ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor,它是一个计划任务线程池,可以执行定时任务或者是计划任务。
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 继承了ThreadPoolExecutor,需要了解 ThreadPoolExecutor 的原理,参考:【Java多线程】线程池ThreadPoolExecutor实现原理(二十二)
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 中的任务队列使用了 阻塞式延迟队列 (DelayedWorkQueue),参考:【Java多线程】DelayQueue源码分析 (二十六)
了解以上2个知识点之后,能更好的理解ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor的原理
参考:【Java多线程】ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor详解(二十八)
本章是对其进行补充
一、ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor原理图
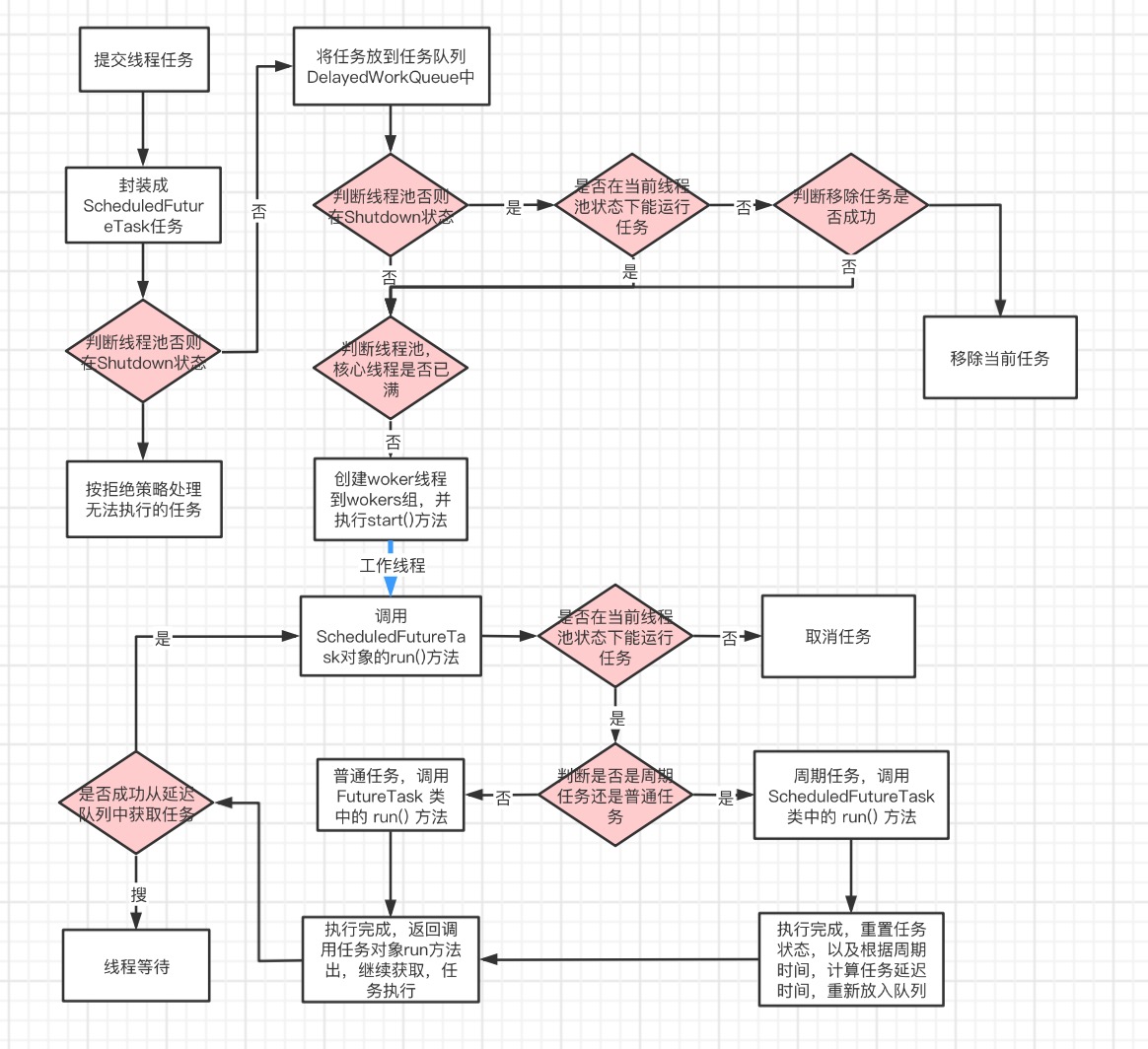
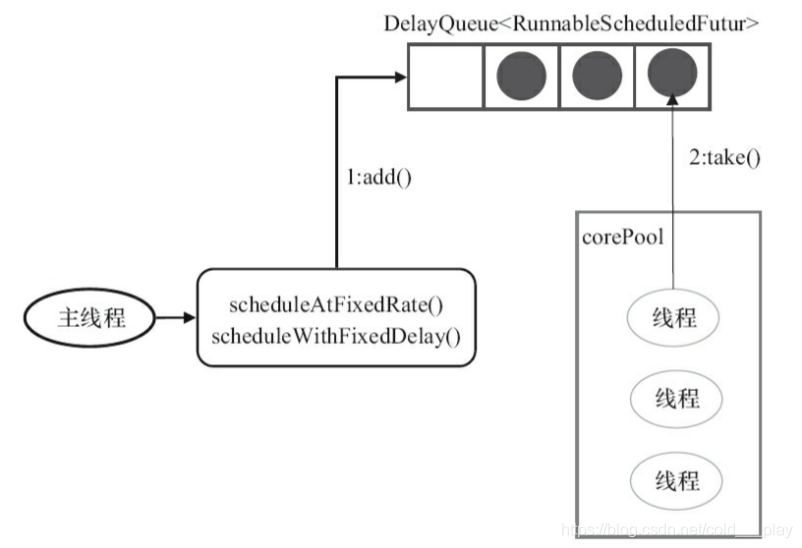
任务传递示意图
二、属性
由于 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 是继承了 ThreadPoolExecutor,ThreadPoolExecutor有的属性它都有,以下是另外增加的属性
1 public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 2 extends ThreadPoolExecutor 3 implements ScheduledExecutorService { 4 5 // shutdown后继续存在周期任务 6 private volatile boolean continueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdown; 7 8 // shutdown后执行存在延迟任务 9 private volatile boolean executeExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdown = true; 10 11 // 取消状态下移除标识 12 private volatile boolean removeOnCancel = false; 13 14 // 序列器 15 private static final AtomicLong sequencer = new AtomicLong(); 16 17 ...... 18 }
三、方法
在ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor线程池提交任务执行,主要使用的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor.java、ThreadPoolExecutor.java、ScheduledFutureTask.java、FutureTask.java、DelayedWorkQueue.java等相关类方法,如下:
1、构造方法
1 // 根据核心线程数创建 ScheduledThreadPool 线程池 2 public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize) { 3 super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, 4 new DelayedWorkQueue()); 5 } 6 7 // 根据核心线程数、线程工厂创建 ScheduledThreadPool 线程池 8 public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, 9 ThreadFactory threadFactory) { 10 super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, 11 new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory); 12 } 13 14 // 根据核心线程数、拒绝策略创建 ScheduledThreadPool 15 public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, 16 RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { 17 super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, 18 new DelayedWorkQueue(), handler); 19 } 20 21 // 根据核心线程数、线程工厂、拒绝策略创建 ScheduledThreadPool 线程池 22 public ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, 23 ThreadFactory threadFactory, 24 RejectedExecutionHandler handler) { 25 super(corePoolSize, Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, NANOSECONDS, 26 new DelayedWorkQueue(), threadFactory, handler); 27 }
2、schedule() 方法
1 public <V> ScheduledFuture<V> schedule(Callable<V> callable, 2 long delay, 3 TimeUnit unit) { 4 if (callable == null || unit == null) 5 throw new NullPointerException(); 6 // 新建一个 RunnableScheduledFuture 对象 7 RunnableScheduledFuture<V> t = decorateTask(callable, 8 new ScheduledFutureTask<V>(callable, 9 triggerTime(delay, unit))); 10 11 // 延迟执行任务 12 delayedExecute(t); 13 return t; 14 }
由上可以看出,主要是新建了一个ScheduledFutureTask对象,然后点用延迟执行任务方法 delayedExecute(t)
3、decorateTask() 方法
1 // 包装任务成一个 RunnableScheduledFuture 对象 2 // 实际就是返回了task对象 3 protected <V> RunnableScheduledFuture<V> decorateTask( 4 Callable<V> callable, RunnableScheduledFuture<V> task) { 5 return task; 6 }
返回任务对象
4、delayedExecute() 方法
1 private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) { 2 // 线程池状态是否 Shutdown 3 if (isShutdown()) 4 // 拒绝任务 5 reject(task); 6 // 7 else { 8 // 获取任务队列,添加任务 9 super.getQueue().add(task); 10 // isShutdown() 再次判断任务状态 11 // canRunInCurrentRunState() 是否在当前状态下能运行 12 // remove() 移除任务 13 if (isShutdown() && 14 !canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) && 15 remove(task)) 16 // 任务取消 17 task.cancel(false); 18 else 19 // 确保线程池能启动任务 20 ensurePrestart(); 21 } 22 }
主要是将任务添加到队列中,然后执行ensurePrestart()确保线程池能启动任务
5、ThreadPoolExecutor 类中的 ensurePrestart() 方法
1 void ensurePrestart() { 2 // 获取工作线程数量 3 int wc = workerCountOf(ctl.get()); 4 // 工作线程数小于 核心线程数 5 if (wc < corePoolSize) 6 // 添加工作线程线,以核心线程池数为上限 7 addWorker(null, true); 8 else if (wc == 0) 9 // 添加工作线程线,以最大线程池线程数为上限 10 addWorker(null, false); 11 }
6、ThreadPoolExecutor 类中的 reject() 方法 拒绝任务

1 // 拒绝任务 2 final void reject(Runnable command) { 3 // 调用创建线程池时,使用的拒绝策略对象处理 4 handler.rejectedExecution(command, this); 5 }
7、ThreadPoolExecutor 类中的 remove() 方法 移除任务

1 public boolean remove(Runnable task) { 2 // 从任务队列中 3 boolean removed = workQueue.remove(task); 4 // 尝试终止线程池 5 tryTerminate(); // In case SHUTDOWN and now empty 6 return removed; 7 }
8、ScheduledFutureTask 类中的 run() 方法
1 // ScheduledFutureTask 的 run() 方法 2 public void run() { 3 // 是否是周期任务 4 boolean periodic = isPeriodic(); 5 // canRunInCurrentRunState() 是否在当前状态下能运行 6 if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(periodic)) 7 cancel(false); 8 // 非周期任务 9 else if (!periodic) 10 // 直接运行任务的run()方法 11 ScheduledFutureTask.super.run(); 12 // FutureTask 类中的 runAndReset()方法 13 // 运行且重置 14 else if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) { 15 // 设置 16 setNextRunTime(); 17 reExecutePeriodic(outerTask); 18 } 19 }
9、ScheduledFutureTask 类中的 setNextRuntime() 方法
