一、事件监听介绍
原理: 观察者模式
spring的事件监听有三个部分组成:
-
事件(ApplicationEvent) 负责对应相应监听器 事件源发生某事件是特定事件监听器被触发的原因。
-
监听器(ApplicationListener) 对应于观察者模式中的观察者。监听器监听特定事件,并在内部定义了事件发生后的响应逻辑。
-
事件发布器(ApplicationEventMulticaster )对应于观察者模式中的被观察者/主题, 负责通知观察者 对外提供发布事件和增删事件监听器的接口,维护事件和事件监听 器之间的映射关系,并在事件发生时负责通知相关监听器。
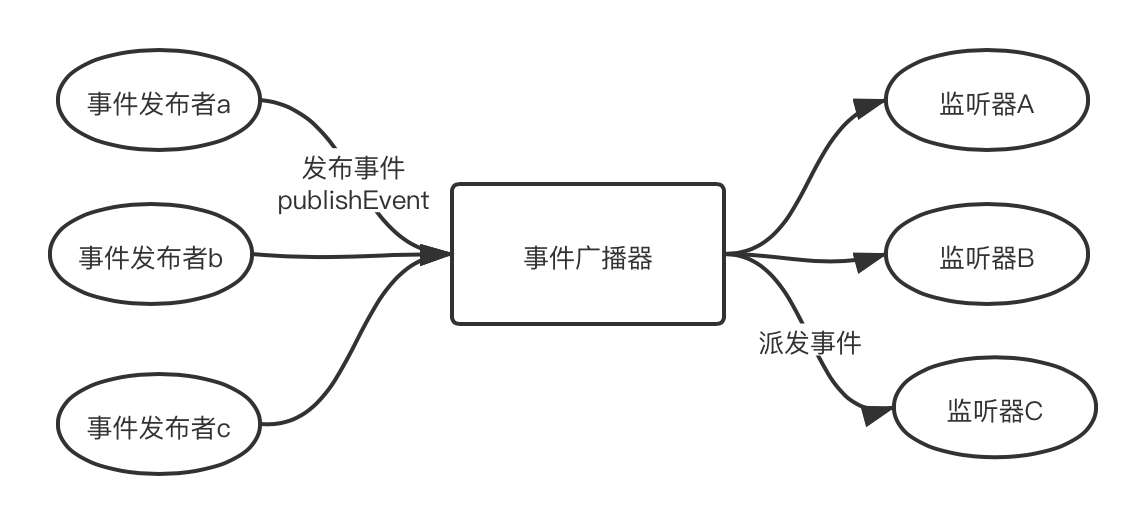
二、事件监听使用
1、事件
1 public class MyApplicationEvent extends ApplicationEvent { 2 3 private String msg; 4 5 public MyApplicationEvent(Object source) { 6 super(source); 7 } 8 9 public MyApplicationEvent(Object source, String msg) { 10 super(source); 11 this.msg = msg; 12 } 13 14 public String getMsg() { 15 return msg; 16 } 17 18 public void setMsg(String msg) { 19 this.msg = msg; 20 } 21 }
2、监听器-接口模式
1 @Component 2 public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener { 3 @Override 4 public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) { 5 System.out.println("MyApplicationListener: " + "正在处理器事件"); 6 System.out.println("MyApplicationListener-事件源:" + event.getSource()); 7 if(event instanceof MyApplicationEvent) { 8 System.out.println("MyApplicationListener-事件msg:" + ((MyApplicationEvent) event).getMsg()); 9 } 10 } 11 }
监听器-注解模式

1 @Component 2 public class MyCustomListener { 3 4 @EventListener 5 public void processEvent(ApplicationEvent event){ 6 System.out.println("MyCustomListener: " + "正在处理器事件"); 7 System.out.println("MyCustomListener-事件源:" + event.getSource()); 8 if(event instanceof MyApplicationEvent) { 9 System.out.println("MyCustomListener-事件msg:" + ((MyApplicationEvent) event).getMsg()); 10 } 11 } 12 13 }
3、事件发布器,使用Spring内置的,配置类
1 @Configuration 2 @ComponentScan("com.test.listener.component") 3 public class MainConfig { 4 public MainConfig(){ 5 System.out.println("MainConfig 构造方法"); 6 } 7 }
4、主方法启动
1 public class MainStarter { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class); 5 // 1、创建一个事件 6 MyApplicationEvent myApplicationEvent = new MyApplicationEvent(new Object(), "这是一个的新事件"); 7 // 2、发布事件 8 context.publishEvent(myApplicationEvent); 9 // 3、监听器处理 10 // ..... 11 context.close(); 12 } 13 14 }
三、原理图
1、事件监听相关类图

2、执行流程图
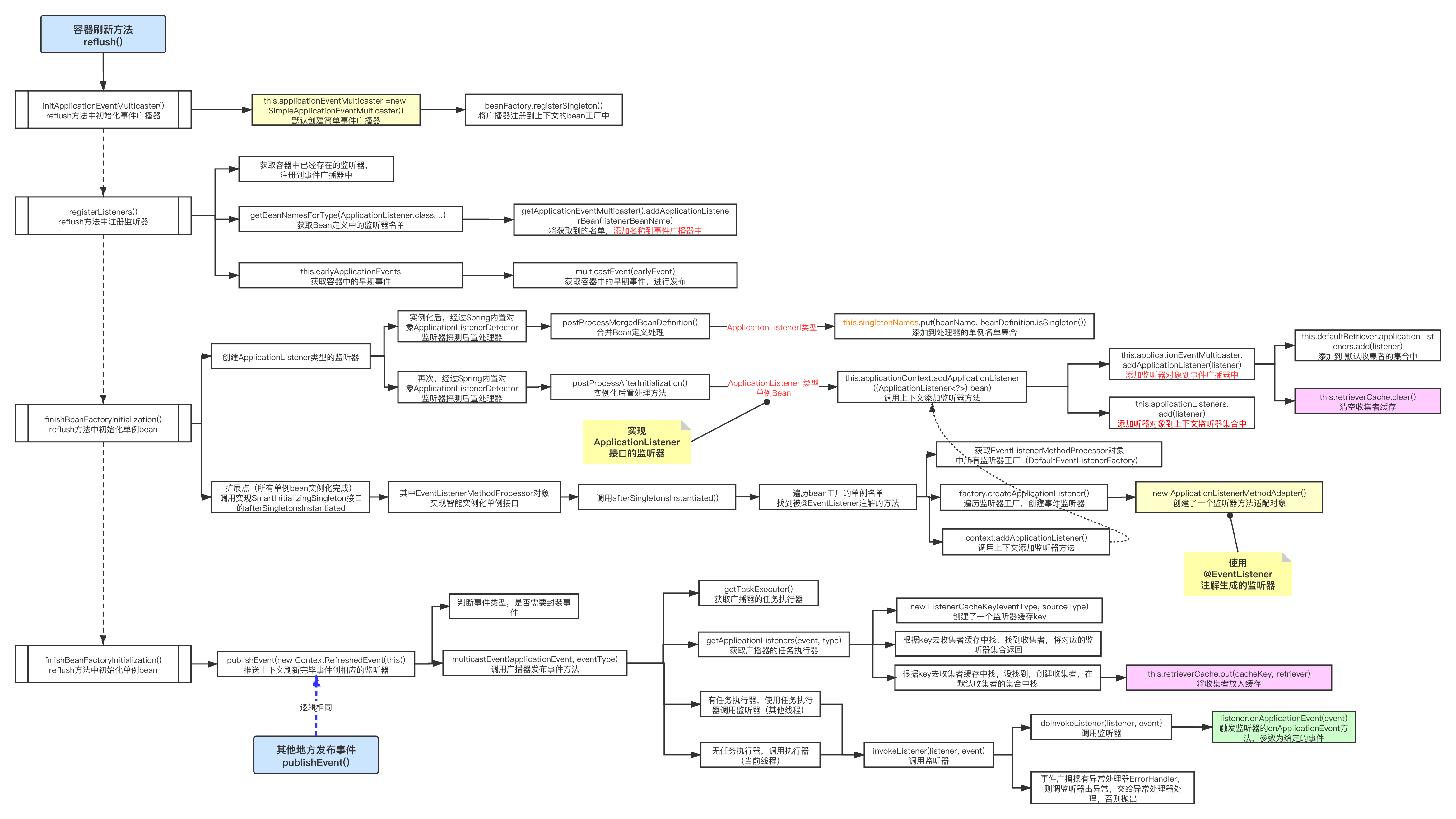
四、Spring事件监听源码分析
1、在reflush(),方法中调用 initApplicationEventMulticaster() 初始化事件广播器
1 protected void initApplicationEventMulticaster() { 2 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory(); 3 // 判断Bean工厂中是有没有applicationEventMulticaster 应用广播器组件 4 if (beanFactory.containsLocalBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME)) { 5 // 直接显示的调用getBean获取出来赋值给的applicationContext对象 6 this.applicationEventMulticaster = 7 beanFactory.getBean(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, ApplicationEventMulticaster.class); 8 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 9 logger.trace("Using ApplicationEventMulticaster [" + this.applicationEventMulticaster + "]"); 10 } 11 } 12 // Bean工厂中没有的话 13 else { 14 // new 一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster对象 15 this.applicationEventMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(beanFactory); 16 // 并且注入到容器中 17 beanFactory.registerSingleton(APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME, this.applicationEventMulticaster); 18 if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { 19 logger.trace("No '" + APPLICATION_EVENT_MULTICASTER_BEAN_NAME + "' bean, using " + 20 "[" + this.applicationEventMulticaster.getClass().getSimpleName() + "]"); 21 } 22 } 23 }
2、在reflush(),方法中调用registerListeners() 注册监听器
1 protected void registerListeners() { 2 // Register statically specified listeners first. 3 // 获取容器中所有的监听器对象(成品对象) 4 for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners()) { 5 // 把监听器的注册到事件广播器上去 6 getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListener(listener); 7 } 8 9 // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans 10 // uninitialized to let post-processors apply to them! 11 // 根据类型从bean工厂的bean定义中,获取bean定义名单 12 String[] listenerBeanNames = getBeanNamesForType(ApplicationListener.class, true, false); 13 for (String listenerBeanName : listenerBeanNames) { 14 // 把监听器的注册到事件广播器上去,只是注册的名单 15 getApplicationEventMulticaster().addApplicationListenerBean(listenerBeanName); 16 } 17 18 // Publish early application events now that we finally have a multicaster... 19 // 获取早期事件 20 Set<ApplicationEvent> earlyEventsToProcess = this.earlyApplicationEvents; 21 this.earlyApplicationEvents = null; 22 if (earlyEventsToProcess != null) { 23 for (ApplicationEvent earlyEvent : earlyEventsToProcess) { 24 // 获取事件广播器,发布早期事件 25 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(earlyEvent); 26 } 27 } 28 }
3、发布事件方法 publishEvent()
