本文主要学习Java多线程的核心类:AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,检查AQS。
先来看一下此类描述:
用来构建锁或其他同步器组件的重要级基础框架及整个JUC体系的基石,通过内置的FIFO队列来完成资源获取线程的排队工作,并通过一个int类型变量表示持有锁的状态。
/** * Provides a framework for implementing blocking locks and related * synchronizers (semaphores, events, etc) that rely on * first-in-first-out (FIFO) wait queues. This class is designed to * be a useful basis for most kinds of synchronizers that rely on a * single atomic {@code int} value to represent state. Subclasses * must define the protected methods that change this state, and which * define what that state means in terms of this object being acquired * or released. Given these, the other methods in this class carry * out all queuing and blocking mechanics. Subclasses can maintain * other state fields, but only the atomically updated {@code int} * value manipulated using methods {@link #getState}, {@link * #setState} and {@link #compareAndSetState} is tracked with respect * to synchronization. * ... * @since 1.5 * @author Doug Lea */ public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer implements java.io.Serializable
FIFO等待队列说明:
共享资源被占用,就需要一定的阻塞等待唤醒机制来保证锁分配。这个机制主要用的是CLH队列的变体实现,将暂时获取不到锁的线程加入到队列中,这个队列就是AQS的抽线表现。它将请求共享资源的线程封装成队列的节点(Node),通过CAS、自选以及LockSupport.park()的方式,维护state变量状态,达到同步控制。
/** * Wait queue node class. * * <p>The wait queue is a variant of a "CLH" (Craig, Landin, and * Hagersten) lock queue. CLH locks are normally used for * spinlocks. We instead use them for blocking synchronizers, but * use the same basic tactic of holding some of the control * information about a thread in the predecessor of its node. A * "status" field in each node keeps track of whether a thread * should block. A node is signalled when its predecessor * releases. Each node of the queue otherwise serves as a * specific-notification-style monitor holding a single waiting * thread. The status field does NOT control whether threads are * granted locks etc though. A thread may try to acquire if it is * first in the queue. But being first does not guarantee success; * it only gives the right to contend. So the currently released * contender thread may need to rewait. * * <p>To enqueue into a CLH lock, you atomically splice it in as new * tail. To dequeue, you just set the head field. * <pre> * +------+ prev +-----+ +-----+ * head | | <---- | | <---- | | tail * +------+ +-----+ +-----+ * </pre> * on the design of this class. */ static final class Node
内部类Node内部属性说明:
Node = waitStatus + 前后指针指向
static final class Node { /** 共享 */ static final Node SHARED = new Node(); /** 独占 */ static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null; /** 线程被取消了 */ static final int CANCELLED = 1; /** 后继线程需要唤醒 */ static final int SIGNAL = -1; /** 等待condition唤醒 */ static final int CONDITION = -2; /** 共享式同步状态获取将会无条件传播下去 */ static final int PROPAGATE = -3; /** * Status field, taking on only the values: * SIGNAL: The successor of this node is (or will soon be) * blocked (via park), so the current node must * unpark its successor when it releases or * cancels. To avoid races, acquire methods must * first indicate they need a signal, * then retry the atomic acquire, and then, * on failure, block. * CANCELLED: This node is cancelled due to timeout or interrupt. * Nodes never leave this state. In particular, * a thread with cancelled node never again blocks. * CONDITION: This node is currently on a condition queue. * It will not be used as a sync queue node * until transferred, at which time the status * will be set to 0. (Use of this value here has * nothing to do with the other uses of the * field, but simplifies mechanics.) * PROPAGATE: A releaseShared should be propagated to other * nodes. This is set (for head node only) in * doReleaseShared to ensure propagation * continues, even if other operations have * since intervened. * 0: None of the above * * The values are arranged numerically to simplify use. * Non-negative values mean that a node doesn't need to * signal. So, most code doesn't need to check for particular * values, just for sign. * * The field is initialized to 0 for normal sync nodes, and * CONDITION for condition nodes. It is modified using CAS * (or when possible, unconditional volatile writes). */ volatile int waitStatus; /** 前置节点 */ volatile Node prev; /** 后继节点 */ volatile Node next; volatile Thread thread; Node nextWaiter; final boolean isShared() { return nextWaiter == SHARED; } final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException { Node p = prev; if (p == null) throw new NullPointerException(); else return p; } Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker } Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter this.nextWaiter = mode; this.thread = thread; } Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition this.waitStatus = waitStatus; this.thread = thread; } }
二、以ReentrantLock作为突破口,其核心内部类Sync继承AQS。
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 7373984872572414699L; private final Sync sync; /** * Base of synchronization control for this lock. Subclassed * into fair and nonfair versions below. Uses AQS state to * represent the number of holds on the lock. */ abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { private static final long serialVersionUID = -5179523762034025860L;
接下来,以实际最常用的lock()方法分析走起:
对于AQS底层源码分析主要分析如下几个:
第一类:① lock() ② acquire() ③ tryAcquire(arg) ④ addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE) ⑤ acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE),arg)
第二类:①unlock()
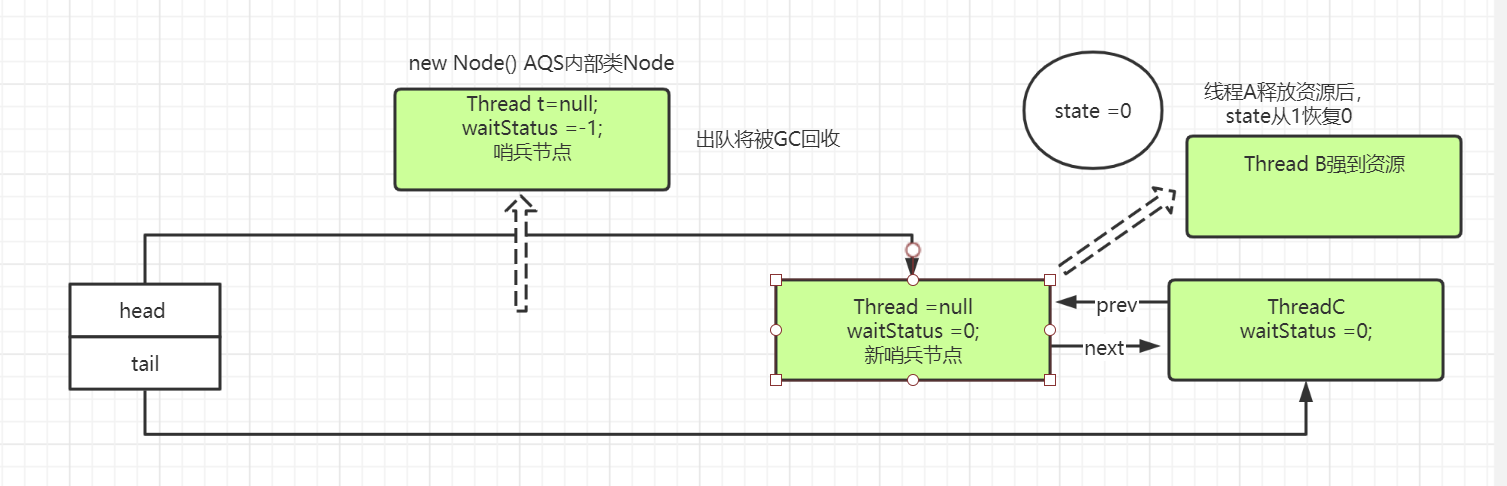
目前三个线程排队等待处理同一个资源:
ThreadA,ThreadB,ThreadC。
① lock():线程A:lock.lock():线程Aj进入if,并且把值state从0设置成1(初始化时,在AQS类中state值为0),并且把当前持有资源的线程设置成线程A。
final void lock() { if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread()); else acquire(1); }
线程B,进来是。只能走else(期望state是0,当时以及被线程A设置成1),
protected final boolean compareAndSetState(int expect, int update) { // See below for intrinsics setup to support this return unsafe.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, expect, update); }
分析② acquire()
public final void acquire(int arg) { if (!tryAcquire(arg) && acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) selfInterrupt(); }
分析③ tryAcquire(arg),AQS方法抛异常,强制子类实现其方法,此处走非公平锁:NonFairSync in ReetrantLock
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) { return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires); }
继续进入方法:nonfairTryAcquire(acquires):线程B进入,设置当前线程为B,c=getState(),c=1(被线程A改了),else if (线程B不等于获取资源的线程),返回false。
/** * Performs non-fair tryLock. tryAcquire is implemented in * subclasses, but both need nonfair try for trylock method. */ final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) { final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); int c = getState(); if (c == 0) { if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) { setExclusiveOwnerThread(current); return true; } } else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) { int nextc = c + acquires; if (nextc < 0) // overflow throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded"); setState(nextc); return true; } return false; }
至此,acquire方法内,if前半段true,继续走后半段:acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg),继续往里走方法 ④addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE)
/** * Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode. * * @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared * @return the new node */ private Node addWaiter(Node mode) { Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode); // Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure Node pred = tail; if (pred != null) { node.prev = pred; if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) { pred.next = node; return node; } } enq(node); return node; }
此时B线程进入,new Node。此时tail==null(刚开始,没有队列),if不进,走下面enq(node):
/** * Inserts node into queue, initializing if necessary. See picture above. * @param node the node to insert * @return node's predecessor */ private Node enq(final Node node) { for (;;) { Node t = tail; if (t == null) { // Must initialize if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) tail = head; } else { node.prev = t; if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) { t.next = node; return t; } } } }
上述t==null,初始化节点,进入if,走方法compareAndSetHead(new Node()),创建空节点作为头节点。
/** * CAS head field. Used only by enq. */ private final boolean compareAndSetHead(Node update) { return unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(this, headOffset, null, update); }
for(;;)第一遍走完:
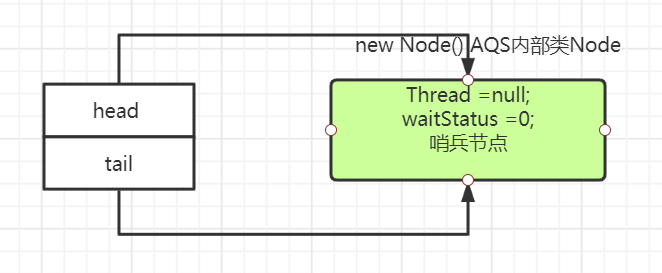
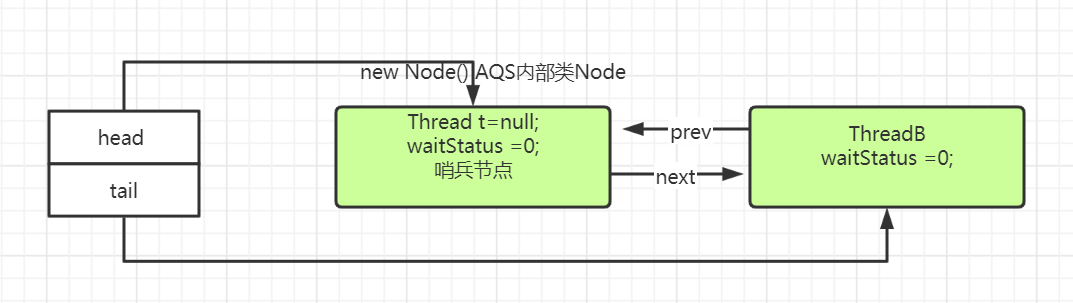
for(;;)第二遍,走else,把线程B所在Node节点,入队,设置Node前后指针,最后return退出 。
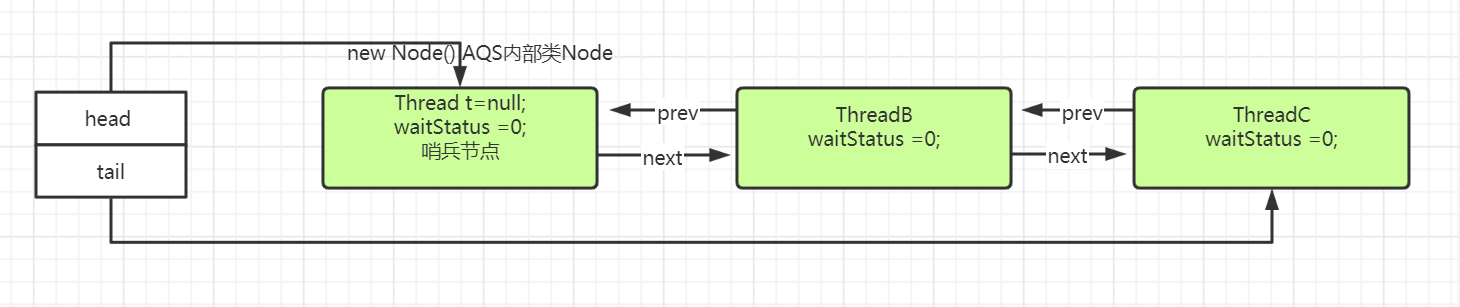
如果线程C也进来抢占资源,在前面方法;addWaiter(Node mode)中,走if内,直接设置了线程C所属的Node节点,并相应的把前后指针设置好。
内层方法addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE)分析完,分析外层方法 ⑤acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg):
/** * Acquires in exclusive uninterruptible mode for thread already in * queue. Used by condition wait methods as well as acquire. * * @param node the node * @param arg the acquire argument * @return {@code true} if interrupted while waiting */ final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
线程B走进for(;;):final Node p = node.predecessor();此时线程B,进入获取了了哨兵节点,if()方法中,p==hean是真,线程B执行tryAcquire(arg)继续试图抢一下资源。
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException { Node p = prev; if (p == null) throw new NullPointerException(); else return p; }
由于抢不到,继续往下走if(shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&parkAndCheckInterrupt()),走前半段,哨兵节点ws一开始是0,哨兵节点走进else内,compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);设置ws =-1,return false;继续回到上面自选for(;;);第二次,进来,此时ws=-1,直接走if(ws==Node.SIGNAL),那么开始走后半段:parkAndCheckInterrupt()
/** * Checks and updates status for a node that failed to acquire. * Returns true if thread should block. This is the main signal * control in all acquire loops. Requires that pred == node.prev. * * @param pred node's predecessor holding status * @param node the node * @return {@code true} if thread should block */ private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) { int ws = pred.waitStatus; if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) /* * This node has already set status asking a release * to signal it, so it can safely park. */ return true; if (ws > 0) { /* * Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and * indicate retry. */ do { node.prev = pred = pred.prev; } while (pred.waitStatus > 0); pred.next = node; } else { /* * waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we * need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to * retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking. */ compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL); } return false; }
进入方法:parkAndCheckInterrupt(),此时this是节点B,B终于被挂起,即阻塞了。线程C对应的节点C,同样走到这里被阻塞。