1 // 设置下次运行时间 2 private void setNextRunTime() { 3 // 周期时间 4 long p = period; 5 6 if (p > 0) 7 // time 任务到期时间 8 // 任务完成后,在任务到期时间上 + 一个周期时间,进行延迟。 9 time += p; 10 else 11 // 现在的时间 + 一个周期时间,进行延迟 12 time = triggerTime(-p); 13 }
重新设置任务的执行时间
10、ScheduledFutureTask 类中的reExecutePeriodic() 方法
1 // 重新设置周期任务 2 void reExecutePeriodic(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) { 3 // canRunInCurrentRunState() 是否在当前状态下能运行 4 if (canRunInCurrentRunState(true)) { 5 // 将周期任务加入队列 6 super.getQueue().add(task); 7 // 再次判断是否在当前状态下能运行 8 // 不能就移除任务,并取消 9 if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(true) && remove(task)) 10 task.cancel(false); 11 else 12 // 确保线程池能启动任务 13 ensurePrestart(); 14 } 15 }
11、ScheduledFutureTask 类中的 compareTo() 方法 任务比较优先级
 View Code
View Code在放入任务到队列或取出时,用到比较方法
12、ScheduledFutureTask 类中的getDelay() 方法 获取延迟时间

1 // 返回当前元素还需要延迟多长时间,单位是纳秒 2 public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) { 3 return unit.convert(time - now(), NANOSECONDS); 4 }
13、ScheduledFutureTask 类中的 cancel() 方法

1 // ScheduledFutureTask类中的 cancel() 方法 2 // 参数 mayInterruptIfRunning :如果任务运行是否可以被中断 3 // 取消任务 4 public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { 5 // 调用 FutureTask类中的 cancel() 方法 6 boolean cancelled = super.cancel(mayInterruptIfRunning); 7 // 取消成功 且 移除取消的成功 且 heapIndex(数组中位置下表) 大于等于0 8 if (cancelled && removeOnCancel && heapIndex >= 0) 9 // 移除自己 10 remove(this); 11 12 return cancelled; 13 }
14、FutureTask类中的run() 方法
1 // FutureTask 类中的 run(); 方法 2 public void run() { 3 // 给任务对象添加runner属性值,值为当前线程 4 if (state != NEW || 5 !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, 6 null, Thread.currentThread())) 7 return; 8 9 try { 10 Callable<V> c = callable; 11 // 判断callable 不为空以及 state状态 为NUM 12 if (c != null && state == NEW) { 13 V result; 14 boolean ran; 15 try { 16 // 调用c的 call返回,并接受返回值 17 result = c.call(); 18 // 运行完成标识 19 ran = true; 20 } catch (Throwable ex) { 21 result = null; 22 ran = false; 23 setException(ex); 24 } 25 // 完成之后,设置结果给属性 26 if (ran) 27 set(result); 28 } 29 } finally { 30 // runner must be non-null until state is settled to 31 // prevent concurrent calls to run() 32 runner = null; 33 // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent 34 // leaked interrupts 35 int s = state; 36 // 是否中断 37 if (s >= INTERRUPTING) 38 // 处理中断情况 39 handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); 40 } 41 }
15、FutureTask类中的run() 方法
