数据可以用不同的形式进行描述或存储在计算机存储器中。最常见的数据描述方法有:公式化描述、链接描述、间接寻址和模拟指针。
公式化描述借助数学公式来确定元素表中的每个元素分别存储在何处(如存储器地址) 。最简单的情形就是把所有元素依次连续存储在一片连续的存储空间中,这就是通常所说的连续线性表。
在链接描述中,元素表中的每个元素可以存储在存储器的不同区域中,每个元素都包含一个指向下一个元素的指针。同样,在间接寻址方式中,元素表中的每个元素也可以存储在存储器的不同区域中,不同的是,此时必须保存一张表,该表的第 i项指向元素表中的第 i个元素,所以这张表是一个用来存储元素地址的表。
在公式化描述中,元素地址是由数学公式来确定的;在链接描述中,元素地址分布在每一个表元素中;而在间接寻址方式下,元素地址则被收集在一张表中。
模拟指针非常类似于链接描述,区别在于它用整数代替了 C + +指针,整数所扮演的角色与指针所扮演的角色完全相同。
数据结构( data structure)包括数据对象和实例以及构成实例的每个元素之间所存在的各种关系。这些关系可由相关的函数来实现。 当我们研究数据结构时,关心的是数据对象(实际上是实例)的描述以及与数据对象相关函数的具体实现。数据对象的良好描述可以有效地促进函数的高效实现。
线性表
线性表( linear list)是这样的数据对象,其实例形式为: (e1 , e2 ,... en ),其中 n 是有穷自然
数。 ei是表中的元素, n 是表的长度。元素可以被视为原子,因为它们本身的结构与线性表的结构无关。当 n = 0 时,表为空;当 n > 0 时, e1是第一个元素, en 是最后一个元素,可以认为 el优先于 e2, e2 优先于 e3,如此等等。除了这种优先关系之外,在线性表中不再有其他的结构。

1 公式化描述
公式化描述( f o r m a l a - b a s e d)采用数组来表示一个对象的实例,数组中的每个位置被称之为单元( c e l l)或节点( n o d e),每个数组单元应该足够大,以便能够容纳数据对象实例中的任意一个元素。在某些情况下,每个实例可分别用一个独立的数组来描述,而在其他情况下,可能要使用一个数组来描述几个实例。实例中每个元素在数组中的位置可以用一个数学公式来指明。假定使用一个数组来描述表,需要把表中的每个元素映射到数组的具体位置上。
l o c a t i on (i )= i - 1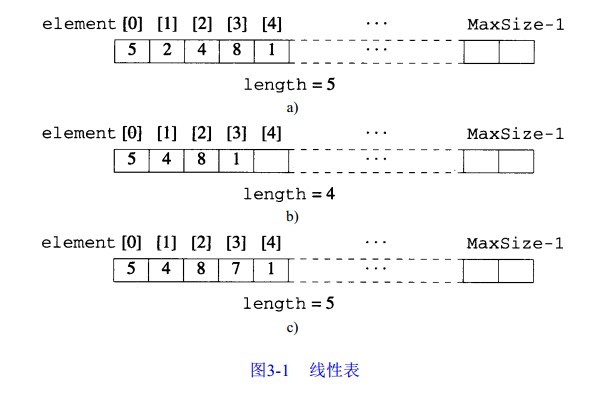
代码实现:

1 #ifndef LINEARLIST_H 2 #define LINEARLIST_H 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include<cstdlib> 5 #include<new> 6 using std::cout; 7 using std::endl; 8 template<class T> 9 class LinearList 10 { 11 public: 12 LinearList(int MaxListSize=10);//构造函数 13 virtual ~LinearList(); 14 bool IsEmpty()const 15 { 16 return length==0; 17 } 18 int Length()const {return length;} 19 bool Find(int k,T& x)const;//返回第K个元素到中 20 int Search(T& x)const;//返回x的位置 21 LinearList<T>& Delete(int k,T& x);//删除位置k的元素,并将元素值存到x 22 LinearList<T>& Insert(int k,const T& x);//将x插入到k位置之后 23 void Output(std::ostream& out)const;//输出到流 24 25 protected: 26 private: 27 int length;//线性表当前长度 28 int MaxSize;//最大长度 29 T *element;//线性表数组 30 }; 31 32 class NoMem 33 { 34 public : 35 NoMem(){ 36 cout<<"No Memory"<<endl; 37 //std::exit(1); 38 } 39 40 }; 41 42 class OutofBounds 43 { 44 public : 45 OutofBounds() 46 { 47 cout<<"Out of Bounds"<<endl; 48 //std::exit(1); 49 } 50 }; 51 52 53 void my_new_handler() 54 { 55 throw NoMem(); 56 } 57 58 template<class T> 59 LinearList<T>::LinearList(int MaxListSize) 60 { 61 std::new_handler old_Handler=std::set_new_handler(my_new_handler); 62 MaxSize=MaxListSize; 63 element=new T[MaxSize]; 64 length=0; 65 66 } 67 68 template<class T> 69 LinearList<T>::~LinearList() 70 { 71 delete[]element; 72 MaxSize=0; 73 length=0; 74 } 75 76 template<class T> 77 bool LinearList<T>::Find(int k,T&x)const 78 { 79 if(k<0||k>length) 80 return false; 81 x=element[k-1]; 82 return true; 83 } 84 85 template<class T> 86 int LinearList<T>::Search(T &x)const 87 { 88 int i=0; 89 while(i<length&&element[i]!=x) 90 { 91 i++; 92 } 93 if(i==length) return 0; 94 else return i+1; 95 } 96 97 template<class T> 98 LinearList<T>& LinearList<T>::Delete(int k,T &x) 99 { 100 if(Find(k,x))//存在位置k 101 { 102 for(int i=k;i<length;++i) 103 { 104 element[i-1]=element[i];//k之后元素向前移动一位 105 } 106 length--; 107 return *this; 108 } 109 else 110 { 111 throw OutofBounds(); 112 } 113 } 114 115 template<class T> 116 LinearList<T>& LinearList<T>::Insert(int k,const T &x) 117 { 118 if(k<0||k>length) 119 { 120 throw OutofBounds(); 121 } 122 else if(length==MaxSize) 123 { 124 throw NoMem(); 125 } 126 else 127 { 128 for(int i=length;i>k;--i) 129 { 130 element[i]=element[i-1];//k之后元素向后移动一位 131 } 132 element[k]=x; 133 length++; 134 return *this; 135 } 136 } 137 138 template<class T> 139 void LinearList<T>::Output(std::ostream& out)const 140 { 141 for(int i=0;i<length;i++) 142 { 143 144 out<<element[i]<<" "; 145 } 146 } 147 148 template<class T> 149 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream &out,const LinearList<T>& x) 150 { 151 x.Output(out); 152 return out; 153 } 154 155 #endif // LINEARLIST_H
评价:这种描述方法的一个缺点是空间的利用率低,尤其是当要维持多个表时。为了提高利用率,可以将多个线性表放在一个数组中进行描述。
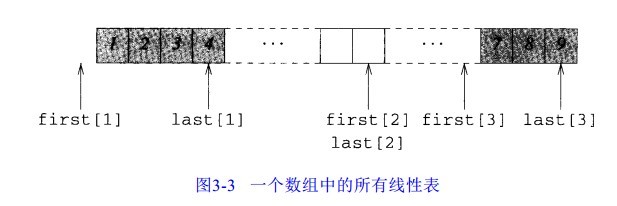
为了在第 i 个表的第 k 个元素之后插入一个元素,首先需要为新元素创建空间。如果l a s t [ i ] = f i r s t [ i + 1 ],则在第 i 个表和第 i + 1 个表之间没有空间,因此不能把第 k + 1 至最后一个元素向后移动一个位置。在这种情况下,通过检查关系式 l a s t [ i - 1 ] < f i r s t [ i ]是否成立,可以确定是否有可能把第 i 个表的 1 至k - 1元素向前移一个位置;如果这个关系式不成立,要么需要把表 1 至表i - 1 的元素向前移一个位置,要么把表 i + 1 至表m 向后移一个位置,然后为表 i创建需要增长的空间。当表中所有的元素总数少于 M a x S i z e时,这种移位的方法是可行的。
尽管在一个数组中描述几个线性表比每个表用一个数组来描述空间的利用率更高,但在最坏的情况下,插入操作将耗费更多的时间。事实上,一次插入操作可能需要移动 M a x S i z e - 1 个元素。
2、链表描述
在链表描述中,数据对象实例的每个元素都放在单元或节点中进行描述。不过,节点不必是一个数组元素,因此没有什么公式可用来定位某个元素。取而代之的是,每个节点中都包含了与该节点相关的其他节点的位置信息。这种关于其他节点的位置信息被称之为链( l i n k)或指针( p o i n t e r)。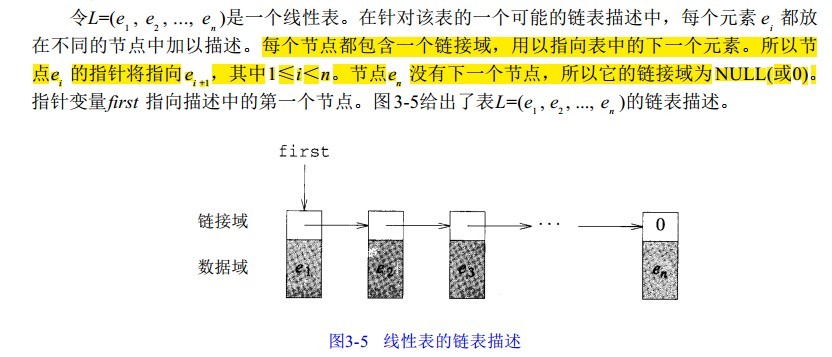
节点定义:
1 template<class T> 2 class ChainNode 3 { 4 friend Chain<T>;//声明为友元,便于访问私有成员6 private: 7 T data; 8 ChainNode<T> *link; 9 };
链表定义:

