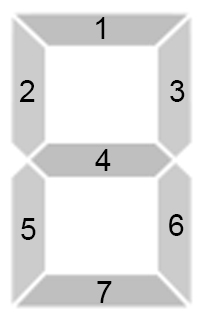
电子管发亮可能会表示为(0)~(9)的数字,如下图:

现在给出(n,nleq 2000)个长度为(7)的(01)字符串,若某个位置为(1),就代表当前位置的电子管发亮,否则就没有。
现在可以点亮(k,kleq 2000)根电子管,问最后得到的最大的数为多少。
思路:
题目相当于求得到字符串的字典序最大,一般这种题的思路就是逐位贪心确定。
但我们确定了前面一位过后,不知道后面的状态是否合法。
注意到一共只有(O(nk))个状态,因为我们确定了前面之后,后面状态仅凭后面若干个位置,还剩多少根电子管这两个变量就可以确定。
那么我们从后往前处理(dp_{i,j}),表示从(i)~(n),有(j)根电子管,状态是否合法。(dp)时直接暴力枚举,然后记忆化一下即可。
时间复杂度(O(nk))。
详见代码:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/23 23:15:45
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 2000 + 5;
const int dig[] = {119, 18, 93, 91, 58, 107, 111, 82, 127, 123};
int n, k;
char s[7];
int a[N];
bool dp[N][N], chk[N][N];
void dfs(int p, int r) {
if(p == 0) return;
if(r > k) return;
if(chk[p][r]) return;
chk[p][r] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if((a[p] & dig[i]) == a[p]) {
int t = __builtin_popcount(a[p] ^ dig[i]);
dp[p][r + t] = true;
dfs(p - 1, r + t);
}
}
}
void run() {
cin >> n >> k;
memset(dp, false, sizeof(dp));
dp[n + 1][0] = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> s;
int x = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
if(s[j] == '1') x += (1 << (7 - j - 1));
}
a[i] = x;
}
dfs(n, 0);
vector <int> ans;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
bool ok = false;
for(int j = 9; j >= 0; j--) if((a[i] & dig[j]) == a[i]) {
int t = __builtin_popcount(a[i] ^ dig[j]);
if(k - t >= 0 && dp[i + 1][k - t]) {
ans.push_back(j);
ok = true;
k -= t;
break;
}
}
if(ok == false) {
cout << -1 << '
';
return;
}
}
for(auto it : ans) cout << it;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}
C. Nastya and Unexpected Guest
题意:
现有一个([0,n])的数轴,上面有(m,mleq 10000)个关键点。
给定(g,r,1leq g,rleq 1000),只有在绿灯状态下可以移动,绿灯持续(g)秒,红灯持续(r)秒。
并且有规定:
- 绿灯状态下每秒必须移动一步。
- 只有在关键点才能改变方向,改变方向不消耗时间。
- 红灯状态必须位于关键点,并且不能移动。
如果最后能够走到(n),那么输出走到(n)的最小时间;否则输出(-1)。
思路:
- 显然我们可以将该数轴离散为(m)个点,然后考虑在该数轴上面行走。
- 有一个观察:就是如果在绿灯状态下相同的时刻走到某一个点,不会重复走,走第二次显然不如直接第一次从这里出发优。
- 这里的性质和(dijkstra)算法思想有点类似,我们考虑通过(dijkstra)求解:用(dist_{i,j})表示走到第(i)个关键点,绿灯状态下还剩(j)秒走到该点的最短距离。那么每次在一个点就可以往左右走,状态空间为(O(mg)),所以这样的做法为(O(mglog))。
- 这个题直接这样做要(TLE),注意到“图”中的边权为(0)或者(1),那么这里可以通过(0/1bfs)来优化掉这个(log)。所以最后的时间复杂度为(O(mg))。
一开始思考的时候将问题复杂化了,在想怎么维护两点之间的可达性,这样就可以构造一个(DAG)然后在上面跑最短路。但其实直接在图上跑最短路就行。。考虑两点间的可达性反而将问题复杂度了,直接简单粗暴一点多好- -还是太菜了。
代码如下:
Code
/*
* Author: heyuhhh
* Created Time: 2020/4/24 9:37:22
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iomanip>
#include <assert.h>
#define MP make_pair
#define fi first
#define se second
#define pb push_back
#define sz(x) (int)(x).size()
#define all(x) (x).begin(), (x).end()
#define INF 0x3f3f3f3f
#define Local
#ifdef Local
#define dbg(args...) do { cout << #args << " -> "; err(args); } while (0)
void err() { std::cout << std::endl; }
template<typename T, typename...Args>
void err(T a, Args...args) { std::cout << a << ' '; err(args...); }
template <template<typename...> class T, typename t, typename... A>
void err(const T <t> &arg, const A&... args) {
for (auto &v : arg) std::cout << v << ' '; err(args...); }
#else
#define dbg(...)
#endif
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
//head
const int N = 1e4 + 5, M = 1e3 + 5;
int n, m, g, r;
int d[N];
int dp[N][M];
void run() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> d[i];
}
sort(d + 1, d + m + 1);
cin >> g >> r;
memset(dp, INF, sizeof(dp));
dp[0][g] = 0;
deque <pii> q;
q.push_front(MP(0, g));
while (!q.empty()) {
pii now = q.front(); q.pop_front();
int i = now.fi, j = now.se;
if (i > 0) {
int r = d[i] - d[i - 1];
if (r < j) {
if (dp[i - 1][j - r] > dp[i][j]) {
q.push_front(MP(i - 1, j - r));
dp[i - 1][j - r] = dp[i][j];
}
} else if (r == j) {
if (dp[i - 1][g] > dp[i][j] + 1) {
q.push_back(MP(i - 1, g));
dp[i - 1][g] = dp[i][j] + 1;
}
}
}
if (i < m) {
int r = d[i + 1] - d[i];
if (r < j) {
if (dp[i + 1][j - r] > dp[i][j]) {
q.push_front(MP(i + 1, j - r));
dp[i + 1][j - r] = dp[i][j];
}
} else if (r == j) {
if (dp[i + 1][g] > dp[i][j] + 1) {
q.push_back(MP(i + 1, g));
dp[i + 1][g] = dp[i][j] + 1;
}
}
}
}
ll ans = 1e18;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
if (n - d[i] <= g && dp[i][g] != INF) {
ans = min(ans, 1ll * dp[i][g] * (g + r) + n - d[i]);
}
}
if(ans == 1e18) ans = -1;
cout << ans << '
';
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0);
cout << fixed << setprecision(20);
run();
return 0;
}