1 // FutureTask 类中的 runAndReset(); 方法 2 protected boolean runAndReset() { 3 // 给任务对象添加runner属性值,值为当前线程 4 if (state != NEW || 5 !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, 6 null, Thread.currentThread())) 7 // 失败返回false 8 return false; 9 10 boolean ran = false; 11 // 任务状态 12 int s = state; 13 try { 14 Callable<V> c = callable; 15 if (c != null && s == NEW) { 16 try { 17 // 调用sft任务对象的callable属性对应的对象,call()方法 18 // 由于是周期任务,调用call返回之后不会接收返回值 19 c.call(); // don't set result 20 // 调用完成标识 21 ran = true; 22 } catch (Throwable ex) { 23 setException(ex); 24 } 25 } 26 } finally { 27 // runner must be non-null until state is settled to 28 // prevent concurrent calls to run() 29 // 任务的运行线程属性置空 30 runner = null; 31 // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent 32 // leaked interrupts 33 // 重置后任务状态不变 34 s = state; 35 if (s >= INTERRUPTING) 36 // 状态改变成中断,进行中断处理 37 handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); 38 } 39 // 运行完成 且 状态还是 NEW 返回成功 40 return ran && s == NEW; 41 } 42
16、FutureTask类中的 cancel() 方法

1 // FutureTask类中的 cancel() 方法 2 // 参数 mayInterruptIfRunning :如果任务运行是否可以被中断 3 // 取消任务 4 public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) { 5 // 任务状态是 新建NEW状态,且CAS修改任务状态为 INTERRUPTING(中断) 或: CANCELLED(取消) 6 if (!(state == NEW && 7 UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, 8 mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED))) 9 // CAS失败,返回false 10 return false; 11 12 try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception 13 if (mayInterruptIfRunning) { 14 try { 15 // 获取运行线程, 16 // runner由来:任务FutureTask,运行时,会CAS设置 runner = Thread.currentThread(); 17 Thread t = runner; 18 if (t != null) 19 // 中断线程 20 t.interrupt(); 21 } finally { // final state 22 // 修改任务状态为INTERRUPTED 中断 23 UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED); 24 } 25 } 26 } finally { 27 // 28 finishCompletion(); 29 } 30 return true; 31 }
17、FutureTask 类中的 finishCompletion() 方法

1 // FutureTask类中的 完成节点设置 2 private void finishCompletion() { 3 // assert state > COMPLETING; 4 // 遍历等待节点 5 for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null;) { 6 // 修改将等待节点设为null,循环节点 7 if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) { 8 for (;;) { 9 Thread t = q.thread; 10 // 节点线程不为空 11 if (t != null) { 12 // 将节点thread属性设为null 13 q.thread = null; 14 // 唤醒线程t 15 LockSupport.unpark(t); 16 } 17 WaitNode next = q.next; 18 if (next == null) 19 break; 20 q.next = null; // unlink to help gc 21 // q指向下一个节点 22 q = next; 23 } 24 break; 25 } 26 } 27 28 // 钩子方法 29 done(); 30 31 callable = null; // to reduce footprint 32 }
18、DelayedWorkQueue 类中的 take() 方法