1 template<class T> 2 class Chain 3 { 4 public: 5 Chain(){ first = 0; }; 6 virtual ~Chain(); 7 bool IsEmpty()const { return first == 0; } 8 int Length()const; 9 bool Find(int k, T& x)const; 10 int Search(const T& x)const; 11 Chain<T>& Delete(int k, T& x); 12 Chain<T>& Insert(int k, const T& x); 13 void Output(std::ostream& out)const; 14 protected: 15 private: 16 ChainNode<T> *first;//Point to first node 17 ChainNode<T> *last; 18 };
操作:
析构函数,删除所有节点:

1 template<class T> 2 Chain<T>::~Chain() 3 { 4 ChainNode<T> *next; 5 while (first) 6 { 7 next = first->link; 8 delete first; 9 first = next; 10 } 11 }
获取链表长度:

1 template<class T> 2 int Chain<T>::Length()const 3 { 4 ChainNode<T> *current = first; 5 int len = 0; 6 while (current) 7 { 8 len++; 9 current = current->link; 10 } 11 return len; 12 }
获取位置k的值:

1 template<class T> 2 bool Chain<T>::Find(int k, T& x)const 3 { 4 if (k < 1) return false; 5 ChainNode<T> *current = first; 6 int index = 1; 7 while (index < k&¤t) 8 { 9 current = current->link; 10 index++; 11 12 } 13 if (current) 14 { 15 x = current->data; 16 return true; 17 } 18 return false; 19 }
查找链表是否含有某个元素:

1 template<class T> 2 int Chain<T>::Search(const T &x)const 3 { 4 ChainNode<T> *current = first; 5 int index = 1; 6 while (current&¤t->data != x) 7 { 8 current = current->link; 9 index++; 10 } 11 if (current) return index; 12 return false; 13 }
删除,和插入元素:

1 template<class T> 2 Chain<T>& Chain<T>::Delete(int k, T& x) 3 { 4 if (k < 1 || !first) 5 throw OutofBounds(); 6 ChainNode<T> *p = first; 7 if (k == 1) 8 first = first->link; 9 else 10 { 11 ChainNode<T> *q = first; 12 for (int index = 1; index < k - 1 && q; index++) 13 { 14 q = q->link; 15 } 16 if (!q || q->link) 17 throw OutofBounds(); 18 p = q->link; 19 if (p == last){ last = q; } 20 q->link = p->link; 21 } 22 x = p->data; 23 delete p; 24 return *this; 25 } 26 27 template<class T> 28 Chain<T>& Chain<T>::Insert(int k, const T &x) 29 { 30 if (k < 0) 31 throw OutofBounds(); 32 ChainNode<T> *p = first; 33 for (int index = 1; index<k&&!p; ++index) 34 { 35 p = p->link; 36 } 37 if (k>0 && !p) throw OutofBounds(); 38 ChainNode<T> *y = new ChainNode<T>; 39 y->data = x; 40 if (k) 41 { 42 y->link = p->link; 43 p->link = y; 44 } 45 else 46 { 47 y->link = first; 48 first = y; 49 } 50 if (!y->link) 51 last = y; 52 return *this; 53 }
扩展:
删除所有元素:

1 template<class T> 2 void Chain<T>::Erase() 3 { 4 ChainNode<T> *next; 5 while (first) 6 { 7 next = first->link; 8 delete first; 9 first = next; 10 } 11 }
链表尾添加元素:

1 template<class T> 2 Chain<T>& Chain<T>::Append(const T& x) 3 { 4 ChainNode<T> *y = new Chain<T>(); 5 y->data = x; 6 y->link = 0; 7 if (first) 8 { 9 last->link = y; 10 last = y; 11 } 12 else 13 { 14 first = last = y; 15 } 16 17 return *this; 18 }
链表遍历器:
许多使用链的应用代码都要求从链表的第一个元素开始,从左至右依次检查每一个元素。采用遍历器( I t e r a t o r)可以大大方便这种从左至右的检查,遍历器的功能是纪录当前位置并每次向前移动一个位置。链表遍历器有两个共享成员 I n i t i a l i z e和N e x t。 I n i t i a l i z e返回一个指针,该指针指向第一个链表节点中所包含的数据,同时把私有变量 l o c a t i o n设置为指向链表的第一个节点,该变量用来跟踪我们在链表中所处的位置。成员 N e x t用来调整 l o c a t i o n,使其指向链表中的下一个节点,并返回指向该节点数据域的指针。

1 template<class T> 2 class ChainIterator 3 { 4 public: 5 T* Initialize(const Chain<T>& c) 6 { 7 location = c.first; 8 if (location) 9 return &location->data; 10 return 0; 11 } 12 T* Next() 13 { 14 if (!location) return 0; 15 location = location->link; 16 if (location) return &location->data; 17 return 0; 18 } 19 private: 20 ChainNode<T> *location; 21 };
链表完整程序:

1 #ifndef CHAIN_H 2 #define CHAIN_H 3 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include "exceptionerror.h" 6 using std::cout; 7 using std::endl; 8 9 template<class T> 10 class Chain; 11 12 template <class T> 13 class ChainIterator; 14 15 template<class T> 16 class ChainNode 17 { 18 friend Chain<T>;//声明为友元,便于访问私有成员 19 friend ChainIterator<T>; 20 private: 21 T data; 22 ChainNode<T> *link; 23 }; 24 25 template<class T> 26 class ChainIterator 27 { 28 public: 29 T* Initialize(const Chain<T>& c) 30 { 31 location = c.first; 32 if (location) 33 return &location->data; 34 return 0; 35 } 36 T* Next() 37 { 38 if (!location) return 0; 39 location = location->link; 40 if (location) return &location->data; 41 return 0; 42 } 43 private: 44 ChainNode<T> *location; 45 }; 46 47 48 template<class T> 49 class Chain 50 { 51 friend ChainIterator<T>; 52 public: 53 Chain(){ first = 0; }; 54 virtual ~Chain(); 55 bool IsEmpty()const { return first == 0; } 56 int Length()const; 57 bool Find(int k, T& x)const; 58 int Search(const T& x)const; 59 Chain<T>& Delete(int k, T& x); 60 Chain<T>& Insert(int k, const T& x); 61 void Erase(); 62 Chain<T>& Append(const T& x); 63 void Output(std::ostream& out)const; 64 void Binsort(int range, int(*value)(T& x)); 65 protected: 66 private: 67 ChainNode<T> *first;//Point to first node 68 ChainNode<T> *last; 69 }; 70 71 template<class T> 72 void Chain<T>::Binsort(int range, int(*value)(T& x)) 73 { 74 int b;//箱子索引号 75 ChainNode<T> **bottom, **top; 76 //箱子初始化 77 bottom = new ChainNode<T>*[range + 1]; 78 top = new ChainNode<T>*[range + 1]; 79 for (b = 0; b <= range; b++) 80 { 81 bottom[b] = 0; 82 } 83 84 for (; first; first = first->link) 85 { 86 b = value(first->data); 87 if (bottom[b]) 88 { 89 top[b]->link = first; 90 top[b] = first; 91 } 92 else 93 { 94 bottom[b] = top[b] = first; 95 } 96 } 97 98 ChainNode<T> *y = 0; 99 for (b = 0; b <= range; b++) 100 { 101 if (bottom[b]) 102 { 103 if (y) 104 y->link = bottom[b]; 105 else 106 first = bottom[b]; 107 108 y = top[b]; 109 } 110 } 111 if (y) y->link = 0; 112 delete[] bottom; 113 delete[] top; 114 115 } 116 117 template<class T> 118 Chain<T>& Chain<T>::Append(const T& x) 119 { 120 ChainNode<T> *y = new Chain<T>(); 121 y->data = x; 122 y->link = 0; 123 if (first) 124 { 125 last->link = y; 126 last = y; 127 } 128 else 129 { 130 first = last = y; 131 } 132 133 return *this; 134 } 135 136 137 138 template<class T> 139 void Chain<T>::Erase() 140 { 141 ChainNode<T> *next; 142 while (first) 143 { 144 next = first->link; 145 delete first; 146 first = next; 147 } 148 } 149 150 template<class T> 151 Chain<T>::~Chain() 152 { 153 ChainNode<T> *next; 154 while (first) 155 { 156 next = first->link; 157 delete first; 158 first = next; 159 } 160 } 161 162 template<class T> 163 int Chain<T>::Length()const 164 { 165 ChainNode<T> *current = first; 166 int len = 0; 167 while (current) 168 { 169 len++; 170 current = current->link; 171 } 172 return len; 173 } 174 175 template<class T> 176 bool Chain<T>::Find(int k, T& x)const 177 { 178 if (k < 1) return false; 179 ChainNode<T> *current = first; 180 int index = 1; 181 while (index < k&¤t) 182 { 183 current = current->link; 184 index++; 185 186 } 187 if (current) 188 { 189 x = current->data; 190 return true; 191 } 192 return false; 193 } 194 195 template<class T> 196 int Chain<T>::Search(const T &x)const 197 { 198 ChainNode<T> *current = first; 199 int index = 1; 200 while (current&¤t->data != x) 201 { 202 current = current->link; 203 index++; 204 } 205 if (current) return index; 206 return false; 207 } 208 209 template<class T> 210 void Chain<T>::Output(std::ostream& out)const 211 { 212 ChainNode<T> *current = first; 213 for (current = first; current; current = current->link) 214 { 215 out << current->data << " "; 216 } 217 218 } 219 220 template<class T> 221 std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& output, const Chain<T> &x) 222 { 223 x.Output(output); 224 return output; 225 } 226 227 template<class T> 228 Chain<T>& Chain<T>::Delete(int k, T& x) 229 { 230 if (k < 1 || !first) 231 throw OutofBounds(); 232 ChainNode<T> *p = first; 233 if (k == 1) 234 first = first->link; 235 else 236 { 237 ChainNode<T> *q = first; 238 for (int index = 1; index < k - 1 && q; index++) 239 { 240 q = q->link; 241 } 242 if (!q || q->link) 243 throw OutofBounds(); 244 p = q->link; 245 if (p == last){ last = q; } 246 q->link = p->link; 247 } 248 x = p->data; 249 delete p; 250 return *this; 251 } 252 253 template<class T> 254 Chain<T>& Chain<T>::Insert(int k, const T &x) 255 { 256 if (k < 0) 257 throw OutofBounds(); 258 ChainNode<T> *p = first; 259 for (int index = 1; index<k&&!p; ++index) 260 { 261 p = p->link; 262 } 263 if (k>0 && !p) throw OutofBounds(); 264 ChainNode<T> *y = new ChainNode<T>; 265 y->data = x; 266 if (k) 267 { 268 y->link = p->link; 269 p->link = y; 270 } 271 else 272 { 273 y->link = first; 274 first = y; 275 } 276 if (!y->link) 277 last = y; 278 return *this; 279 } 280 #endif // CHAIN_H
3、间接寻址
间接寻址( indirect addressing)是公式化描述和链表描述的组合。采用这种描述方法,可以保留公式化描述方法的许多优点——可以根据索引在 ( 1 )的时间内访问每个元素、可采用二叉搜索方法在对数时间内对一个有序表进行搜索等等。与此同时,也可以获得链表描述方法的重要特色——在诸如插入和删除操作期间不必对元素进行实际的移动。因此,大多数间接寻址链表操作的时间复杂性都与元素的总数无关。
在间接寻址方式中,使用一个指针表来跟踪每个元素。可采用一个公式(如公式( 3 - 1 ))来定位每个指针的位置,以便找到所需要的元素。元素本身可能存储在动态分配的节点或节点数组之中。图 3 - 1 0给出了一个采用间接寻址表 table 描述的5元素线性表。其中 t a b l e [ i ] 是一个指针,它指向表中的第i + 1 个元素, length 是表的长度。
与公式化描述不同的是,间接寻址的删除和插入操作均只需要对指针表进行操作,因此与数据元素的类型和大小无关,时间复杂度更低。
代码:

1 #ifndef INDIRECTLIST_H 2 #define INDIRECTLIST_H 3 4 #include<iostream> 5 #include "OutofBound.h" 6 using std::ostream; 7 using std::cout; 8 template<class T> 9 class IndirectList 10 { 11 public: 12 IndirectList(int MaxListSize=10); 13 virtual ~IndirectList(); 14 bool IsEmpty() const{return length==0;} 15 int Length()const{return length;} 16 bool Find(int k,T& x)const; 17 int Search(const T& x)const; 18 IndirectList<T>& Delete(int k,T& x); 19 IndirectList<T>& Insert(int k,const T& x); 20 void Output(ostream& out)const; 21 protected: 22 private: 23 int length; 24 int MaxSize; 25 T** table; 26 }; 27 28 template<class T> 29 IndirectList<T>::IndirectList(int MaxListSize) 30 { 31 MaxSize=MaxListSize; 32 length=0; 33 table=new T*[MaxSize]; 34 } 35 36 template<class T> 37 IndirectList<T>::~IndirectList() 38 { 39 for(int i=0;i<length;i++) 40 { 41 delete []table[i]; 42 } 43 delete[] table; 44 } 45 46 template<class T> 47 bool IndirectList<T>::Find(int k,T& x)const 48 { 49 if(k<1||k>length) return false; 50 x=*table[k-1]; 51 return true; 52 } 53 54 template<class T> 55 int IndirectList<T>::Search(const T& x)const 56 { 57 int index=0; 58 while(index<length&&*table[index]!=x) 59 { 60 index++; 61 } 62 63 if(index<length) return index+1; 64 else return false; 65 } 66 67 template<class T> 68 IndirectList<T>& IndirectList<T>::Delete(int k,T& x) 69 { 70 71 if(Find(k,x)) 72 { 73 for(int i=k;i<length;++i) 74 { 75 table[i-1]=table[i]; 76 } 77 length--; 78 return *this; 79 } 80 else throw OutofBound(); 81 } 82 83 template<class T> 84 IndirectList<T>& IndirectList<T>::Insert(int k,const T&x) 85 { 86 if(k<0||k>length) throw OutofBound(); 87 if(length==MaxSize) throw OutofBound(); 88 for(int i=length;i>k;i--) 89 { 90 table[i]=table[i-1]; 91 } 92 table[k]=new T; 93 *table[k]=x; 94 length++; 95 96 return *this; 97 98 } 99 100 template<class T> 101 void IndirectList<T>::Output(ostream& out)const 102 { 103 for(int i=0;i<length;i++) 104 { 105 out<<*table[i]<<" "; 106 } 107 } 108 109 template<class T> 110 ostream& operator<<(ostream& output,const IndirectList<T>& x) 111 { 112 x.Output(output); 113 return output; 114 } 115 116 #endif // INDIRECTLIST_H
4、
