一 figure使用
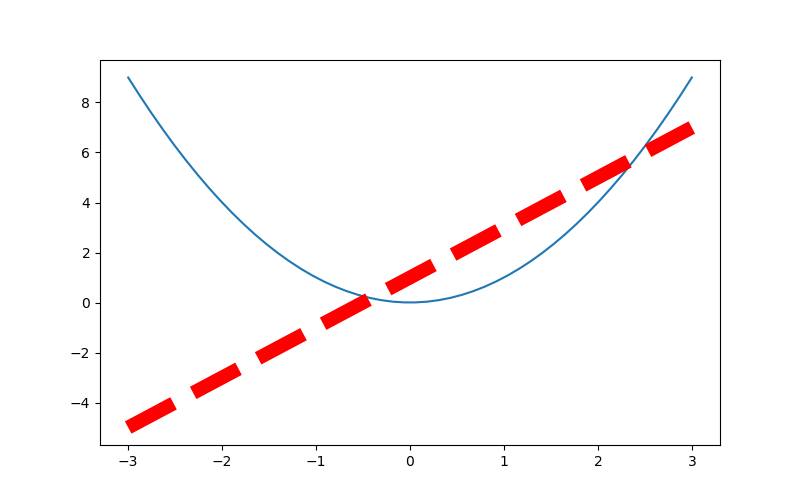
1 import numpy as np 2 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 3 4 # 从-3到中取50个数 5 x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50) 6 print(x) 7 y1 = 2*x+1 8 y2 = x**2 9 plt.figure() 10 plt.plot(x, y1) 11 plt.figure(num=3, figsize=(8, 5)) # figsize的设置长和宽 12 plt.plot(x, y2) 13 plt.plot(x, y1, color='red', linewidth=10.0, linestyle='--') # linewidth 设置线的宽度, linesyyle设置线的形状 14 # savefig 保存图片 15 plt.savefig("./image_dir/xianxing.png") 16 plt.show()
二: 设置坐标轴
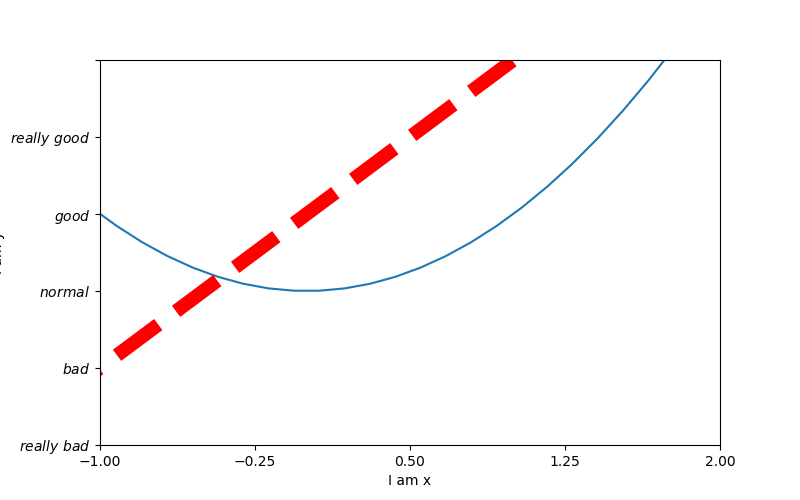
# 从-3到中取50个数 x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50) y1 = 2 * x + 1 y2 = x ** 2 plt.figure(num=3, figsize=(8, 5)) # figsize的设置长和宽 plt.plot(x, y2) plt.plot(x, y1, color='red', linewidth=10.0, linestyle='--') plt.xlim((-1, 2)) # 设置x轴的范围 plt.ylim((-2, 3)) # 设置y轴的范围 plt.xlabel('I am x') # 设置x轴的名称 plt.ylabel('I am y') # 设置y轴额名称 new_ticks = np.linspace(-1, 2, 5) print(new_ticks) plt.xticks(new_ticks) # 设置x轴的范围的刻度值 # 设置y轴的范围的刻度值 plt.yticks([-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3], [r'$really bad$', r'$bad$', r'$normal$', r'$good$', r'$really good$']) plt.savefig('./image_dir/xlim.png') plt.show()
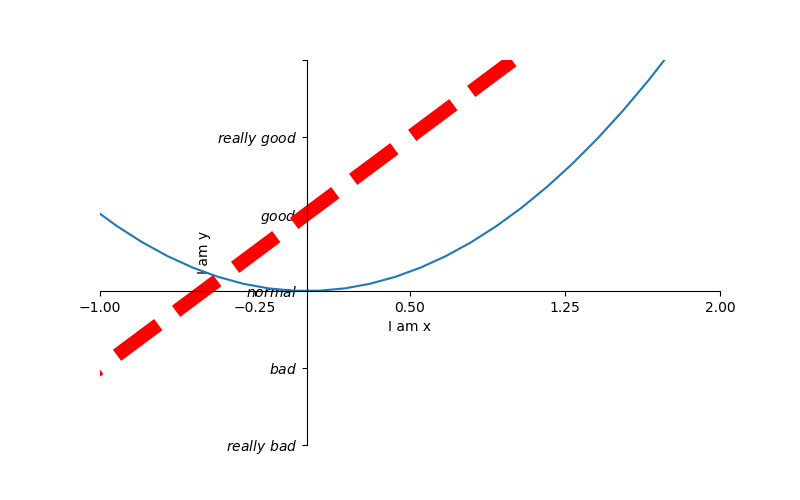
1 # 从-3到中取50个数 2 x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50) 3 4 y1 = 2 * x + 1 5 y2 = x ** 2 6 plt.figure(num=3, figsize=(8, 5)) # figsize的设置长和宽 7 plt.plot(x, y2) 8 plt.plot(x, y1, color='red', linewidth=10.0, linestyle='--') 9 plt.xlim((-1, 2)) # 设置x轴的范围 10 plt.ylim((-2, 3)) # 设置y轴的范围 11 plt.xlabel('I am x') # 设置x轴的名称 12 plt.ylabel('I am y') # 设置y轴额名称 13 new_ticks = np.linspace(-1, 2, 5) 14 print(new_ticks) 15 plt.xticks(new_ticks) # 设置x轴的范围的刻度值 16 # 设置y轴的范围的刻度值 17 plt.yticks([-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3], 18 [r'$really bad$', r'$bad$', r'$normal$', r'$good$', r'$really good$']) 19 # gca = 'get current axis' 20 ax = plt.gca() 21 # 将轴的右边去掉 22 ax.spines['right'].set_color('none') 23 # 将轴的上边去掉 24 ax.spines['top'].set_color('none') 25 # 将下轴设置为x 26 ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom') 27 # 将左轴设置为y 28 ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left') 29 # 设置下轴的位置 set_position(outward, axes) 30 ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0)) 31 # 设置左轴位置 32 ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', '0')) 33 plt.savefig('./image_dir/xlim2.png') 34 plt.show()
三: legend 图例
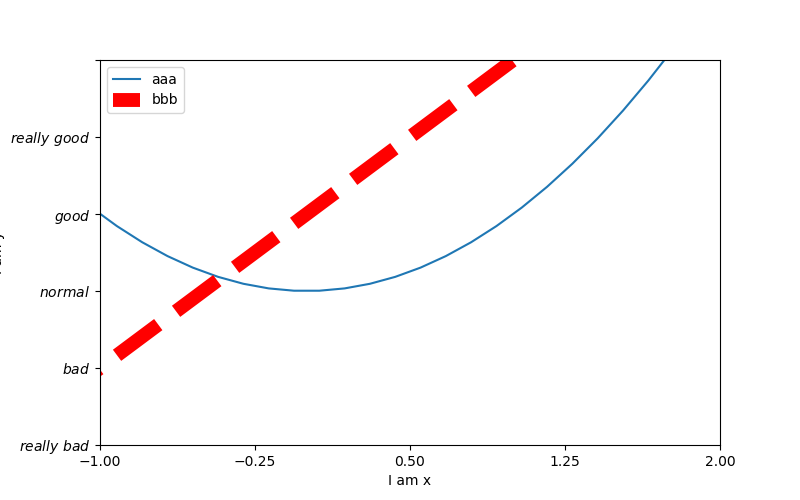
1 # 从-3到中取50个数 2 x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50) 3 4 y1 = 2 * x + 1 5 y2 = x ** 2 6 plt.figure(num=3, figsize=(8, 5)) # figsize的设置长和宽 7 8 plt.xlim((-1, 2)) # 设置x轴的范围 9 plt.ylim((-2, 3)) # 设置y轴的范围 10 plt.xlabel('I am x') # 设置x轴的名称 11 plt.ylabel('I am y') # 设置y轴额名称 12 new_ticks = np.linspace(-1, 2, 5) 13 print(new_ticks) 14 plt.xticks(new_ticks) # 设置x轴的范围的刻度值 15 # 设置y轴的范围的刻度值 16 plt.yticks([-2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3], 17 [r'$really bad$', r'$bad$', r'$normal$', r'$good$', r'$really good$']) 18 19 # plt.plot是有返回值的 20 l1, = plt.plot(x, y2, label='up') 21 l2, = plt.plot(x, y1, color='red', linewidth=10.0, linestyle='--', label='down') 22 # handles, labels是设置名称, loc是设置位置 23 plt.legend(handles=[l1, l2], labels=['aaa', 'bbb'], loc='best') 24 plt.savefig('./image_dir/xlim3.png') 25 plt.show()
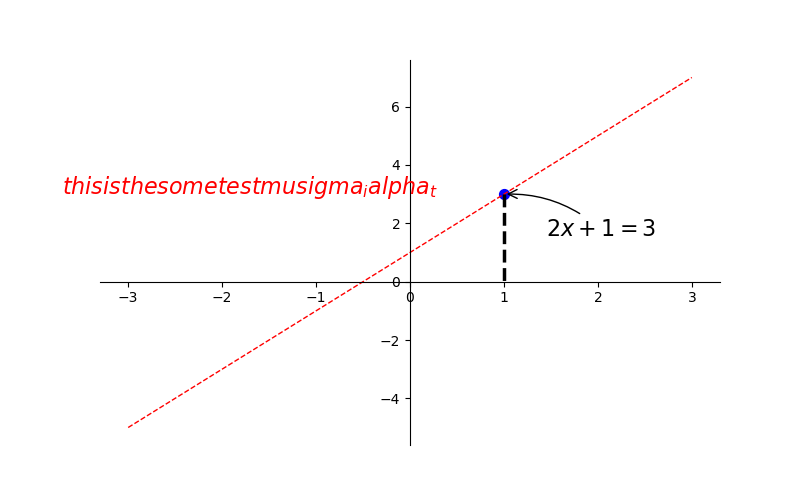
四: annotation标注
