除了公式化即数组的实现方式,堆栈还可以用链表的方式实现,这种方式对空间利用率更高。
在使用链表来表示堆栈时,必须确定链表的哪一端对应于栈顶。如果把链表的右端作为栈顶,那么可以利用链表操作 I n s e r t ( n , x )和D e l e t e ( n , x )来实现堆栈的插入和删除操作,其中 n为链表中的节点数目。这两种链表操作的时间复杂性均为 O( n )。另一方面,如果把链表的左端作为栈顶,则可以利用链表操作 I n s e r t ( 0 , x )和D e l e t e ( 1 , x )来实现堆栈的插入和删除操作。这两种链表操作的时间复杂性均为O ( 1 )。以上分析表明,应该把链表的左端作为栈顶。
C++代码实现:
Node.h:
1 #ifndef NODE_H 2 #define NODE_H 3 template<class T> 4 class LinkedStack;//声明模板类 5 6 template<class T> 7 class Node 8 { 9 public: 10 friend class LinkedStack<T>;//声明为友元,因为需要访问Node的私有成员 11 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& output, const LinkedStack<T>& s); 12 private: 13 Node<T> *next; 14 T data; 15 }; 16 #endif
Stack:
(exceptionerror见队列的实现:公式化描述)
1 #ifndef LINKEDSTACK_H 2 #define LINKEDSTACK_H 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include "Node.h" 5 #include "exceptionerror.h" 6 7 template<class T> 8 class LinkedStack 9 { 10 public: 11 LinkedStack():top(0){} 12 ~LinkedStack(); 13 friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& output,const LinkedStack& s) 14 { 15 if (s.IsEmpty()) 16 { 17 output << "empty stack" << std::endl; 18 } 19 else 20 { 21 Node<T>* p = s.top; 22 while (p) 23 { 24 output << p->data << " "; 25 p = p->next; 26 } 27 } 28 29 return output; 30 } 31 bool IsEmpty()const{ return top == 0; } 32 T Top()const; 33 int Suantity()const; 34 LinkedStack<T>& Add(const T& x); 35 LinkedStack<T>& Delete(T& x); 36 private: 37 Node<T>* top; 38 }; 39 40 template<class T> 41 LinkedStack<T>::~LinkedStack() 42 { 43 Node<T>* next; 44 while (top) 45 { 46 next = top->next; 47 delete top; 48 top = next; 49 } 50 } 51 52 template<class T> 53 T LinkedStack<T>::Top()const 54 { 55 if (IsEmpty()) 56 { 57 throw OutofBounds(); 58 } 59 return top->data; 60 } 61 62 template<class T> 63 LinkedStack<T>& LinkedStack<T>::Add(const T& x) 64 { 65 Node<T>* p = new Node<T>; 66 p->data = x; 67 p->next = top; 68 top = p; 69 70 return *this; 71 } 72 73 template<class T> 74 LinkedStack<T>& LinkedStack<T>::Delete(T& x) 75 { 76 if (IsEmpty()) 77 { 78 throw OutofBounds(); 79 } 80 else 81 { 82 x = top->data; 83 Node<T>* p = top; 84 top = top->next; 85 delete p; 86 87 return *this; 88 89 } 90 } 91 92 template<class T> 93 int LinkedStack<T>::Suantity()const 94 { 95 Node<T>* p=top; 96 int cnt = 0; 97 while (p) 98 { 99 p = p->next; 100 cnt++; 101 } 102 return cnt; 103 } 104 #endif
测试:
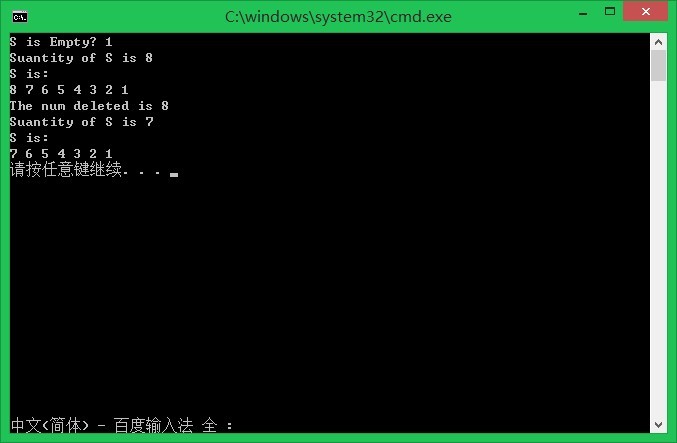
1 #include "LinkedStack.h" 2 3 int main() 4 { 5 LinkedStack<int> S; 6 std::cout << "S is Empty? " << S.IsEmpty() << std::endl; 7 S.Add(1); 8 S.Add(2); 9 S.Add(3); 10 S.Add(4); 11 S.Add(5); 12 S.Add(6); 13 S.Add(7); 14 S.Add(8); 15 std::cout << "Suantity of S is " << S.Suantity() << std::endl; 16 std::cout << "S is:" << std::endl; 17 std::cout << S << std::endl; 18 int x; 19 S.Delete(x); 20 std::cout << "The num deleted is " << x << std::endl; 21 std::cout << "Suantity of S is " << S.Suantity() << std::endl; 22 std::cout << "S is:" << std::endl; 23 std::cout << S << std::endl; 24 system("pause"); 25 return 0; 26 }
输出: