继续学习数据结构递归,什么是递归呢?字面理解就是先递出去,然后回归,递归核心思想就是直接或间接调用本身,好比从前有座山,山里有位老和尚,在给小和尚讲故事,讲的是从前有座山,山里有位老和尚,在给小和尚讲故事,如此依次递出去,直到判断结束条件,然后依次回归。
我们还是通过一些例题来理解吧。
一、三角数字(递归和非递归实现)
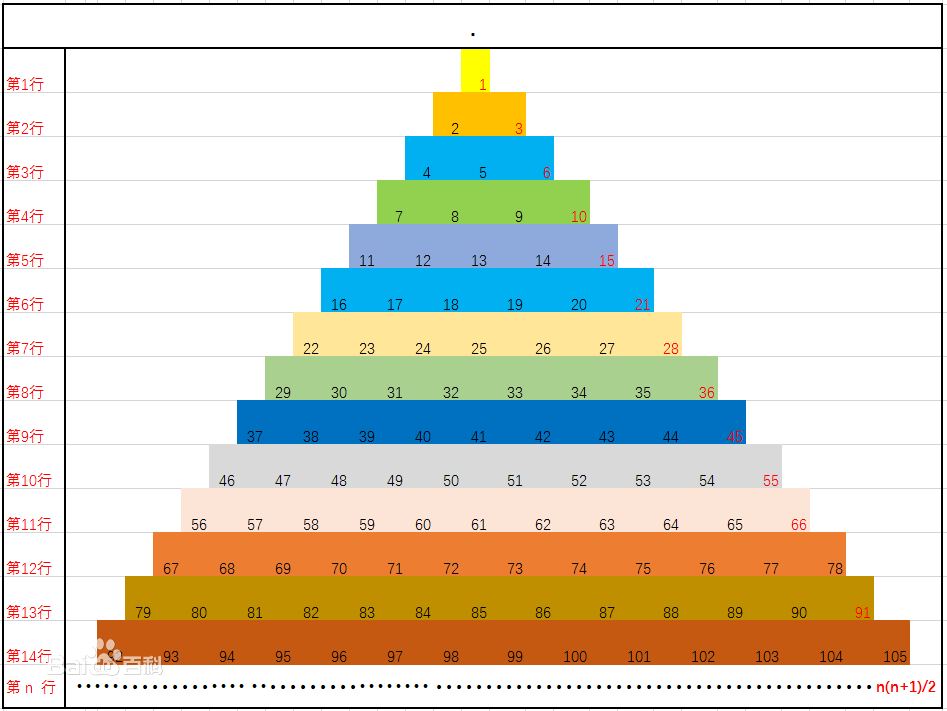

1 //三角数字,n+n-1 2 //1,3,6,10,15 3 public class TriangleNumber { 4 5 public static void main(String[] args) { 6 TriangleNumber tn = new TriangleNumber(); 7 8 System.out.println(tn.recursiondemo(2020)); 9 System.out.println(tn.demo(2020)); 10 } 11 12 public int demo(int n) {//非递归 13 int tatal = 0; 14 while (n > 0) { 15 tatal += n; 16 n--; 17 } 18 return tatal; 19 } 20 21 public int recursiondemo(int n) { 22 if (n == 1) { 23 return 1; 24 } else { 25 return n + recursiondemo(n - 1); 26 } 27 } 28 }
二、Fibonacci数列(递归和非递归实现)


1 //1,1,2,3,5,8,13 2 public class Fibonacci { 3 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Fibonacci f = new Fibonacci(); 6 7 System.out.println(f.recursiondemo(40)); 8 System.out.println(f.demo(40)); 9 } 10 11 public int demo(int n) {//非递归 12 int total = 0; 13 int tota2 = 1; 14 int tota3 = 1; 15 16 if (n == 1 || n == 2) { 17 return 1; 18 } 19 while (n >= 3) { 20 total = tota2 + tota3; 21 tota2 = tota3; 22 tota3 = total; 23 --n; 24 } 25 return total; 26 } 27 28 public int recursiondemo(int n) { 29 if (n == 1 || n == 2) { 30 return 1; 31 } else { 32 return recursiondemo(n - 1) + recursiondemo(n - 2); 33 } 34 } 35 }
