socket Function
To perform network I/O, the first thing a process must do is call the socket function, specifying the type of communication protocol desired (TCP using IPv4, UDP using IPv6, Unix domain stream protocol, etc.).
#include <sys/socket.h> int socket (int family, int type, int protocol); Returns: non-negative descriptor if OK, -1 on error
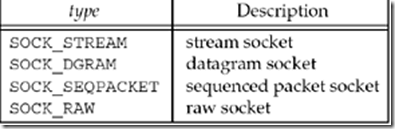
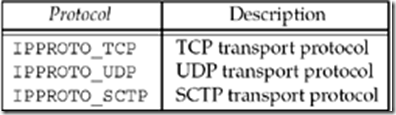
family specifies the protocol family and is one of the constants shown in Figure 4.2. This argument is often referred to as domain instead of family. The socket type is one of the constants shown in Figure 4.3. The protocol argument to the socket function should be set to the specific protocol type found in Figure 4.4, or 0 to select the system's default for the given combination of family and type.
Figure 4.2. Protocol family constants for socket function.
Figure 4.3. type of socket for socket function.
Figure 4.4. protocol of sockets for AF_INET or AF_INET6.
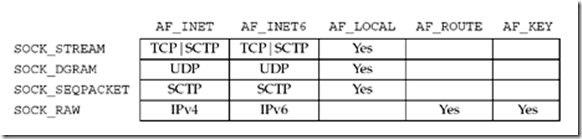
Not all combinations of socket family and type are valid. Figure 4.5 shows the valid combinations, along with the actual protocols that are valid for each pair. The boxes marked "Yes" are valid but do not have handy acronyms. The blank boxes are not supported.
Figure 4.5. Combinations of family and type for the socket function.
其他参考:
Creating a Socket
The primitive for creating a socket is the socket function, declared in sys/socket.h.
— Function: int socket (int namespace, int style, int protocol)
This function creates a socket and specifies communication style style, which should be one of the socket styles listed in Communication Styles. The namespace argument specifies the namespace; it must be PF_LOCAL (see Local Namespace) or PF_INET (see Internet Namespace). protocol designates the specific protocol (see Socket Concepts); zero is usually right for protocol.
The return value from socket is the file descriptor for the new socket, or -1 in case of error. The following errno error conditions are defined for this function:
EPROTONOSUPPORT
The protocol or style is not supported by the namespace specified.
EMFILE
The process already has too many file descriptors open.
ENFILE
The system already has too many file descriptors open.
EACCES
The process does not have the privilege to create a socket of the specified style or protocol.
ENOBUFS
The system ran out of internal buffer space.
The file descriptor returned by the socket function supports both read and write operations. However, like pipes, sockets do not support file positioning operations.
For examples of how to call the socket function, see Local Socket Example, or Inet Example.