2017-2018-1 20155205 实现mypwd
课堂总结
根据上课对ls -l功能的实现,我总结了实现一个linux命令需要的步骤:
- 使用
man -k xx | grep xx查看帮助文档,这里需要查看相关函数的参数、返回值和头文件,同时也要看一下SEE ALSO里与我们查找的功能相关的其他函数。 - 借鉴实现其他命令的思路,比如实现myod时,我们要opendir、readdir和closedir,其实每个命令都需要执行这两步,我们就可以按这个思路来写其他的命令。
mypwd的实现
- 查看pwd帮助文档,看到一个getcwd,又查看了一下getcwd帮助文档发现这个函数可以直接获取当前路径!
参考getcwd()函数的用法的代码可以实现pwd的功能。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
int main(void)
{
char *path = NULL;
path = getcwd(NULL,0);
puts(path);
free(path);
return 0;
}
2.按照老师上课的教学内容,我们还可以用stat来实现pwd。
首先在学习过程中,我们知道了上一级“.”和上上级“..”的结点信息的关系。
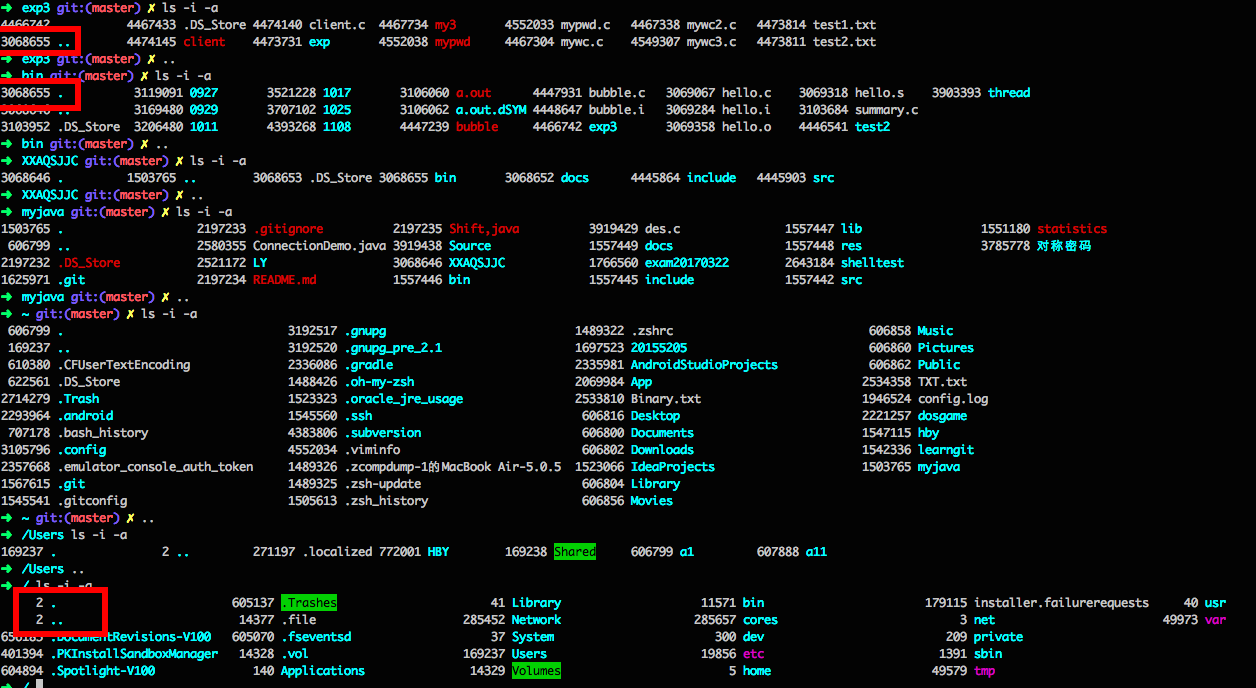
先看一下stat中的结构体,可以看到ino_t是存储结点数的,所以我们编程序要用到它。
struct stat { /* when _DARWIN_FEATURE_64_BIT_INODE is NOT defined */
dev_t st_dev; /* device inode resides on */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode's number */
mode_t st_mode; /* inode protection mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links to the file */
uid_t st_uid; /* user-id of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group-id of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device type, for special file inode */
struct timespec st_atimespec; /* time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtimespec; /* time of last data modification */
struct timespec st_ctimespec; /* time of last file status change */
off_t st_size; /* file size, in bytes */
quad_t st_blocks; /* blocks allocated for file */
u_long st_blksize;/* optimal file sys I/O ops blocksize */
u_long st_flags; /* user defined flags for file */
u_long st_gen; /* file generation number */
};
上网查了相关资料后,发现我们还需要掌握一个DIR结构体:
struct __dirstream
{
void *__fd; // `struct hurd_fd' pointer for descriptor.
char *__data; // Directory block.
int __entry_data; // Entry number `__data' corresponds to.
char *__ptr; // Current pointer into the block.
int __entry_ptr; // Entry number `__ptr' corresponds to.
size_t __allocation;// Space allocated for the block.
size_t __size; // Total valid data in the block.
__libc_lock_define (, __lock) // Mutex lock for this structure.
};
typedef struct __dirstream DIR;
DIR结构体类似于FILE,是一个内部结构,以下几个函数用这个内部结构保存当前正在被读取的目录的有关信息。函数 DIR *opendir(const char *pathname),即打开文件目录,返回的就是指向DIR结构体的指针,而该指针由以下几个函数使用:
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dp);
void rewinddir(DIR *dp);
int closedir(DIR *dp);
long telldir(DIR *dp);
void seekdir(DIR *dp,long loc);
接着是dirent结构体,首先我们要弄清楚目录文件(directory file)的概念:这种文件包含了其他文件的名字以及指向与这些文件有关的信息的指针。从定义能够看出,dirent不仅仅指向目录,还指向目录中的具体文件,readdir函数同样也读取目录下的文件,这就是证据。以下为dirent结构体的定义:
struct dirent
{
long d_ino; /* inode number 索引节点号 */
off_t d_off; /* offset to this dirent 在目录文件中的偏移 */
unsigned short d_reclen; /* length of this d_name 文件名长 */
unsigned char d_type; /* the type of d_name 文件类型 */
char d_name [NAME_MAX+1]; /* file name (null-terminated) 文件名,最长255字符 */
}
- 伪代码
获取当前文件名和结点数;
if("."与".."结点数不相等)
{
打印当前文件名;
cd上一级;
}
- 测试代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#define SIZE 128
ino_t getinode(char *dirname); //获取文件名称
void getwork(ino_t inode_num);
void dirname(ino_t inode_num, char *buf, int buflen);
int main(void)
{
getwork(getinode("."));
printf("
");
return 0;
}
ino_t getinode(char *dirname) //通过stat得到文件名
{
struct stat name;
if (stat(dirname, &name) == -1)
{
perror("dirname");
exit(1);
}
return name.st_ino;
}
void getwork(ino_t inode_num)
{
ino_t parent_inode;
char buf[SIZE];
if (getinode("..") != inode_num)
{
chdir(".."); //到达..文件
dirname(inode_num, buf, SIZE);
parent_inode = getinode(".");
getwork(parent_inode); //此处通过递归来不断到达上一级
printf("/%s", buf);
}
}
void dirname(ino_t inode_num, char *buf,int buflen) //
{
DIR *dir_ptr;
struct dirent *dirt;
if ((dir_ptr = opendir(".")) == NULL)
{
perror(".");
exit(1);
}
while ((dirt = readdir(dir_ptr)) != NULL)
{
if (dirt->d_ino == inode_num)
{
strncpy(buf, dirt->d_name, buflen);
buf[strlen(buf)] = '�';
closedir(dir_ptr);
return ;
}
}
exit(1);
}
- 测试结果
