springboot集成rabbitmq
- RabbitMQ 6种模式
参考官网地址
步骤
1. 导入相应模块
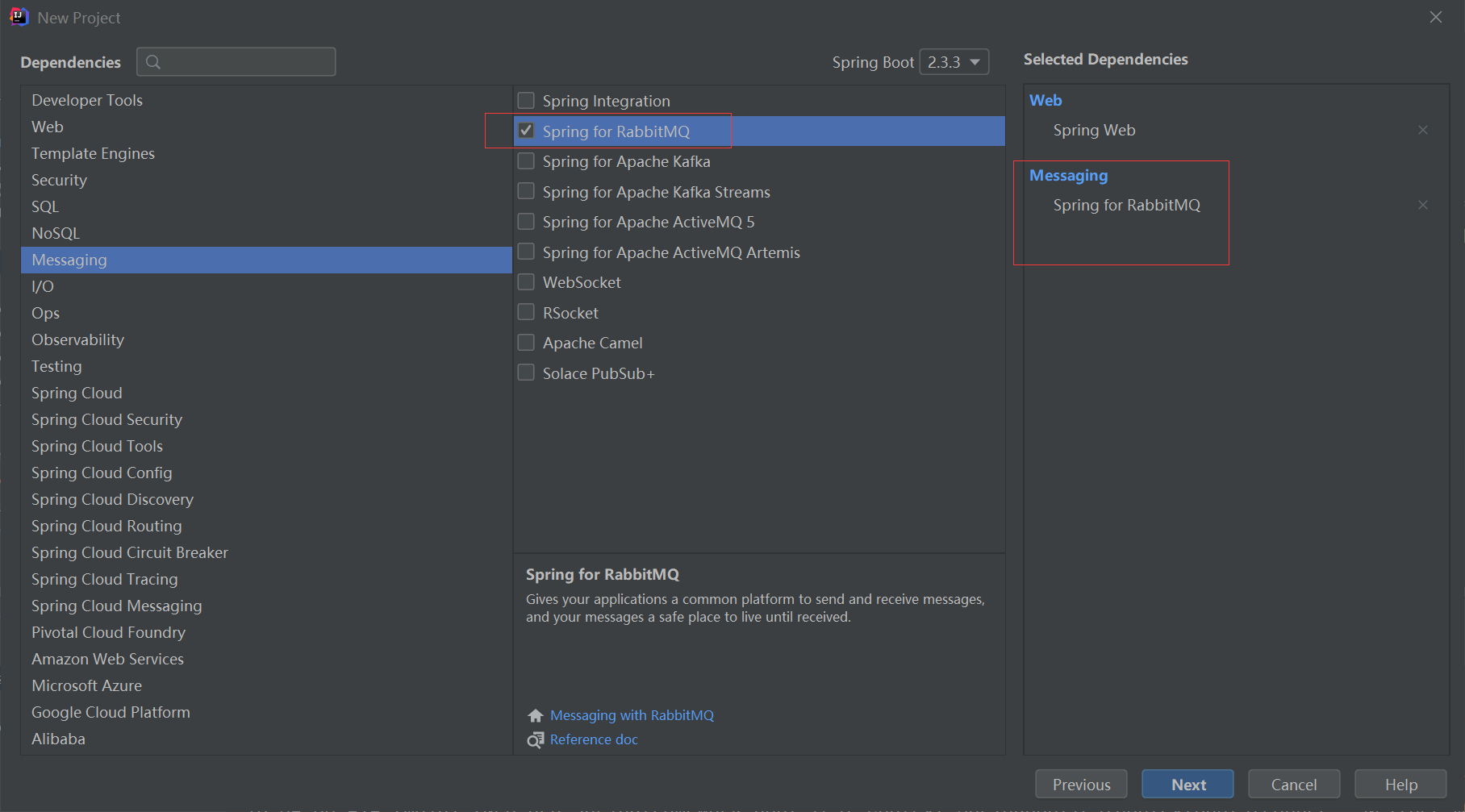
2. 配置yml文件
spring:
application:
name: springboot-rabbitmq # 工程名
# 配置rabbitmq
rabbitmq:
host: localhost
port: 5672
username: guest
password: guest
virtual-host: / # 虚拟主机
第一种hello world模式
一个提供者,一个消费者
- 编写提供者
@SpringBootTest
class Spriingboot07RabbitmqApplicationTests {
//注入rabbitmq
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
//1. 简单模式
@Test
void hello_world() {
//发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("hello","你好,这是一条消息");
}
}
- 编写消费者
@Component
//指定这个类是一个监听者,queuesToDeclare代表没有队列则创建队列,
//@Queue创建一个队列,指定队列的名字,参数等
//默认是持久化,不自动删除,不独占一个连接
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "hello",autoDelete = "false",exclusive = "false"))
public class HelloConsumer {
@RabbitHandler //代表这是一个回调函数,能接收队列中的消息
public void resolverMsg(String message) {
//message就是队列中的消息
System.out.println("message = " + message);
}
}
第二种work模式
一个提供者,两个消费者
- 编写提供者
@SpringBootTest
class Spriingboot07RabbitmqApplicationTests {
//注入rabbitmq
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
void work_model() {
//发送消息
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("work","工作第"+(i+1)+"天");
}
}
}
- 编写消费者
@Component
public class WorkConsumer {
//消费者1
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "work"))
public void consumer1(String message) {
System.out.println("message1 = " + message);
}
//消费者2
@RabbitListener(queuesToDeclare = @Queue(value = "work"))
public void consumer2(String message) {
System.out.println("message2 = " + message);
}
}
第三种发布订阅模式
一个提供者,一个交换机,两个队列,两个消费者
- 编写提供者
@SpringBootTest
class Spriingboot07RabbitmqApplicationTests {
//注入rabbitmq
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
//3.广播模式
@Test
void fanout_model() {
//发送消息
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//广播模式不需要路由key
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("fanoutExchange","","工作第"+(i+1)+"天");
}
}
}
- 编写消费者
package com.atguigu.fanout;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* ClassName: FanoutModel
* Description:
* date: 2020/9/6 17:26
*
* @author July
* @since JDK 1.8
*/
@Component
public class FanoutModel {
//创建一个消费者
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {@QueueBinding( //将队列与交换机绑定
value = @Queue, //不指定队列名字则为创建一个临时队列
exchange = @Exchange(value = "fanoutExchange", type = "fanout") //绑定交换机
)
})
public void consumer1(String message) {
System.out.println("message1 = " + message);
}
//创建消费者2
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {@QueueBinding( //将队列与交换机绑定
value = @Queue, //不指定队列名字则为创建一个临时队列
exchange = @Exchange(value = "fanoutExchange", type = "fanout") //绑定交换机
)
})
public void consumer2(String message) {
System.out.println("message2 = " + message);
