一、创建Event类 Trade
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; public class Trade { private String id; private String name; private double price; private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public double getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(double price) { this.price = price; } public AtomicInteger getCount() { return count; } public void setCount(AtomicInteger count) { this.count = count; } }
二、构建 Disruptor
1.创建测试类并构建Disruptor
import com.lmax.disruptor.BusySpinWaitStrategy; import com.lmax.disruptor.EventFactory; import com.lmax.disruptor.RingBuffer; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.ProducerType; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; public class TestMain { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //构建一个线程池用于提交任务 ExecutorService es = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4); ExecutorService es2 = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5); //1 构建disruptor Disruptor<Trade> disruptor = new Disruptor<Trade>(new EventFactory<Trade>() { @Override public Trade newInstance() { return new Trade(); } }, 1024 * 1024, es2, ProducerType.SINGLE, new BusySpinWaitStrategy()); //2 把消费者设置到Disruptor中HandleEventsWtith //2.1 串行操作 // disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1()) // .handleEventsWith(new Handler2()) // .handleEventsWith(new Handler3()); //2.2 并行操作 // disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1()); // disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler2()); // disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler3()); //或者 // disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1(), new Handler2(), new Handler3()); //2.3 菱形操作 一,即并行加串行执行 此处是 handler1 和 handler2执行完之后再执行handler3 // disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1(), new Handler2()) // .handleEventsWith(new Handler3()); //2.3 菱形操作 二 // EventHandlerGroup<Trade> ehGrop = disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1(), new Handler2()); // ehGrop.then(new Handler3()); //2.4 六边形操作 由于此处使用了5个Handler需要启动5个线程,此时需要修改disruptor的线程池es2的大小为5 Handler1 h1 = new Handler1(); Handler2 h2 = new Handler2(); Handler3 h3 = new Handler3(); Handler4 h4 = new Handler4(); Handler5 h5 = new Handler5(); disruptor.handleEventsWith(h1, h4); disruptor.after(h1).handleEventsWith(h2); disruptor.after(h4).handleEventsWith(h5); disruptor.after(h2, h5).handleEventsWith(h3); //3 启动disruptor RingBuffer<Trade> ringBuffer = disruptor.start(); long begin = System.currentTimeMillis(); //异步提交 CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1); es.submit(new TradePushlisher(disruptor, latch)); // 异步代码执行完毕 向下进行 latch.await(); disruptor.shutdown(); es.shutdown(); es2.shutdown(); System.out.println("总耗时:"+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - begin)); } }
2.创建异步提交类
import com.lmax.disruptor.EventTranslator; import com.lmax.disruptor.dsl.Disruptor; import java.util.Random; import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch; public class TradePushlisher implements Runnable{ private Disruptor<Trade> disruptor; private CountDownLatch latch; private static int PUBLISH_COUNT = 10; public TradePushlisher(Disruptor<Trade> disruptor, CountDownLatch latch) { this.disruptor = disruptor; this.latch = latch; } @Override public void run() { TradeEventTranslator tradeEventTranslator = new TradeEventTranslator(); // 使用disruptor提交任务 disruptor.publishEvent(tradeEventTranslator); latch.countDown(); } } class TradeEventTranslator implements EventTranslator<Trade> { private Random random = new Random(); @Override public void translateTo(Trade event, long sequence) { generateTrade(event); } private void generateTrade(Trade trade) { trade.setPrice(random.nextDouble() * 9999); } }
三、链路讲解
1.创建5个Handler
import com.lmax.disruptor.EventHandler; import com.lmax.disruptor.WorkHandler; public class Handler1 implements EventHandler<Trade>, WorkHandler<Trade> { //EventHandler @Override public void onEvent(Trade event, long sequence, boolean endOfBatch) throws Exception { this.onEvent(event); } //WorkHandler @Override public void onEvent(Trade event) throws Exception { System.out.println("handler 1 : SET NAME"); event.setName("H1"); Thread.sleep(1000); } }
import com.lmax.disruptor.EventHandler; import java.util.UUID; public class Handler2 implements EventHandler<Trade> { @Override public void onEvent(Trade event, long sequence, boolean endOfBatch) throws Exception { System.out.println("handler 2 : SET ID"); Thread.sleep(1000); event.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); } }
import com.lmax.disruptor.EventHandler; public class Handler3 implements EventHandler<Trade> { @Override public void onEvent(Trade event, long sequence, boolean endOfBatch) throws Exception { System.out.println("handler 3 : Name:"+ event.getName() + ", ID:" + event.getId() + ",price:" + event.getPrice()); } }
import com.lmax.disruptor.EventHandler; public class Handler4 implements EventHandler<Trade> { @Override public void onEvent(Trade event, long sequence, boolean endOfBatch) throws Exception { System.out.println("handler 4 : SET PRICE"); event.setPrice(17.0); } }
import com.lmax.disruptor.EventHandler; public class Handler5 implements EventHandler<Trade> { @Override public void onEvent(Trade event, long sequence, boolean endOfBatch) throws Exception { System.out.println("handler 5 : GET PRICE: " + event.getPrice()); event.setPrice(event.getPrice() + 3.0); } }
2.消费者链路说明 上面测试类中已经包含有代码了,此处画个图做个说明
① 串行操作
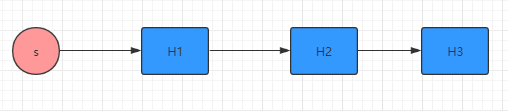
disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1()) .handleEventsWith(new Handler2()) .handleEventsWith(new Handler3());
② 并行操作
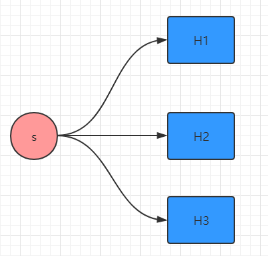
disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1()); disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler2()); disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler3()); // 或者 disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1(), new Handler2(), new Handler3());
③ 菱形操作
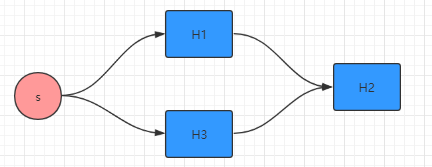
disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1(), new Handler2()) .handleEventsWith(new Handler3());
//或者
EventHandlerGroup<Trade> ehGrop = disruptor.handleEventsWith(new Handler1(), new Handler2());
ehGrop.then(new Handler3());
④ 六边形操作
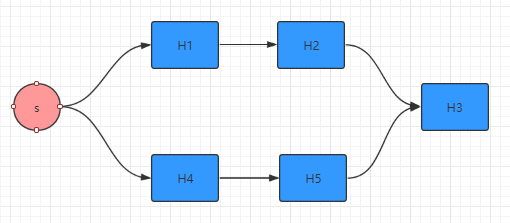
Handler1 h1 = new Handler1(); Handler2 h2 = new Handler2(); Handler3 h3 = new Handler3(); Handler4 h4 = new Handler4(); Handler5 h5 = new Handler5(); disruptor.handleEventsWith(h1, h4); disruptor.after(h1).handleEventsWith(h2); disruptor.after(h4).handleEventsWith(h5); disruptor.after(h2, h5).handleEventsWith(h3);