1 在azure 上创建一个 azure service bus
步骤请参考 

2 创建完service bus后,配置一个消息队列
3 获取 消息队列的连接字符串
4 使用Dynamics 365 插件注册工具,注册一个 Service Endpoint,将上一步的连接字符串放一起保存
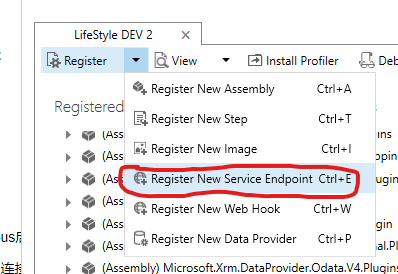
5 注册一个消息 ,使用4 步创建service endpoint

这样就完成了在azure service bus 消息队列上查看CRM下发的消息。也可以使用代码监听消息
static async Task ProcessMessagesAsync(Message message, CancellationToken token) { // Process the message Console.WriteLine($"Received message: SequenceNumber:{message.SystemProperties.SequenceNumber} Body:{Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message.Body)}"); if (message.ContentType == "application/msbin1") { RemoteExecutionContext context = message.GetBody<RemoteExecutionContext>(); } else if (message.ContentType == "application/json") { //string jsonBody = new StreamReader(receivedMessage.GetBody<Stream>(), Encoding.UTF8).ReadToEnd(); RemoteExecutionContext contextFromJSON = message.GetBody<RemoteExecutionContext>( new DataContractJsonSerializer(typeof(RemoteExecutionContext))); } else if (message.ContentType == "application/xml") { //string xmlBody = new StreamReader(receivedMessage.GetBody<Stream>(), Encoding.UTF8).ReadToEnd(); RemoteExecutionContext contextFromXML = message.GetBody<RemoteExecutionContext>( new DataContractSerializer(typeof(RemoteExecutionContext))); } // Complete the message so that it is not received again. // This can be done only if the queueClient is created in ReceiveMode.PeekLock mode (which is default). await queueClient.CompleteAsync(message.SystemProperties.LockToken); // Note: Use the cancellationToken passed as necessary to determine if the queueClient has already been closed. // If queueClient has already been Closed, you may chose to not call CompleteAsync() or AbandonAsync() etc. calls // to avoid unnecessary exceptions. }
整个类如下 ,需要引用nuget 包
using Microsoft.Azure.ServiceBus; using Microsoft.Azure.ServiceBus.InteropExtensions; using Microsoft.Xrm.Sdk; using System; using System.Runtime.Serialization; using System.Runtime.Serialization.Json; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace BasicSendReceiveQuickStart { class Program { static IQueueClient queueClient; static void Main(string[] args) { var serviceBusConnectionString = string.Empty; var queueName = string.Empty; for (var i = 0; i < args.Length; i++) { switch (args[i]) { case "-ConnectionString": Console.WriteLine($"ConnectionString: {args[i + 1]}"); serviceBusConnectionString = args[i + 1]; // Alternatively enter your connection string here. break; case "-QueueName": Console.WriteLine($"QueueName: {args[i + 1]}"); queueName = args[i + 1]; // Alternatively enter your queue name here. break; } } if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(serviceBusConnectionString) && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(queueName)) MainAsync(serviceBusConnectionString, queueName).GetAwaiter().GetResult(); else { Console.WriteLine("Specify -ConnectionString and -QueueName to execute the example."); Console.ReadKey(); } } static async Task MainAsync(string serviceBusConnectionString, string queueName) { const int numberOfMessages = 10; queueClient = new QueueClient(serviceBusConnectionString, queueName); Console.WriteLine("======================================================"); Console.WriteLine("Press any key to exit after receiving all the messages."); Console.WriteLine("======================================================"); // Register QueueClient's MessageHandler and receive messages in a loop RegisterOnMessageHandlerAndReceiveMessages(); // Send Messages await SendMessagesAsync(numberOfMessages); Console.ReadKey(); await queueClient.CloseAsync(); } static void RegisterOnMessageHandlerAndReceiveMessages() { // Configure the MessageHandler Options in terms of exception handling, number of concurrent messages to deliver etc. var messageHandlerOptions = new MessageHandlerOptions(ExceptionReceivedHandler) { // Maximum number of Concurrent calls to the callback `ProcessMessagesAsync`, set to 1 for simplicity. // Set it according to how many messages the application wants to process in parallel. MaxConcurrentCalls = 1, // Indicates whether MessagePump should automatically complete the messages after returning from User Callback. // False below indicates the Complete will be handled by the User Callback as in `ProcessMessagesAsync` below. AutoComplete = false }; // Register the function that will process messages queueClient.RegisterMessageHandler(ProcessMessagesAsync, messageHandlerOptions); } static async Task ProcessMessagesAsync(Message message, CancellationToken token) { // Process the message Console.WriteLine($"Received message: SequenceNumber:{message.SystemProperties.SequenceNumber} Body:{Encoding.UTF8.GetString(message.Body)}"); if (message.ContentType == "application/msbin1") { RemoteExecutionContext context = message.GetBody<RemoteExecutionContext>(); } else if (message.ContentType == "application/json") { //string jsonBody = new StreamReader(receivedMessage.GetBody<Stream>(), Encoding.UTF8).ReadToEnd(); RemoteExecutionContext contextFromJSON = message.GetBody<RemoteExecutionContext>( new DataContractJsonSerializer(typeof(RemoteExecutionContext))); } else if (message.ContentType == "application/xml") { //string xmlBody = new StreamReader(receivedMessage.GetBody<Stream>(), Encoding.UTF8).ReadToEnd(); RemoteExecutionContext contextFromXML = message.GetBody<RemoteExecutionContext>( new DataContractSerializer(typeof(RemoteExecutionContext))); } // Complete the message so that it is not received again. // This can be done only if the queueClient is created in ReceiveMode.PeekLock mode (which is default). await queueClient.CompleteAsync(message.SystemProperties.LockToken); // Note: Use the cancellationToken passed as necessary to determine if the queueClient has already been closed. // If queueClient has already been Closed, you may chose to not call CompleteAsync() or AbandonAsync() etc. calls // to avoid unnecessary exceptions. } // Use this Handler to look at the exceptions received on the MessagePump static Task ExceptionReceivedHandler(ExceptionReceivedEventArgs exceptionReceivedEventArgs) { Console.WriteLine($"Message handler encountered an exception {exceptionReceivedEventArgs.Exception}."); var context = exceptionReceivedEventArgs.ExceptionReceivedContext; Console.WriteLine("Exception context for troubleshooting:"); Console.WriteLine($"- Endpoint: {context.Endpoint}"); Console.WriteLine($"- Entity Path: {context.EntityPath}"); Console.WriteLine($"- Executing Action: {context.Action}"); return Task.CompletedTask; } static async Task SendMessagesAsync(int numberOfMessagesToSend) { try { for (var i = 0; i < numberOfMessagesToSend; i++) { // Create a new message to send to the queue var messageBody = $"Message {i}"; var message = new Message(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(messageBody)); // Write the body of the message to the console Console.WriteLine($"Sending message: {messageBody}"); // Send the message to the queue await queueClient.SendAsync(message); } } catch (Exception exception) { Console.WriteLine($"{DateTime.Now} :: Exception: {exception.Message}"); } } } }