}
}
第四种路由模式
一个提供者,一个交换机,带有路由key,两个队列,两个消费者
- 编写提供者
@SpringBootTest
class Spriingboot07RabbitmqApplicationTests {
//注入rabbitmq
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
//4.路由模式
@Test
void route_model() {
//发送消息
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//发送路由key 为 queue1的信息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("routeExchange","queue1","工作第"+(i+1)+"天");
}
}
}
- 编写消费者
@Component
public class RouteModel {
//创建一个消费者
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue("queue1"), //创建一个名为queue1的队列
exchange = @Exchange(value = "routeExchange", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
//指定路由key,接收{"queue1","info","warn"}相关信息
key = {"queue1","info","warn"}
)
}
)
public void consumer1(String message) {
System.out.println("message = " + message);
}
//创建一个消费者
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue, //创建临时队列
//指定交换机
exchange = @Exchange(value = "routeExchange", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
//指定路由key,接收{"info","warn"}相关信息
key = {"info","warn"}
)
}
)
public void consumer2(String message) {
System.out.println("message2 = " + message);
}
}
第五种通配符模式
在路由key上加了通配符,通常用.分割单词
#匹配一个或多个单词:info.#匹配info.abc.log*只匹配一个单词:info.*匹配info.log
一个提供者,一个交换机,带有路由key,两个队列,两个消费者
- 编写提供者
@SpringBootTest
class Spriingboot07RabbitmqApplicationTests {
//注入rabbitmq
@Autowired
RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
//5.通配符模式
@Test
void topics_model() {
//发送消息
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
//发送路由key 为 queue1的信息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("topicsExchange","info.abc.log","工作第"+(i+1)+"天");
}
}
}
- 编写消费者
package com.atguigu.topics;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.ExchangeTypes;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Exchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.QueueBinding;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* ClassName: TopicsModel
* Description:
* date: 2020/9/6 18:05
*
* @author July
* @since JDK 1.8
*/
@Component
public class TopicsModel {
//消费者1
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue,
//设置为路由模式ExchangeTypes.TOPIC
exchange = @Exchange(value = "topicsExchange", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
//接收任何多个单词.log,abc.一个单词
key = {"*.log", "#.log", "abc.*"}
)
}
)
public void consumer1(String message) {
System.out.println("message1 = " + message);
}
//消费者2
@RabbitListener(
bindings = {
@QueueBinding(
value = @Queue,
//设置为路由模式ExchangeTypes.TOPIC
exchange = @Exchange(value = "topicsExchange", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
//设置路由key规则
key = {"*.info.*", "abc.log", "info.#"}
)
}
)
public void consumer2(String message) {
System.out.println("message2 = " + message);
}
}