1 public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> take() throws InterruptedException { 2 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 3 // 获取锁 4 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 5 try { 6 for (;;) { 7 // 查看队列头的元素 8 RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0]; 9 if (first == null) 10 // 队列无用元素,线程等待可用 11 available.await(); 12 else { 13 // 第一个,也是最近一个可用元素的延迟时间 14 long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS); 15 // <= 0表示队头元素有过期或者已到期 16 if (delay <= 0) 17 // 完成拉取相关操作 18 return finishPoll(first); 19 // 不存在过期元素 20 first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting 21 // 前面是否还有消费线程等待消费 22 if (leader != null) 23 // 等待 24 available.await(); 25 else { 26 // 设置本线程为最先消费线程 27 Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread(); 28 leader = thisThread; 29 try { 30 // 本线程等待 delay 时长,后被唤醒 31 // delay 时长 后,队列头第一个元素会过期 32 available.awaitNanos(delay); 33 } finally { 34 if (leader == thisThread) 35 leader = null; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 } 40 } finally { 41 // 如果 leader 为空,且队列不为空,唤醒一个消费线程 42 if (leader == null && queue[0] != null) 43 // 通知消费线程,延迟队列可用 44 available.signal(); 45 // 释放锁 46 lock.unlock(); 47 } 48 }
19、DelayedWorkQueue 类中的 finishPoll() 方法
1 // 完成拉取相关操作 2 private RunnableScheduledFuture<?> finishPoll(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> f) { 3 int s = --size; 4 // 队列最后一个元素,由于数组第一位置空出来了,最后一个元素就需要上浮 5 RunnableScheduledFuture<?> x = queue[s]; 6 // 数组位置空出来 7 queue[s] = null; 8 if (s != 0) 9 // 二叉堆中的最小堆,下浮操作 10 siftDown(0, x); 11 // 设置数组下标,f是已取出来的元素,下标设为-1 12 setIndex(f, -1); 13 return f; 14 }
四、示例
1 public class TestScheduledThreadPool { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { 4 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(1); 5 6 ScheduledFuture<Integer> future1 = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.schedule(() -> { 7 System.out.println("我要延迟30s执行"); 8 return 1; 9 }, 30_000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 10 11 ScheduledFuture<Integer> future2 = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.schedule(() -> { 12 System.out.println("我要延迟20s执行"); 13 return 2; 14 }, 20_000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 15 16 ScheduledFuture<Integer> future3 = scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.schedule(() -> { 17 System.out.println("我要延迟8s执行"); 18 return 1; 19 }, 8_000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); 20 21 22 scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.shutdown(); 23 24 System.out.println(future1.get()); 25 System.out.println(future2.get()); 26 System.out.println(future3.get()); 27 28 // while (!scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.isTerminated()) { 29 // Thread.sleep(1000); 30 // } 31 System.out.println("Game Over~~~"); 32 33 34 } 35 }
