题目描述:
某软件公司正在规划一项n天的软件开发计划,根据开发计划第i天需要ni个软件开发人员,为了提高软件开发人员的效率,公司给软件人员提供了很多的服务,其中一项服务就是要为每个开发人员每天提供一块消毒毛巾,这种消毒毛巾使用一天后必须再做消毒处理后才能使用。消毒方式有两种,A种方式的消毒需要a天时间,B种方式的消毒需要b天(b>a),A种消毒方式的费用为每块毛巾fA, B种消毒方式的费用为每块毛巾fB,而买一块新毛巾的费用为f(新毛巾是已消毒的,当天可以使用);而且f>fA>fB。公司经理正在规划在这n天中,每天买多少块新毛巾、每天送多少块毛巾进行A种消毒和每天送多少块毛巾进行B种消毒。当然,公司经理希望费用最低。你的任务就是:为该软件公司计划每天买多少块毛巾、每天多少块毛巾进行A种消毒和多少毛巾进行B种消毒,使公司在这项n天的软件开发中,提供毛巾服务的总费用最低。
题解:
十分巧妙的建模方式.
首先,设超级源点 $S$ 和超级汇点 $T$.
1、从 $S$ 向每个 $X_{i}$ 连一条容量为$r_{i}$,费用为 $0$ 的有向边.
2、从每个 $Y_{i}$ 向 $T$ 连一条容量为 $r_{i}$, 费用为 $0$ 的有向边.
3、从 $S$ 向每个 $Y_{i}$ 连一条容量为无穷大,费用为 $f$ 的有向边.
4、从每个 $X_{i}$ 向 $X_{i+1}$ $(i+1<=N)$ 连一条容量为无穷大,费用为 $0$ 的有向边.
5、从每个 $X_{i}$ 向 $Y_{i+a+1}$ $(i+a+1<=N)$连一条容量为无穷大,费用为 $f_{a}$的有向边.
6、从每个 $X_{i}$ 向 $Y_{i+b+1}$ $(i+b+1<=N)$ 连一条容量为无穷大,费用为 $f_{b}$ 的有向边.
上一个图片:
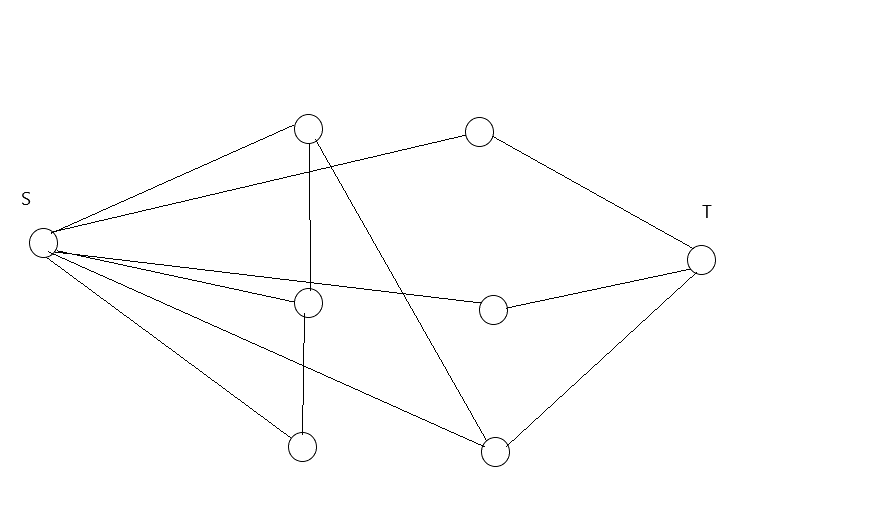
观察上述建模方式与“形象化”图片,我们发现我们构建的网络模型满足流出量与流入量守恒.
每个 $y_{i}$ 会由先前剩下的 $f_{a}$ 与 $f_{b}$ 填充,再由源点直接流入 $y_{i}$ 的 $f$ 所填入.
一个十分巧妙的网络流模型.
Code:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define setIO(s) freopen(s".in","r",stdin)
#define maxn 300000
#define inf 1000000
#define N 3005
#define nex(n) (n + 1002)
using namespace std;
struct Edge
{
int from,to,cap,cost;
Edge(int from = 0,int to = 0,int cap = 0,int cost = 0) : from(from),to(to),cap(cap),cost(cost){}
};
vector<Edge>edges;
vector<int>G[maxn];
void addedge(int u,int v,int c,int d)
{
edges.push_back(Edge(u,v,c,d));
edges.push_back(Edge(v,u,0,-d));
int m = edges.size();
G[u].push_back(m - 2);
G[v].push_back(m - 1);
}
int flow2[maxn],d[maxn],inq[N],pre[N],nn[N];
int ans,s,t;
queue <int> Q;
int spfa()
{
for(int i = 0;i < N; ++i) d[i] = flow2[i] = inf;
memset(inq,0,sizeof(inq));
d[s] = 0, inq[s] = 1;
Q.push(s);
while(!Q.empty())
{
int u = Q.front(); Q.pop();
inq[u] = 0;
for(int sz = G[u].size(),i = 0; i < sz ; ++i)
{
Edge e = edges[G[u][i]];
if(d[e.to] > d[u] + e.cost && e.cap > 0)
{
d[e.to] = d[u] + e.cost;
flow2[e.to] = min(e.cap, flow2[u]);
pre[e.to] = G[u][i];
if(!inq[e.to])
{
Q.push(e.to);
inq[e.to] = 1;
}
}
}
}
if(flow2[t] == inf) return 0;
int f = flow2[t];
edges[pre[t]].cap -= f, edges[pre[t] ^ 1].cap += f;
int u = edges[pre[t]].from;
while(u != s)
{
edges[pre[u]].cap -= f, edges[pre[u] ^ 1].cap += f;
u = edges[pre[u]].from;
}
ans += f * d[t];
return 1;
}
int getcost()
{
while(spfa());
return ans;
}
int main()
{
// setIO("input");
int n,a,b,f,fa,fb;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d",&n,&a,&b,&f,&fa,&fb);
for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++i) scanf("%d",&nn[i]);
s = 0,t = 2500;
for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++i)
{
addedge(s, i, nn[i], 0);
addedge(nex(i), t, nn[i], 0);
addedge(s, nex(i), inf, f);
if(i + 1 <= n) addedge(i, i + 1, inf,0);
}
for(int i = 1;i <= n; ++i)
{
if(i + a + 1 <= n) addedge(i,nex(i + 1 + a),inf,fa);
if(i + b + 1 <= n) addedge(i,nex(i + b + 1),inf,fb);
}
printf("%d",getcost());
return 0;
}