问题:
给出一颗二叉树,两个节点p和q,求出这两节点的最近公共父节点(LCA)。
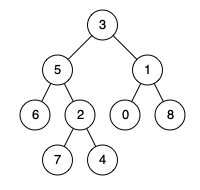
Example 1: Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1 Output: 3 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3. Example 2: Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4 Output: 5 Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition. Note: All of the nodes' values will be unique. p and q are different and both values will exist in the binary tree.
解法:Binary Tree(二叉树)
递归
1. 函数定义:
-> 找p和q的最近公共父节点
1 TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q)
- 参数:
- 当前node:root
- 寻找目标节点:p,q
- 返回值:
- 未找到:
- case_1: p和q都没找到(!p and !q):返回 null
- case_2: (2-1)找到其中一个(p or q):返回 找到的对象 !p?q:p
- 找到:case_3:
- (3-1)之前的节点处已经找到:返回 上一次调用递归函数的结果 left or right
- (3-2)刚好,当前节点处找到:返回 root
- 未找到:
2. 状态:(每次调用函数的变化的参数)root
3. 选择:(得到递归结果后的处理)
- left==null && right==null
- -> return null
- left!=null && right!=null
- -> return root
- left!=null || right!=null
- left!=null
- -> return left
- right!=null
- -> return right
- left!=null
4. base case:
- root==null
- -> return null
- root==p || root==q
- -> return root
代码参考:
1 /** 2 * Definition for a binary tree node. 3 * struct TreeNode { 4 * int val; 5 * TreeNode *left; 6 * TreeNode *right; 7 * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} 8 * }; 9 */ 10 class Solution { 11 public: 12 //DEF of fun: From root, return the LCA node of p and q. 13 //Mutative Param of fun: root 14 //Opt: 15 //case_1: neither of them, under root: 16 // -> return null 17 //case_2: one of them, under root: 18 // -> return itself (2-1) 19 //case_3: both of them, under root: 20 // both of them, under left(right) tree: 21 // -> return the pre-result (3-1) 22 // one under left tree, the other one under right tree: 23 // -> return root(cur-node) (3-2) 24 //base case: 25 //root==null, but can't find p or q: 26 // -> return null (case_1) 27 //root==p or q: 28 // -> return root (case_2) 29 TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) { 30 //base 31 if(!root) return nullptr; 32 if(root == p || root == q) return root; 33 //recursion 34 TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q); 35 TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q); 36 //opt 37 //case_1: 38 if(!left && !right) return nullptr; 39 //case_3:(3-2) 40 if(left && right) return root; 41 //case_2:(2-1) && case_3:(3-1) 42 //left or right (one of them) is null 43 return (!left)?right:left; 44 } 45 };