哈希表提供了快速的插入操作和查找操作,每一个元素是一个key-value对,其基于数组来实现。
一、Java中HashMap与Hashtable的区别:
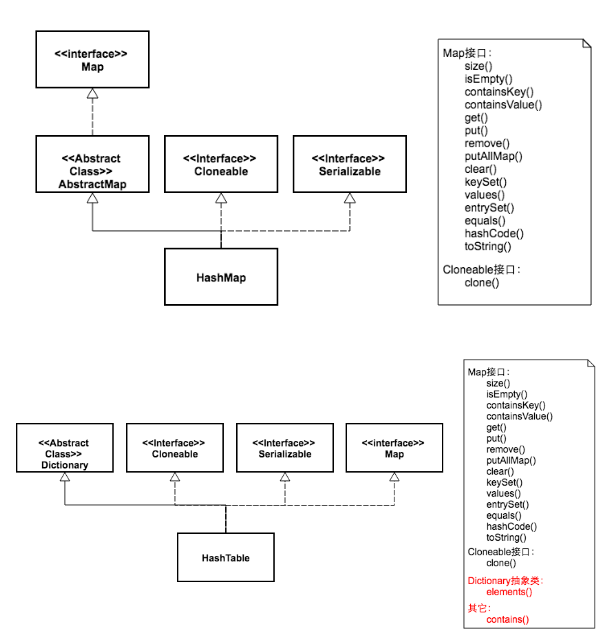
HashMap可以接受null键值和值,而Hashtable则不能。
Hashtable是线程安全的,通过synchronized实现线程同步。而HashMap是非线程安全的,但是速度比Hashtable快。
这两个类有许多不同的地方,下面列出了一部分:
a) Hashtable 是 JDK 1 遗留下来的类,而 HashMap 是后来增加的。
b)Hashtable 是同步(synchronized)的,比较慢,但 HashMap 没有同步策略,所以会更快。
c)Hashtable 不允许有个空的 key,但是 HashMap 允许出现一个 null key。

public class Employee { private String key; private String name; public String getKey() { return key; } public void setKey(String key) { this.key = key; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Employee(String key, String name) { this.key = key; this.name = name; } }

import java.math.BigInteger; public class HashTable { private Employee[] arr; public HashTable() { arr = new Employee[1000]; } public HashTable(int Maxsize) { arr = new Employee[Maxsize]; } // public void Insert(Employee emplo) {//以整型作为索引 // arr[emplo.getKey()] = emplo; // } public void Insert(Employee emplo) {// 以字符串作为索引 arr[hashTable(emplo.getKey())] = emplo; } // public Employee Find(int key) { // return arr[key]; // } public Employee Find(String key) { return arr[hashTable(key)]; } public int hashTable(String key) {// 转换AscII码存储,但存在码值重复问题 BigInteger hashVal = new BigInteger("0"); BigInteger pow27 = new BigInteger("1"); // int hashVal = 0; int i = key.length() - 1; // int pow27 = 1;// 27^0 // for (; i >= 0; i--) { // int letter = key.charAt(i) - 96; // hashVal += letter; // } // return hashVal; // } for (; i >= 0; i--) { int letter = key.charAt(i) - 96; BigInteger letterB = new BigInteger(String.valueOf(letter)); hashVal = hashVal.add(letterB.multiply(pow27));// hashVal += letter * pow27; // hashVal += letter * pow27;// 这里会溢出 // pow27*=27 pow27 = pow27.multiply(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(27))); } //return hashVal % arr.length; return hashVal.mod(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(arr.length))).intValue(); } }

public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { HashTable ht = new HashTable(); /*ht.Insert(new Employee(1, "Ally")); ht.Insert(new Employee(2, "Jion")); ht.Insert(new Employee(3, "Micale")); ht.Insert(new Employee(4, "Lily")); System.out.println(ht.Find(2).getName());*/ ht.Insert(new Employee("aka", "74")); System.out.println(ht.Find("aka").getName()); } }
链地址法

public class LinkList { private Node first;// 火车头,保存头结点的一个指向 public LinkList() {// 初始化 first = null; } public Node deleteFirst() {// 删除头结点 first = first.next;// 头结点为头结点的下一个 return first; } public Node find(String key) {// 按值查找,返回null或索引值 Node current = first;// 从头结点开始 while (!key.equals(current.emplo.getKey())) { if (current.next == null) {// 尾结点后继为null return null; } current = current.next; } return current;// 找到返回 } public Node delete(String key) {// 删除任意结点 Node current = first; Node previous = first; while (!key.equals(current.emplo.getKey())) {//找到current返回true !true = false if (current.next == null) {// 没有找到 return null; } previous = current;// 保存邻近的两个结点 current = current.next; } if (current == first) {// 第一个结点 first = first.next; } else {// 后面的结点 previous.next = current.next;// 上一个结点的下一个变为当前结点的下一个,当前结点删除 } return current;// 结点类,返回结点类型 } public void insert(Employee emplo) {// 在头结点之后插入 Node node = new Node(emplo);// 创建新的结点 // 这里深深体会一下精妙之处,first保存着一个指向 node.next = first;// 图示第一步 first = node;// 图示第二步 } }

public class Node {// 包装车厢 /** * 链结点 */ public Employee emplo;// 数据域 public Node next;// 指针域,后指针 public Node(Employee emplo) {// 构造函数 this.emplo = emplo; } }

import java.math.BigInteger; public class HashTable { private LinkList[] arr; // 每个数值对应一个链表 public HashTable() { arr = new LinkList[100]; } public HashTable(int Maxsize) { arr = new LinkList[Maxsize]; } public void Insert(Employee emplo) {// 以字符串作为索引 String key = emplo.getKey(); int hashVal = hashTable(key); if (arr[hashVal] == null) { arr[hashVal] = new LinkList(); } arr[hashVal].insert(emplo); } public Employee Find(String key) { int hashVal = hashTable(key); return arr[hashVal].find(key).emplo; } public Employee Delete(String key) { int hashVal = hashTable(key); return arr[hashVal].delete(key).emplo; } public int hashTable(String key) {// 转换AscII码存储,但存在码值重复问题 BigInteger hashVal = new BigInteger("0"); BigInteger pow27 = new BigInteger("1"); int i = key.length() - 1; for (; i >= 0; i--) { int letter = key.charAt(i) - 96; BigInteger letterB = new BigInteger(String.valueOf(letter)); hashVal = hashVal.add(letterB.multiply(pow27)); pow27 = pow27.multiply(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(27))); } return hashVal.mod(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(arr.length))).intValue(); } }

public class Demo { public static void main(String[] args) { HashTable ht = new HashTable(); /*ht.Insert(new Employee(1, "Ally")); ht.Insert(new Employee(2, "Jion")); ht.Insert(new Employee(3, "Micale")); ht.Insert(new Employee(4, "Lily")); System.out.println(ht.Find(2).getName());*/ ht.Insert(new Employee("a", "Jack")); // 开放地址法 ht.Insert(new Employee("ct","Rose")); ht.Insert(new Employee("b", "Upon")); System.out.println(ht.Find("a").getName());//打印对象 System.out.println(ht.Find("ct").getName()); System.out.println(ht.Find("b").getName()); System.out.println(ht.hashTable("a")); System.out.println(ht.hashTable("ct")); } }

参考文献:
https://www.cnblogs.com/aeolian/p/8468632.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/williamjie/p/9099141.html
http://www.luyixian.cn/news_show_10979.aspx
