一、前言
组内现在用的是redis 的sentinel。
本着实践的原则,对sentinel的几台服务器进行了网络或者抓包方面的实践。
一共三台redis服务器,
10.10.20.6, 10.10.20.9, 10.10.20.11
其中,10.10.20.11为主。
我代码里是这么配置的:
#集群名称
redis.sentinel.master=redisMaster
redis.sentinel.nodes=10.10.20.6:26379,10.10.20.9:26379,10.10.20.11:26379
二、实践
1、进程查看
每台服务器上都开启了两个进程,各监听一个端口,一个26379,一个6379.
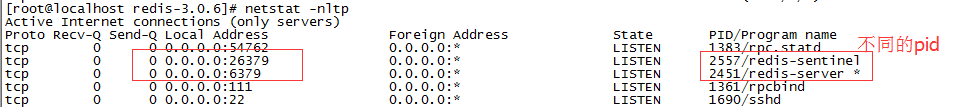
以上只看了一台,实则,三台都是类似的。
2、长连接查看
另外,三台服务器的sentinel进程之间,应该都是有建立长连接的。我们看看是不是这么回事?
2.1 10.10.20.11上看到的长连接:
下面是从服务器上抓的11和6之间的长连接:

下面是从服务器上抓的11和9之间的长连接:

2.2 10.10.20.9上看到的长连接:

可以看出来,sentinel进程和另外两台服务器上的sentinel进程,都建立了长连接。(另外一台就不一一截图了)
那么,长连接上交换什么数据呢?
三、sentinel之间的数据
我这里,在11上抓了个包:(保存到了11cap这个文件)
tcpdump -i eth1 -w 11cap port 26379
在windows上用wireshark打开后,

这个图里,可以看到,有大量的ping/pong心跳消息。
另外,也可以看到,有下面这样的:

上面提到了53635端口,是sentinel进程打开的,而不是6379端口的进程打开的:

(lsof -p 2557 查看进程打开的文件)
这个我理解,应该就是各个sentinel之间,向别的sentinel表示自己观察到master是谁,方便后续进行投票吧。
这部分我还没有特别懂。
2、sentinel结构是否能够实现读写分离?
答案:不能。
程序端采用spring-data-redis与sentinel集群连接后,
2019-07-10 16:22:56.249 [main] INFO [] redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool - Trying to find master from available Sentinels... 2019-07-10 16:22:56.295 [main] INFO [] redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool - Redis master running at 192.168.17.129:6379, starting Sentinel listeners... 2019-07-10 16:22:56.327 [main] INFO [] redis.clients.jedis.JedisSentinelPool - Created JedisPool to master at 192.168.17.129:6379
上面可以看到,192.168.17.129是我们的master所在服务器。 我们用netstat 看下,我们客户端和另外两台slave是否有连接呢?(slave为:192.168.17.128/192.168.17.130)
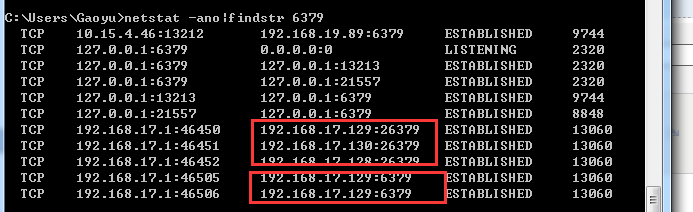
可以看到,只连接到了master。
3、模拟master宕机后,客户端的反应
首先:
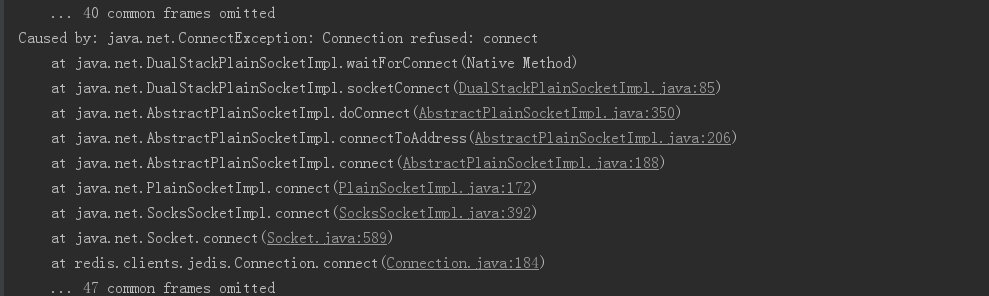
接下来:
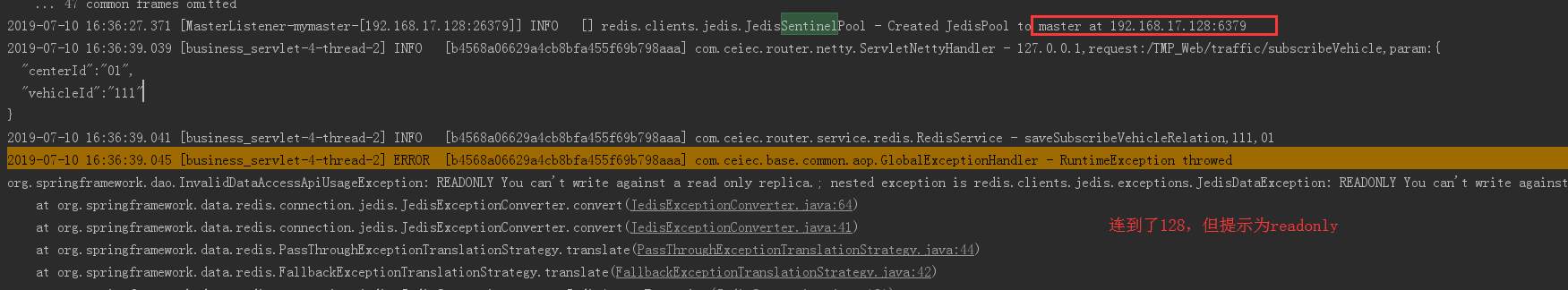
Caused by: redis.clients.jedis.exceptions.JedisDataException: READONLY You can't write against a read only replica.
接着,这次才连到正确的新的master:

经过一番查找,发现第二步之所以有那个readonly提示,是因为128中配置了:

所以可看到,sentinel 选主期间(新的 master 还没选出来之前),是不可用的。
4、sentinel的缺点
1、不支持读写分离,也就无法负载均衡
2、master挂掉,选主期间,不可用;如果master 和 其他服务器发生脑裂(master 没挂,其他服务器和master之间网络中断),则客户端会依然写旧的master,新的master选出来后,旧的master的数据会被清掉,导致数据丢失,避免数据丢失的方式是设置下面两个参数,当没有slave时,不准写,此时,也会丧失可用性:
# It is possible for a master to stop accepting writes if there are less than # N replicas connected, having a lag less or equal than M seconds. # # The N replicas need to be in "online" state. # # The lag in seconds, that must be <= the specified value, is calculated from # the last ping received from the replica, that is usually sent every second. # # This option does not GUARANTEE that N replicas will accept the write, but # will limit the window of exposure for lost writes in case not enough replicas # are available, to the specified number of seconds. # # For example to require at least 3 replicas with a lag <= 10 seconds use: # # min-replicas-to-write 3 # min-replicas-max-lag 10
四、参考资料
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33394088/article/details/80587588
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d1636776bb40
https://blog.csdn.net/sunweiguo1/article/details/80303565#commentsedit
https://blog.csdn.net/pzysoft/article/details/75577534