/** * Convenience method to park and then check if interrupted * * @return {@code true} if interrupted */ private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() { LockSupport.park(this); return Thread.interrupted(); }
综上,第一类lock()方法已经分析完毕。
接下里来分析第二类:unlock()方法:
public void unlock() { sync.release(1); }
public final boolean release(int arg) { if (tryRelease(arg)) { Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) unparkSuccessor(h); return true; } return false; }
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) { int c = getState() - releases; if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread()) throw new IllegalMonitorStateException(); boolean free = false; if (c == 0) { free = true; setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); } setState(c); return free; }
上述线程A资源用完,释放资源,c = 1-1(入参1)。free =true;设置当前拥有资源线程为null。返回true。
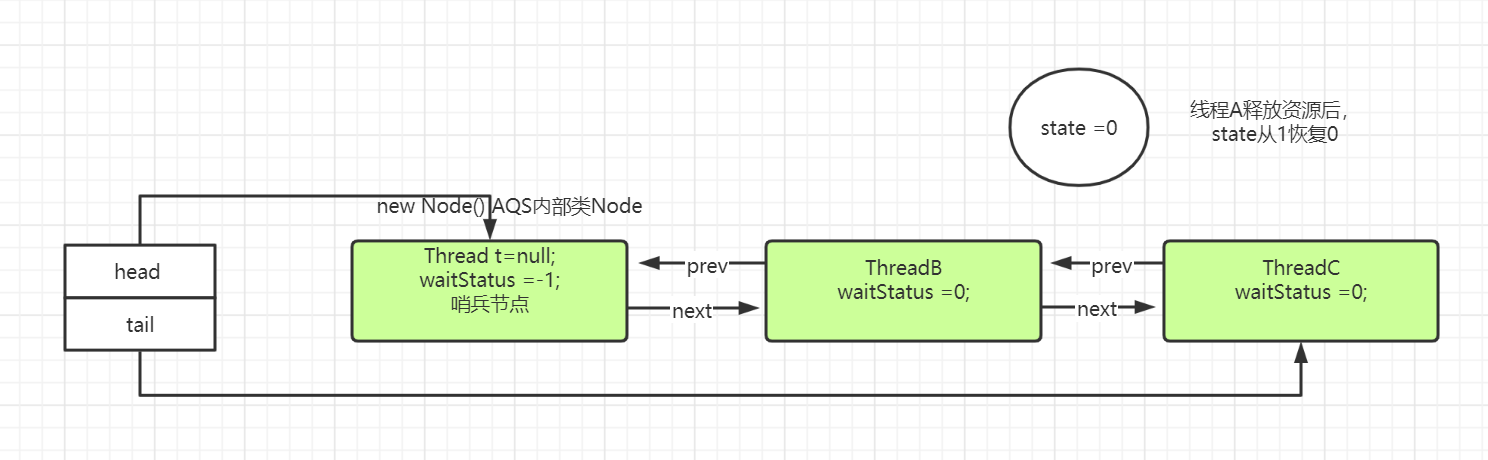
回到上面,继续走:Node h = head; if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0):头节点是哨兵节点,进入方法unparkSuccessor(h);
/** * Wakes up node's successor, if one exists. * * @param node the node */ private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) { /* * If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try * to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this * fails or if status is changed by waiting thread. */ int ws = node.waitStatus; if (ws < 0) compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0); /* * Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally * just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null, * traverse backwards from tail to find the actual * non-cancelled successor. */ Node s = node.next; if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) { s = null; for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev) if (t.waitStatus <= 0) s = t; } if (s != null) LockSupport.unpark(s.thread); }
第一个if进去(之前哨兵节点ws被设置了-1),进去之后被设置了0。第一个if不进,s==节点B。进入第三个if,此处线程B被unpark,唤醒。
关键点:此处回到⑤acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg):
for(;;)在这里自旋呢:tryAcquire(arg)进入后。最总返回真(由于c = getState()此时为0,进入if,返回true)。
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) { boolean failed = true; try { boolean interrupted = false; for (;;) { final Node p = node.predecessor(); if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) { setHead(node); p.next = null; // help GC failed = false; return interrupted; } if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) && parkAndCheckInterrupt()) interrupted = true; } } finally { if (failed) cancelAcquire(node); } }
进入if后,执行三个方法;
setHead(node);设置队列中B节点线程为null,把头设置成节点B,把节点B前指针设置null。
p.next = null; // help GC 把原哨兵节点出队,将被下次GC回收。至此,新的节点B成为了新哨兵节点。
failed = false;