1 protected void publishEvent(Object event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { 2 Assert.notNull(event, "Event must not be null"); 3 4 // Decorate event as an ApplicationEvent if necessary 5 // 1、如有必要,将事件装饰为ApplicationEvent 6 ApplicationEvent applicationEvent; 7 if (event instanceof ApplicationEvent) { 8 applicationEvent = (ApplicationEvent) event; 9 } 10 else { 11 applicationEvent = new PayloadApplicationEvent<>(this, event); 12 if (eventType == null) { 13 eventType = ((PayloadApplicationEvent<?>) applicationEvent).getResolvableType(); 14 } 15 } 16 17 // Multicast right now if possible - or lazily once the multicaster is initialized 18 if (this.earlyApplicationEvents != null) { 19 this.earlyApplicationEvents.add(applicationEvent); 20 } 21 else { 22 // 2、使用事件广播器广播事件到相应的监听器 23 getApplicationEventMulticaster().multicastEvent(applicationEvent, eventType); 24 } 25 26 // Publish event via parent context as well... 27 // 3、如果有父容器 28 if (this.parent != null) { 29 if (this.parent instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { 30 // 使用父容器,带事件类型参数的, 发布事件 31 ((AbstractApplicationContext) this.parent).publishEvent(event, eventType); 32 } 33 else { 34 // 使用父容器发布事件 35 this.parent.publishEvent(event); 36 } 37 } 38 }
4、广播器广播事件方法 multicastEvent()
1 @Override 2 public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) { 3 ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event)); 4 // 1、返回此广播器的当前任务执行器 5 Executor executor = getTaskExecutor(); 6 // 2、、getApplicationListeners:返回与给定事件类型匹配的应用监听器集合 7 for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) { 8 // 3.1 executor不为null,则使用executor调用监听器 9 if (executor != null) { 10 executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event)); 11 } 12 // 3.2 否则,直接调用监听器 13 else { 14 invokeListener(listener, event); 15 } 16 } 17 }
5、广播器广播事件方法 multicastEvent() , 其中 doInvokeListener() 就去调用了监听器的处理事件方法
1 protected void invokeListener(ApplicationListener<?> listener, ApplicationEvent event) { 2 // 1.返回此广播器的当前错误处理器 3 ErrorHandler errorHandler = getErrorHandler(); 4 if (errorHandler != null) { 5 try { 6 // 2.1 如果errorHandler不为null,则使用带错误处理的方式调用给定的监听器 7 doInvokeListener(listener, event); 8 } 9 catch (Throwable err) { 10 errorHandler.handleError(err); 11 } 12 } 13 else { 14 // 2.2 否则,直接调用调用给定的监听器 15 doInvokeListener(listener, event); 16 } 17 }
