题目大意:
题目链接:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P4001
现在小朋友们最喜欢的"喜羊羊与灰太狼",话说灰太狼抓羊不到,但抓兔子还是比较在行的,而且现在的兔子还比较笨,它们只有两个窝,现在你做为狼王,面对下面这样一个网格的地形:
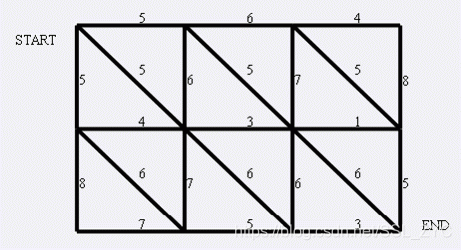
左上角点为,右下角点为(上图中)。有以下三种类型的道路
道路上的权值表示这条路上最多能够通过的兔子数,道路是无向的. 左上角和右下角为兔子的两个窝,开始时所有的兔子都聚集在左上角的窝里,现在它们要跑到右下角的窝中去,狼王开始伏击这些兔子.当然为了保险起见,如果一条道路上最多通过的兔子数为,狼王需要安排同样数量的只狼,才能完全封锁这条道路,你需要帮助狼王安排一个伏击方案,使得在将兔子一网打尽的前提下,参与的狼的数量要最小。因为狼还要去找喜羊羊麻烦。
思路:
最小割等于最大流。
然后就是一道板子题了。注意这道题的边是双向的,所以反向边和正向边的流量是一样的。
点数,最好加上当前弧优化。
代码:
#include <queue>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=1000010,Inf=1e9;
int n,m,tot=1,S,T,maxflow,head[N],cur[N],dep[N];
bool vis[N];
struct edge
{
int next,to,flow;
}e[N*6];
int C(int x,int y)
{
return (x-1)*m+y;
}
int read()
{
int d=0;
char ch=getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch)) ch=getchar();
while (isdigit(ch))
d=(d<<3)+(d<<1)+ch-48,ch=getchar();
return d;
}
void add(int from,int to,int flow)
{
e[++tot].to=to;
e[tot].flow=flow;
e[tot].next=head[from];
head[from]=tot;
}
bool bfs()
{
memcpy(cur,head,sizeof(cur));
memset(dep,0x3f3f3f3f,sizeof(dep));
queue<int> q;
q.push(S);
dep[S]=1;
while (q.size())
{
int u=q.front(),v;
q.pop();
for (int i=head[u];~i;i=e[i].next)
{
v=e[i].to;
if (dep[v]>dep[u]+1&&e[i].flow)
{
dep[v]=dep[u]+1;
q.push(v);
}
}
}
return dep[T]<Inf;
}
int dfs(int x,int flow)
{
int low=0;
if (x==T)
{
maxflow+=flow;
return flow;
}
int used=0;
for (int i=cur[x];~i;i=e[i].next)
{
int y=e[i].to;
cur[x]=i;
if (dep[y]==dep[x]+1&&e[i].flow)
{
low=dfs(y,min(e[i].flow,flow-used));
if (low)
{
used+=low;
e[i].flow-=low;
e[i^1].flow+=low;
if (used==flow) break;
}
}
}
return used;
}
void dinic()
{
while (bfs())
dfs(S,Inf);
}
int main()
{
memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));
n=read(); m=read();
S=n*m+1; T=n*m+2;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<m;j++)
{
int x;
x=read();
add(C(i,j),C(i,j+1),x);
add(C(i,j+1),C(i,j),x);
}
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<=m;j++)
{
int x;
x=read();
add(C(i,j),C(i+1,j),x);
add(C(i+1,j),C(i,j),x);
}
for (int i=1;i<n;i++)
for (int j=1;j<m;j++)
{
int x;
x=read();
add(C(i,j),C(i+1,j+1),x);
add(C(i+1,j+1),C(i,j),x);
}
add(S,1,Inf); add(1,S,0);
add(C(n,m),T,Inf); add(T,C(n,m),0);
dinic();
printf("%d",maxflow);
return 0;
}