IOC
IOC(Inversion of Control)控制反转:所谓的控制反转,就是把原先需要我们代码自己实现对象的创建和依赖,反转给容器来实现。那么必然Spring需要创建一个容器,同时需要创建一种描述对象与对象之间的依赖关系,这个描述就是Spring的配置文件。
假设我们自己设计Spring框架我们应该怎样考虑:
1.怎么表示对象与对象之间的关系
可以用 xml,properties 文件等语义化配置文件表示。
2.描述对象和对象之间关系的文件存放在哪里
可能是classpath、filesystem、URL网络资源、ServletContext等。
3.不同的配置文件对于对象的描述不一样应该如何统一
内部需要一个统一的关于对象的定义,所有外部描述都需要转化为统一的描述定义
4.如何对不同的配置文件解析
需要对不同的配置文件语法,采用不同的解析器
Spring核心容器
1.BeanFactory
spring Bean的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的Bean工厂,也即IOC容器为开发者管理对象间的依赖关系提供了很多便利和基础服务,在Spring中有许多IOC容器的实现供用户选择和使用
其相关关系如下:
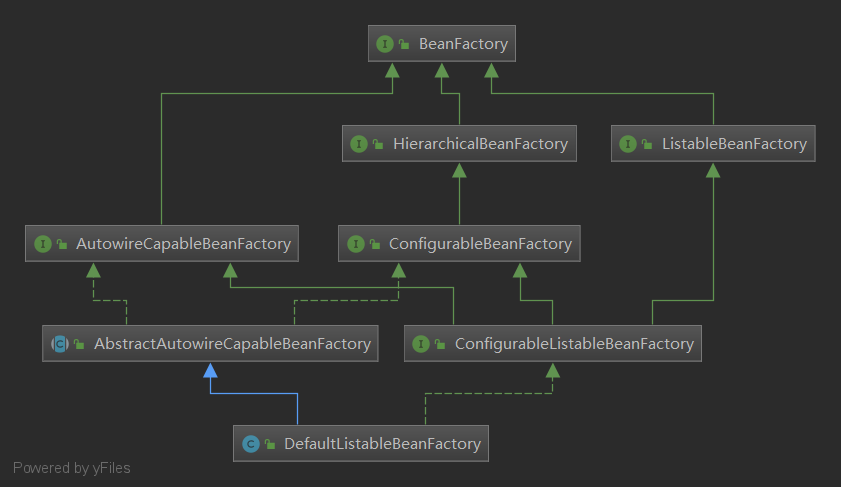 BeanFactory作为最顶层接口,定义了IOC容器的基本功能规范,它有三个重要的子类ListableBeanFactory、HierarchicalBeanFactory和AutowireCapableBeanFactory都是对它本身的扩展,从类图中我们可以发现最终的默认实现类是 DefaultListableBeanFactory,它实现了所有的接口
BeanFactory作为最顶层接口,定义了IOC容器的基本功能规范,它有三个重要的子类ListableBeanFactory、HierarchicalBeanFactory和AutowireCapableBeanFactory都是对它本身的扩展,从类图中我们可以发现最终的默认实现类是 DefaultListableBeanFactory,它实现了所有的接口
那为何要定义这么多层次的接口呢?查阅这些接口的源码和说明发现,每个接口都有它使用的场合,它主要是为了区分在 Spring 内部在操作过程中对象的传递和转化过程时,对对象的数据访问所做的限制。例如 ListableBeanFactory 接口表示这些 Bean 是可列表化的,而 HierarchicalBeanFactory 表示的是这些 Bean 是有继承关系的,也就是每个 Bean 有可能有父 Bean。AutowireCapableBeanFactory 接口定义 Bean 的自动装配规则。这三个接口共同定义了 Bean 的集合、Bean 之间的关系、以及 Bean 行为。最基本的 IOC 容器接口BeanFactory,来看一下它的源码(Spring源码自行下载):
public interface BeanFactory { //对FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象, //如果需要得到工厂本身,需要转义 String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&"; //根据bean的名字,获取在IOC容器中得到bean实例 Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException; //根据bean的名字和Class类型来得到bean实例,增加了类型安全验证机制。 <T> T getBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException; Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException; <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException; <T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException; //提供对bean的检索,看看是否在IOC容器有这个名字的bean boolean containsBean(String name); //根据bean名字得到bean实例,并同时判断这个bean是不是单例 boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; boolean isTypeMatch(String name, @Nullable Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; //得到bean实例的Class类型 @Nullable Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException; //得到bean的别名,如果根据别名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来 String[] getAliases(String name); }
在BeanFactory 里只对 IOC 容器的基本行为作了定义,根本不关心你的 Bean 是如何定义怎样加载的。正如我们只关心工厂里得到什么的产品对象,至于工厂是怎么生产这些对象的,这个基本的接口不关心。
而要知道工厂如何产生对象的,我们需要看具体的IOC容器实现,Spring提供许多的IOC容器实现,比如GenericApplicationContext、ClassPathXmlApplicationContext等
2.BeanDefinition
SpringIOC 容器管理了我们定义的各种 Bean 对象及其相互的关系,Bean 对象在 Spring 实现中是以 BeanDefinition 来描述的,其继承体系如下:
 BeanDefinition里面记录了Bean的信息beanClassName、FactoryBeanName和LazyInit等等
BeanDefinition里面记录了Bean的信息beanClassName、FactoryBeanName和LazyInit等等
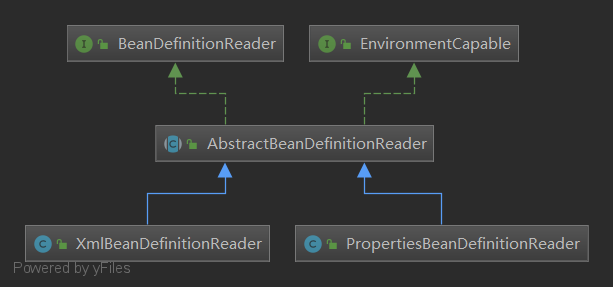
3.BeanDefinitionReader
Bean 的解析过程非常复杂,功能被分的很细,因为这里需要被扩展的地方很多,必须保证有足够的灵活性,以应对可能的变化。Bean 的解析主要就是对 Spring 配置文件的解析。这个解析过程主要通过BeanDefintionReader 来完成,最后看看 Spring 中 BeanDefintionReader 的类结构图: