Fox Ciel is playing a mobile puzzle game called "Two Dots". The basic levels are played on a board of size n × m cells, like this:
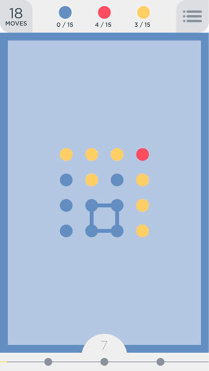
Each cell contains a dot that has some color. We will use different uppercase Latin characters to express different colors.
The key of this game is to find a cycle that contain dots of same color. Consider 4 blue dots on the picture forming a circle as an example. Formally, we call a sequence of dots d1, d2, ..., dk a cycle if and only if it meets the following condition:
- These k dots are different: if i ≠ j then di is different from dj.
- k is at least 4.
- All dots belong to the same color.
- For all 1 ≤ i ≤ k - 1: di and di + 1 are adjacent. Also, dk and d1 should also be adjacent. Cells x and y are called adjacent if they share an edge.
Determine if there exists a cycle on the field.
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50): the number of rows and columns of the board.
Then n lines follow, each line contains a string consisting of m characters, expressing colors of dots in each line. Each character is an uppercase Latin letter.
Output "Yes" if there exists a cycle, and "No" otherwise.
3 4 AAAA ABCA AAAA
Yes
3 4 AAAA ABCA AADA
No
4 4 YYYR BYBY BBBY BBBY
Yes
7 6 AAAAAB ABBBAB ABAAAB ABABBB ABAAAB ABBBAB AAAAAB
Yes
2 13 ABCDEFGHIJKLM NOPQRSTUVWXYZ
No
In first sample test all 'A' form a cycle.
In second sample there is no such cycle.
The third sample is displayed on the picture above ('Y' = Yellow, 'B' = Blue, 'R' = Red).
法一:bfs 这题一开始把队列开成10^7,结果超时了,后来再把队列开成10^5,15ms过了,这里注意几点:开方向数组的时候,每一个要用大括号,不能用小括号,还有写bfs的时候,一开始front=rear=0;之后每一个数据进队,rear++,再是q[rear].x=x;q[rear].y=y;判断退出的条件是while(front<=rear)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char a[200][200];
int m,n,flag,t;
int tab[10][2]={{0,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0}},vis[200][200];
struct node
{
int x,y;
}q[11111],pre[11111];
void bfs(int x,int y)
{
int i,j,front=0,rear=0,xx,yy,x1,y1;
memset(q,-1,sizeof(q));
q[rear].x=x;
q[rear].y=y;
memset(pre,-1,sizeof(pre));
while(front<=rear)
{
x1=q[front].x;
y1=q[front].y;
vis[x1][y1]=1;
front++;
for(i=1;i<=4;i++)
{
xx=x1+tab[i][0];
yy=y1+tab[i][1];
if(xx>=0 && xx<n && yy>=0 && yy<m && a[xx][yy]==a[x1][y1]){
if(pre[front-1].x==xx && pre[front-1].y==yy)
continue;
if(vis[xx][yy]==1){
flag=1;break;
}
rear++;vis[xx][yy]=1;
q[rear].x=xx;q[rear].y=yy;pre[rear].x=x1;pre[rear].y=y1;
}
}
if(flag==1)break;
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,u,v;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%s",a[i]);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<m;j++){
if(vis[i][j]==1)
continue;
flag=0;
bfs(i,j);
if(flag==1)
break;
}
if(flag==1)break;
}
if(flag==1){
printf("Yes
");
}
else printf("No
");
}
return 0;
}
法二:dfs 要注意不能走回头路
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char a[200][200];
int m,n,flag,t;
int tab[10][2]={{0,0},{0,1},{-1,0},{0,-1},{1,0}},vis[200][200];
void dfs(int x,int y,int prex,int prey)
{
int i,j,xx,yy;
for(i=1;i<=4;i++){
xx=x+tab[i][0];
yy=y+tab[i][1];
if(xx>=0 && xx<n && yy>=0 && yy<m && a[xx][yy]==a[x][y]){
if(xx==prex && yy==prey){
continue;
}
if(vis[xx][yy]==1){
flag=1;break;
}
vis[xx][yy]=1;
dfs(xx,yy,x,y);
}
if(flag==1)break;
}
return;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,u,v;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%s",a[i]);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
for(j=0;j<m;j++){
if(vis[i][j]==1)
continue;
flag=0;
vis[i][j]=1;
dfs(i,j,-1,-1);
if(flag==1)
break;
}
if(flag==1)break;
}
if(flag==1){
printf("Yes
");
}
else printf("No
");
}
return 0;
}