问题:
给定二叉树,
求层元素和为最大的最小层数。
Example 1: Input: root = [1,7,0,7,-8,null,null] Output: 2 Explanation: Level 1 sum = 1. Level 2 sum = 7 + 0 = 7. Level 3 sum = 7 + -8 = -1. So we return the level with the maximum sum which is level 2. Example 2: Input: root = [989,null,10250,98693,-89388,null,null,null,-32127] Output: 2 Constraints: The number of nodes in the tree is in the range [1, 104]. -105 <= Node.val <= 105
example 1:
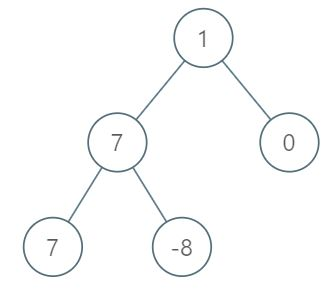
解法:BFS
- level记录当前层次,reslevel记录所要求的:层元素和最大的层数。
- cursum记录当前层和,sum记录最大层和。
遍历queue,
对于每层元素求和,
若当前层和cursum>sum最大层和,
- 更新sum为cursum
- 更新reslevel为当前层level。
代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 8 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {} 9 * TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {} 10 * }; 11 */ 12 class Solution { 13 public: 14 int maxLevelSum(TreeNode* root) { 15 int reslevel = 1, level = 1; 16 int sum = INT_MIN; 17 queue<TreeNode*> q; 18 if(root) q.push(root); 19 while(!q.empty()) { 20 int sz = q.size(); 21 int cursum = 0; 22 for(int i=0; i<sz; i++) { 23 TreeNode* cur = q.front(); 24 q.pop(); 25 cursum += cur->val; 26 if(cur->left) q.push(cur->left); 27 if(cur->right) q.push(cur->right); 28 } 29 if(cursum > sum) { 30 sum = cursum; 31 reslevel = level; 32 } 33 level++; 34 } 35 return reslevel; 36 } 37 };