scatter/gather用于描述从Channel中读取或者写入到Channel的操作。
分散(scatter):从Channel中读取在读操作中将读取的数据写入多个Buffer中。因此,Channel将从Channel中读取的数据分散(scatter)到多个Buffer中。
聚集(gather):写入Channel中将多个Buffer的数据写入同一个Channel,因此,Channel将多个Buffer中的数据聚集(gather)后发送到Channel
scatter/gather经常用于需要将传输的数据分开处理的场合,例如传输一个由消息头和消息体组成的数据,你可以将消息头和消息体分散到不通的buffer中,这样就可以方便的处理
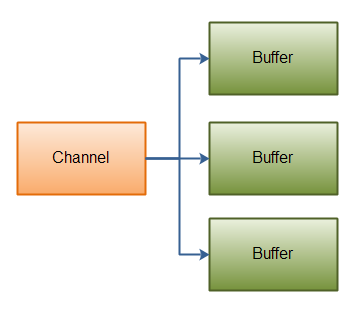
Scattering Reads
Scattering Reads是指数据从一个channel读取到多个buffer中。如下图描述:
ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(128); ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); ByteBuffer[] bufferArray = { header, body }; channel.read(bufferArray);
buffer首先被插入到数组,然后再将数组作channel.read()的输出参数。read()方法按照buffer再数组中的顺序将channel中读取的数据写入到buffer,当一个buffer被写满之后,channel紧接着向另一个buffer写入
Scattering Reads再移动下一个buffer前,必须填满当前的buffer,这意味着它不适用于动态消息(消息大小不固定)。
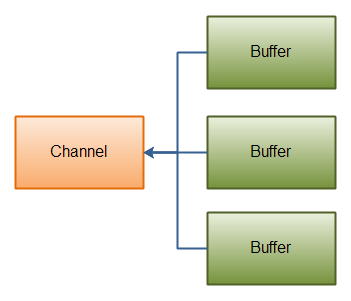
Gathering Writes
Gathering Writes是指从多个buffer写入到同一个channel,如下图
ByteBuffer header = ByteBuffer.allocate(128); ByteBuffer body = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); //write data into buffers ByteBuffer[] bufferArray = { header, body }; channel.write(bufferArray);
buffers数组是write方法的入参,writer()会按照buffer在数组中的顺序,将数据写入到channel,注意只有position和limit之间的数据才会被写入,因此,如果一个buffer容量为128byte,但是仅仅包含58byte,那么这58byte的数据将会被写入到channel中,因此和Scattering Reads相反,Gathering Writes能较好的处理动态消息。