1. TreeSet保证元素唯一性和自然排序的原理和图解
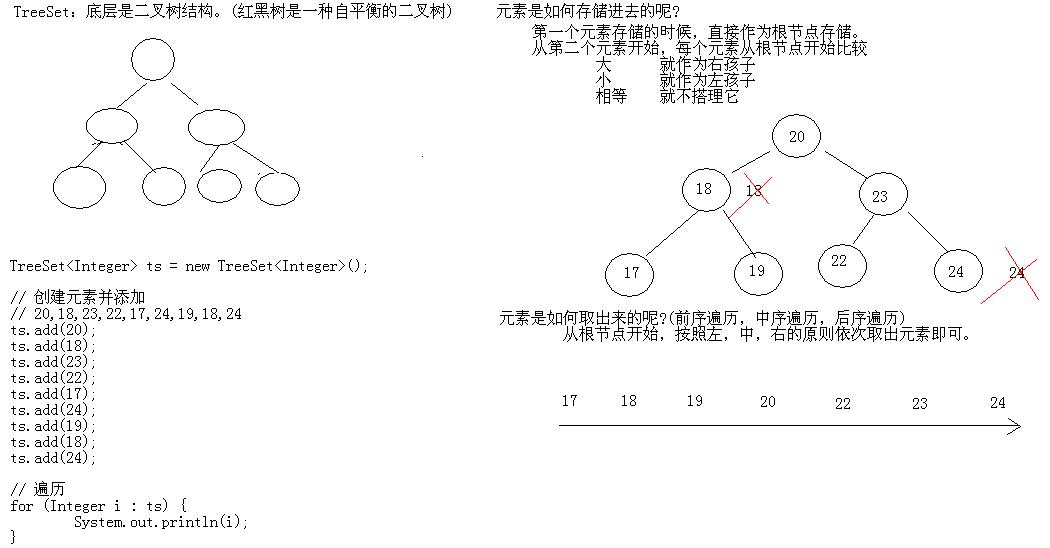
2. TreeSet唯一性以及有序性底层剖析:
通过观察TreeSet的add()方法,我们知道最终要看TreeMap的put()方法。
跟踪进入源码:
1 interface Collection {...} 2 3 interface Set extends Collection {...} 4 5 interface NavigableMap { 6 7 } 8 9 class TreeMap implements NavigableMap { 10 public V put(K key, V value) { 11 Entry<K,V> t = root; 12 if (t == null) { 13 compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check 14 15 root = new Entry<>(key, value, null); 16 size = 1; 17 modCount++; 18 return null; 19 } 20 int cmp; 21 Entry<K,V> parent; 22 // split comparator and comparable paths 23 Comparator<? super K> cpr = comparator; 24 if (cpr != null) { 25 do { 26 parent = t; 27 cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key); 28 if (cmp < 0) 29 t = t.left; 30 else if (cmp > 0) 31 t = t.right; 32 else 33 return t.setValue(value); 34 } while (t != null); 35 } 36 else { 37 if (key == null) 38 throw new NullPointerException(); 39 Comparable<? super K> k = (Comparable<? super K>) key; 40 do { 41 parent = t; 42 cmp = k.compareTo(t.key); 43 if (cmp < 0) 44 t = t.left; 45 else if (cmp > 0) 46 t = t.right; 47 else 48 return t.setValue(value); 49 } while (t != null); 50 } 51 Entry<K,V> e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent); 52 if (cmp < 0) 53 parent.left = e; 54 else 55 parent.right = e; 56 fixAfterInsertion(e); 57 size++; 58 modCount++; 59 return null; 60 } 61 } 62 63 class TreeSet implements Set { 64 private transient NavigableMap<E,Object> m; 65 66 public TreeSet() { 67 this(new TreeMap<E,Object>()); 68 } 69 70 public boolean add(E e) { 71 return m.put(e, PRESENT)==null; 72 } 73 }
总结:
真正的比较是依赖于元素的compareTo()方法,而这个方法是定义在 Comparable里面的。所以,你要想重写该方法,就必须是先 Comparable接口。这个接口表示的就是自然排序。
通过观察TreeSet的底层源码发现,TreeSet的add(E e)方法,底层是根据实现Comparable的方式来实现的唯一性,通过compare(Object o)的返回值是否为0来判断是否为同一元素。
compare() == 0,元素不入集合。
compare() > 0 ,元素入右子树。
compare() < 0,元素入左子树。
而对其数据结构:自平衡二叉树做前(常用)、中、后序遍历即可保证TreeSet的有序性。