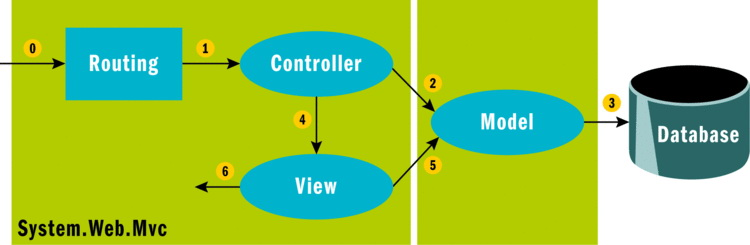
URL构造
命名参数规范+匿名对象
routes.MapRoute( name: "Default", url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}", defaults: new { controller = "Perpon", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } //constraints: new { controller=@"^\w+$", id=@"^\d+$" } //约束 //namespaces: new string[] { "Mvc4.Models" } //控制器命名空间的约束 );
构造路由然后添加
Route myRoute = new Route("{controller}/{action}/{id}", new MvcRouteHandler());
routes.Add(myRoute);
直接方法重载+匿名对象
routes.MapRoute(
"Default1",//name: "Default1",
"{controller}/{action}/{id}",//url: "{controller}/{action}/{id}",
new { controller = "Test", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }//defaults: new { controller = "Perpon", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }
);
路由规则
1.默认路由(MVC自带)
routes.MapRoute( "Default",//路由名称,不可重复 "{controller}/{action}/{id}",//带有参数的 URL new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } //参数默认值 (UrlParameter.Optional-可选的意思) );
2.静态URL段
routes.MapRoute( "ShopSchema2", "Shop/OldAction", new { controller = "Home", action = "Index"}); routes.MapRoute( "ShopSchema", "Shop/{action}", new {controller = "Home"} ); routes.MapRoute( "ShopSchema2", "Shop/OldAction.js", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index"} );
没有占位符路由就是现成的写死的。
比如这样写然后去访问http://localhost:XXX/Shop/OldAction.js,response也是完全没问题的。 controller , action , area这三个保留字就别设静态变量里面了。
3.自定义常规变量URL段
routes.MapRoute( "MyRoute2", "{controller}/{action}/{id}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = "DefaultId"} );
这种情况如果访问 /Home/Index 的话,因为第三段(id)没有值,根据路由规则这个参数会被设为DefaultId
这个用viewbag给title赋值就能很明显看出
ViewBag.Title = RouteData.Values["id"];
图不贴了,结果是标题显示为DefaultId。 注意要在控制器里面赋值,在视图赋值没法编译的。
4.再述默认路由
然后再回到默认路由。 UrlParameter.Optional这个叫可选URL段.路由里没有这个参数的话id为null。 照原文大致说法,这个可选URL段能用来实现一个关注点的分离。刚才在路由里直接设定参数默认值其实不是很好。照我的理解,实际参数是用户发来的,我们做的只是定义形式参数名。但是,如果硬要给参数赋默认值的话,建议用语法糖写到action参数里面。比如:
public ActionResult Index(string id = "abcd") { ViewBag.Title = RouteData.Values["id"]; returnView(); }
5.可变长度路由。
routes.MapRoute( "MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional } );
在这里id和最后一段都是可变的,所以 /Home/Index/dabdafdaf 等效于 /Home/Index//abcdefdjldfiaeahfoeiho 等效于 /Home/Index/All/Delete/Perm/.....
