一、概念
二叉树(Binary Tree)是另一种树形结构,特点是每个节点至多只有两颗子树(即二叉树中不存在度大于2的节点),并且二叉树的子树有左右之分,其次序不能任意颠倒。
五种基本形态:(a)空二叉树 (b)仅有根节点的二叉树 (c)右子树为空的二叉树 (d)左右子树均非空的二叉树 (e)左子树为空的二叉树
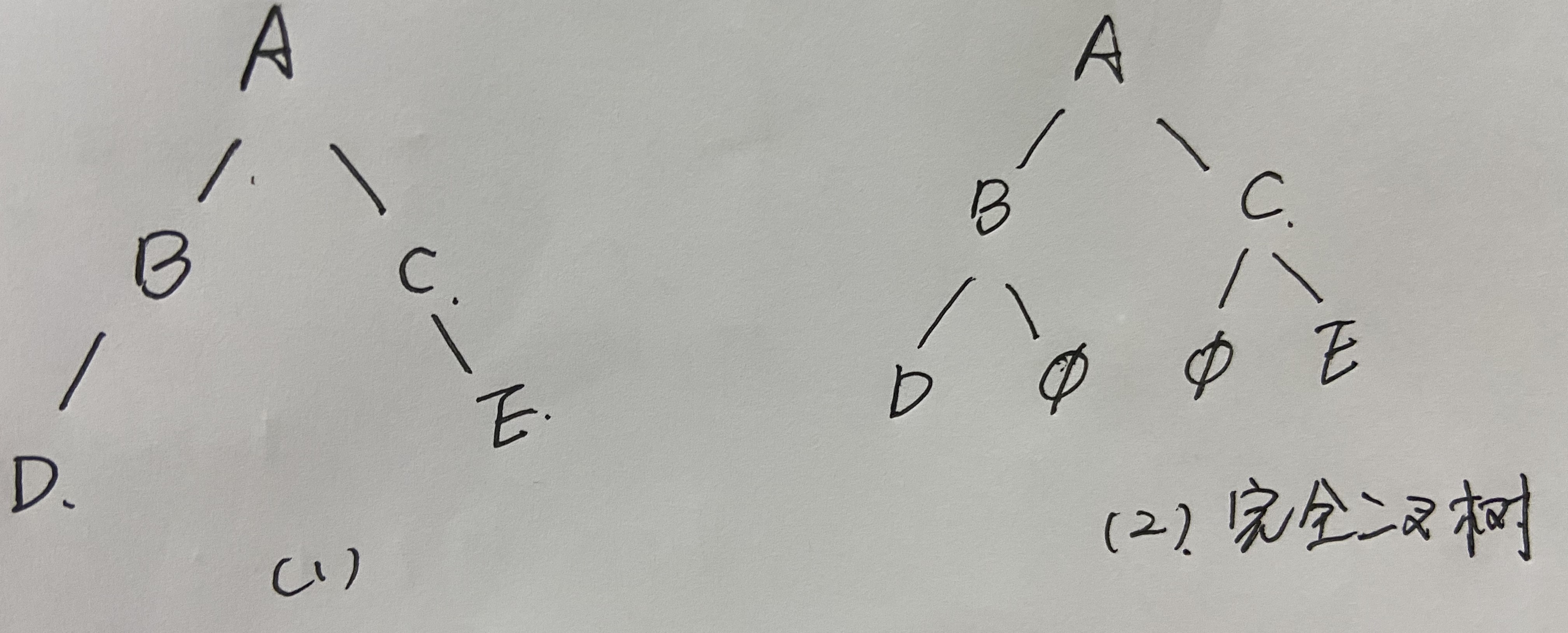
完全二叉树:一棵二叉树中,只有最下面两层结点的度可以小于2,并且最下层的叶结点集中在靠左的若干位置上,这样的二叉树称为完全二叉树。
满二叉树:高度为h,并且由2h-1个结点组成的二叉树,称为满二叉树
二叉排序树(Binary sort tree,BST),又称为二叉查找树,或者是一棵空树;或者是具有下列性质的二叉树:
(1)若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
(2)若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
(3)它的左、右子树也分别为二叉排序树。
二、性质
性质1:二叉树第i层上的结点数目最多为2i-1(i>=1)
性质2:深度为k的二叉树至多有2k-1个结点(k>=1)
性质3:包含n个结点的二叉树的高度至少为(log2n)+1
性质4:在任意一棵二叉树中,若终端结点的个数为n0,度为2的结点数为n2,则n0=n2+1
性质5:n个节点的完全二叉树,按从上到下,从左到右排序,第i(1<=i<=n)个节点:
(1)i=1,则i是二叉树的根,如果i>1,则双亲是节点i/2向下取整
(2)如果2i>n,则i无左孩子;否则左孩子为2i
(3)如果2i+>n,则i无右孩子;否则左孩子为2i+1
三、二叉树的存储结构
1.顺序存储结构: A B C D 空 空 E 补充成完全二叉树再显示
2.链式存储结构: 用链表来表示一棵二叉树,即用链来指示元素的逻辑关系。
通常的方法是链表中每个结点由三个域组成,数据域和左右指针域,左右指针分别用来给出该结点左孩子和右孩子所在的链结点的存储地址。其结点结构为:

三叉链表:给链表结点增加一个双亲字段parent,用来指向其双亲结点。
四、遍历二叉树
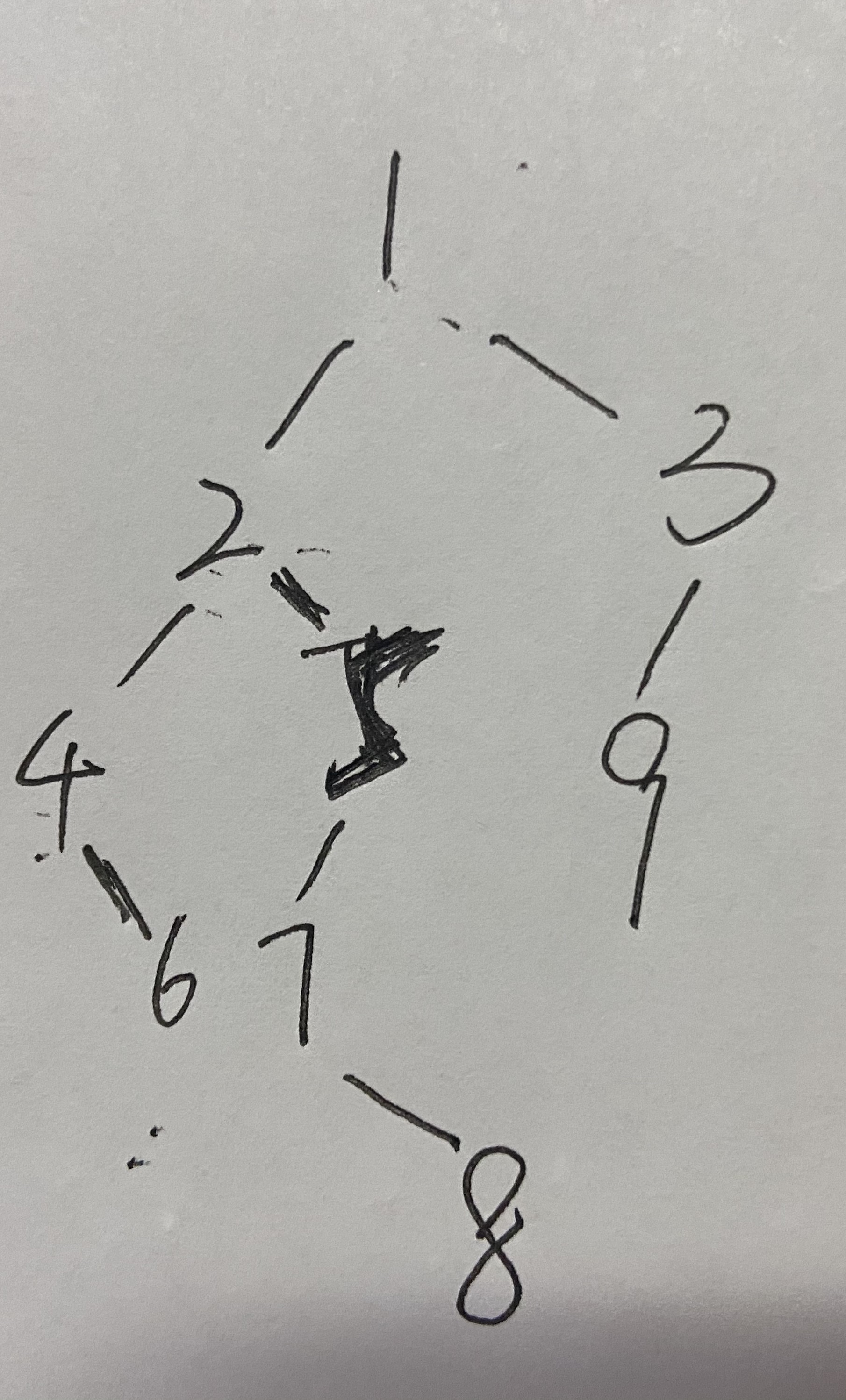
/** * 二叉树 * @author helq3 * */ public class BinaryTree { /** * * @param binaryList * @return */ public Node initBinaryTree(LinkedList binaryList){ //二叉链表为空 if(binaryList.isEmpty()){ return null; } Node node = null; Object data = (Object) binaryList.removeFirst(); if(data != null){ node = new Node(); node.setData(data); node.setlNode(initBinaryTree(binaryList)); node.setrNode(initBinaryTree(binaryList)); } return node; } /**--------------------------递归方式----------------------------*/ /** * 先序遍历DLR * @param node */ public void proOrderTraversal(Node node){ if(node == null){ return; } System.out.print(node.getData()+" "); proOrderTraversal(node.getlNode()); proOrderTraversal(node.getrNode()); } /** * 中序遍历LDR * @param node */ public void inOrderTraversal(Node node){ if(node == null){ return ; } inOrderTraversal(node.getlNode()); System.out.print(node.getData()+" "); inOrderTraversal(node.getrNode()); } /** * 后续遍历LRD lrd * @param node */ public void postOrderTraversal(Node node){ if(node == null){ return ; } postOrderTraversal(node.getlNode()); postOrderTraversal(node.getrNode()); System.out.print(node.getData()+" "); } /** * 层序遍历 * @param node */ public void cexuTraversal(Node node){ if(node == null){ return; } } /**--------------------------非递归方式----------------------------*/ public BTNode createBiTree(LinkedList binaryList){ if(binaryList.size()==0){ return null; }else{ BTNode node = null; Object data = binaryList.removeFirst(); if(data != null){ node = new BTNode(); node.data = data; node.leftNode = createBiTree(binaryList); node.rightNode = createBiTree(binaryList); } return node; } } /** * 先序遍历 * @param node */ public void preOrderTra(BTNode node){ if(node != null){ Stack<BTNode> stack = new Stack<BTNode>(); stack.push(node); while(!stack.isEmpty()){ BTNode curNode = stack.pop(); System.out.print(curNode.data + " "); if(curNode.rightNode != null){ stack.push(curNode.rightNode); } if(curNode.leftNode != null){ stack.push(curNode.leftNode); } } } System.out.println(); } /** * 中序遍历 * @param head */ public void inOrderTra(BTNode head){ if(head != null){ Stack<BTNode> stack = new Stack<BTNode>(); while(!stack.isEmpty() || head != null){ if(head != null){ stack.push(head); head = head.leftNode; }else{ head = stack.pop(); System.out.print(head.data+" "); head = head.rightNode; } } } System.out.println(); } /** * 后续遍历 * @param head */ public void postOrderTra(BTNode head){ if(head != null){ Stack<BTNode> s1 = new Stack<BTNode>(); Stack<BTNode> s2 = new Stack<BTNode>(); while(!s1.isEmpty() || head != null){ if(head != null){ s1.push(head); s2.push(head); head = head.rightNode; }else{ head = s1.pop(); head = head.leftNode; } } while(!s2.isEmpty()){ System.out.print(s2.pop().data+" "); } } System.out.println(); } }
mian方法调用
public static void main(String[] args){ //1 2 4 空 6 空 空 5 7 空 8 空 空 空 3 9 空 空 空 LinkedList binaryTreeList = new LinkedList(); LinkedList biTreeList = new LinkedList(); binaryTreeList.add(1); binaryTreeList.add(2); binaryTreeList.add(4); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(6); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(5); binaryTreeList.add(7); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(8); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(3); binaryTreeList.add(9); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(null); binaryTreeList.add(null); biTreeList.addAll(binaryTreeList); BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree(); Node node = binaryTree.initBinaryTree(binaryTreeList); System.out.println("------先序遍历------"); binaryTree.proOrderTraversal(node); System.out.println(); System.out.println("------中序遍历------"); binaryTree.inOrderTraversal(node); System.out.println(); System.out.println("------后序遍历------"); binaryTree.postOrderTraversal(node); System.out.println(); System.out.println("***********************非递归方式*********************"); BTNode btNode = binaryTree.createBiTree(biTreeList); System.out.println("------先序遍历------"); binaryTree.preOrderTra(btNode); System.out.println("------中序遍历------"); binaryTree.inOrderTra(btNode); System.out.println("------后序遍历------"); binaryTree.postOrderTra(btNode); }
执行结果:

层序遍历:
/** * 层序遍历:使用队列queue * @param node */ public void levelOrderTra(BTNode node){ if(node == null){ return; }else{ Queue<BTNode> queue = new LinkedList<BTNode>(); queue.add(node); while(!queue.isEmpty()){ BTNode cur = queue.poll(); System.out.print(cur.data+" "); if(cur.leftNode != null){ queue.add(cur.leftNode); } if(cur.rightNode != null){ queue.add(cur.rightNode); } } } System.out.println(); }
运行结果:

五、线索二叉树
六、森林和二叉树
七、赫夫曼树及应用
·