1 # 从-3到中取50个数 2 x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50) 3 y1 = 2 * x + 1 4 # y2 = x ** 2 5 plt.figure(num=3, figsize=(8, 5)) # figsize的设置长和宽 6 # plt.plot(x, y2) 7 plt.plot(x, y1, color='red', linewidth=1.0, linestyle='--') 8 # gca = 'get current axis' 9 ax = plt.gca() 10 # 将轴的右边去掉 11 ax.spines['right'].set_color('none') 12 # 将轴的上边去掉 13 ax.spines['top'].set_color('none') 14 # 将下轴设置为x 15 ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom') 16 # 将左轴设置为y 17 ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left') 18 # 设置下轴的位置 set_position(outward, axes) 19 ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0)) 20 # 设置左轴位置 21 ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', '0')) 22 x0 = 1 23 y0 = 2 * x0 + 1 24 plt.scatter(x0, y0, s=50, color='b') 25 plt.plot([x0, x0], [y0, 0], 'k--', lw=2.5) 26 27 # method1 xycoords依赖的数据集 28 plt.annotate(r'$2x+1=%s$' % y0, xy=(x0, y0), xycoords='data', xytext=(+30, -30), textcoords='offset points', 29 fontsize=16, arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle='->', connectionstyle='arc3, rad=.2')) 30 31 # method2 32 plt.text(-3.7, 3, r'$ this is the some test mu sigma_i alpha_t$', fontdict={'size':16, 'color':'r'}) 33 plt.savefig('./image_dir/xlim4.png') 34 plt.show()
五:tick能见度
1 # 从-3到中取50个数 2 x = np.linspace(-3, 3, 50) 3 y1 = 0.1*x 4 # y2 = x ** 2 5 plt.figure(num=3, figsize=(8, 5)) # figsize的设置长和宽 6 # plt.plot(x, y2) 7 plt.plot(x, y1, linewidth=10) 8 plt.ylim(-2, 2) 9 # gca = 'get current axis' 10 ax = plt.gca() 11 # 将轴的右边去掉 12 ax.spines['right'].set_color('none') 13 # 将轴的上边去掉 14 ax.spines['top'].set_color('none') 15 # 将下轴设置为x 16 ax.xaxis.set_ticks_position('bottom') 17 # 将左轴设置为y 18 ax.yaxis.set_ticks_position('left') 19 # 设置下轴的位置 set_position(outward, axes) 20 ax.spines['bottom'].set_position(('data', 0)) 21 # 设置左轴位置 22 ax.spines['left'].set_position(('data', '0')) 23 for label in ax.get_xticklabels() + ax.get_yticklabels(): 24 label.set_fontsize(12) 25 label.set_bbox(dict(facecolor='blue', edgecolor='None', alpha=0.9)) 26 plt.savefig('./image_dir/xlim5.png') 27 plt.show()