6.跨命名空间路由
这个提醒一下记得引用命名空间,开启IIS网站不然就是404。这个非常非主流,不建议瞎搞。
routes.MapRoute( "MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new[] {"URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers","UrlsAndRoutes.Controllers"} );
但是这样写的话数组排名不分先后的,如果有多个匹配的路由会报错。 然后作者提出了一种改进写法。
routes.MapRoute( "AddContollerRoute", "Home/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers"} ); routes.MapRoute( "MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.Controllers"} );
这样第一个URL段不是Home的都交给第二个处理 最后还可以设定这个路由找不到的话就不给后面的路由留后路啦,也就不再往下找啦。
Route myRoute = routes.MapRoute("AddContollerRoute", "Home/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.AdditionalControllers"}); myRoute.DataTokens["UseNamespaceFallback"] = false;
7.正则表达式匹配路由
routes.MapRoute( "MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new{ controller = "^H.*"}, new[] {"URLsAndRoutes.Controllers"} );
约束多个URL
routes.MapRoute( "MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new{ controller = "^H.*", action = "^Index$|^About$"}, new[] { "URLsAndRoutes.Controllers"} );
8.指定请求方法
routes.MapRoute( "MyRoute", "{controller}/{action}/{id}/{*catchall}", new{ controller = "Home", action = "Index", id = UrlParameter.Optional }, new{ controller = "^H.*", action = "Index|About", httpMethod = newHttpMethodConstraint("GET")}, new[]{ "URLsAndRoutes.Controllers"} );
9. WebForm支持
routes.MapPageRoute("","","~/Default.aspx"); routes.MapPageRoute( "list", "Items/{action}", "~/Items/list.aspx", false, newRouteValueDictionary{{ "action","all" }} ); routes.MapPageRoute( "show", "Show/{action}", "~/show.aspx", false, newRouteValueDictionary{ { "action","all" }} ); routes.MapPageRoute( "edit", "Edit/{id}", "~/edit.aspx", false, new RouteValueDictionary{ { "id","1" }}, new RouteValueDictionary{ { "id",@"\d+" }} );
10.MVC5的RouteAttribute
首先要在路由注册方法那里
//启用路由特性映射 routes.MapMvcAttributeRoutes();
这样
[Route("Login")]
route特性才有效.该特性有好几个重载.还有路由约束啊,顺序啊,路由名之类的.
其他的还有路由前缀,路由默认值
[RoutePrefix("reviews")] [Route("{action=index}")] publicclassReviewsController : Controller { }
路由构造
//eg: /users/5 [Route("users/{id:int}"] public ActionResult GetUserById(int id) { } //eg: users/ken [Route("users/{name}"] public ActionResult GetUserByName(string name) { }
参数限制
//eg: /users/5 //but not /users/10000000000 because it is larger than int.MaxValue, //and not /users/0 because of the min(1) constraint. [Route("users/{id:int:min(1)}")] public ActionResult GetUserById(int id) { }
| Constraint | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| alpha | Matches uppercase or lowercase Latin alphabet characters (a-z, A-Z) | {x:alpha} |
| bool | Matches a Boolean value. | {x:bool} |
| datetime | Matches a DateTime value. | {x:datetime} |
| decimal | Matches a decimal value. | {x:decimal} |
| double | Matches a 64-bit floating-point value. | {x:double} |
| float | Matches a 32-bit floating-point value. | {x:float} |
| guid | Matches a GUID value. | {x:guid} |
| int | Matches a 32-bit integer value. | {x:int} |
| length | Matches a string with the specified length or within a specified range of lengths. | {x:length(6)} {x:length(1,20)} |
| long | Matches a 64-bit integer value. | {x:long} |
| max | Matches an integer with a maximum value. | {x:max(10)} |
| maxlength | Matches a string with a maximum length. | {x:maxlength(10)} |
| min | Matches an integer with a minimum value. | {x:min(10)} |
| minlength | Matches a string with a minimum length. | {x:minlength(10)} |
| range | Matches an integer within a range of values. | {x:range(10,50)} |
| regex | Matches a regular expression. | {x:regex(^\d{3}-\d{3}-\d{4}$)} |
对我来说,这样的好处是分散了路由规则的定义.有人喜欢集中,我个人比较喜欢这种灵活的处理.因为这个action定义好后,我不需要跑到配置那里定义对应的路由规则
11.访问本地文档
routes.RouteExistingFiles = true; routes.MapRoute( "DiskFile", "Content/StaticContent.html", new{ controller = "Customer", action = "List"} );
浏览网站,以开启 IIS Express,然后点显示所有应用程序-点击网站名称-配置(applicationhost.config)-搜索UrlRoutingModule节点
<add name="UrlRoutingModule-4.0" type="System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule" preCondition="managedHandler,runtimeVersionv4.0"/>
把这个节点里的preCondition删除,变成
<add name="UrlRoutingModule-4.0" type="System.Web.Routing.UrlRoutingModule" preCondition="" />
12.直接访问本地资源,绕过了路由系统
routes.IgnoreRoute("Content/{filename}.html");
文件名还可以用 {filename}占位符。
IgnoreRoute方法是RouteCollection里面StopRoutingHandler类的一个实例。路由系统通过硬-编码识别这个Handler。如果这个规则匹配的话,后面的规则都无效了。 这也就是默认的路由里面routes.IgnoreRoute("{resource}.axd/{*pathInfo}");写最前面的原因。
路由测试代码: