一、Why Composition API?
创建Vue组件使我们能够将接口的可重复部分及其功能提取到可重用的代码段中。就可维护性和灵活性而言,仅此一项就可以使我们的应用程序发展得很远。但是,我们的集体经验证明,仅凭这一项可能还不够,尤其是当您的应用程序变得非常大时-考虑数百个组件。当处理如此大的应用程序时,共享和重用代码变得尤为重要。
二、Options API
1. 设计动机
- 包含一个描述组件选项 ( data, methods, props 等) 的对象
- Options APi 开发复杂组件,同一个功能逻辑的代码被拆分到不同选项
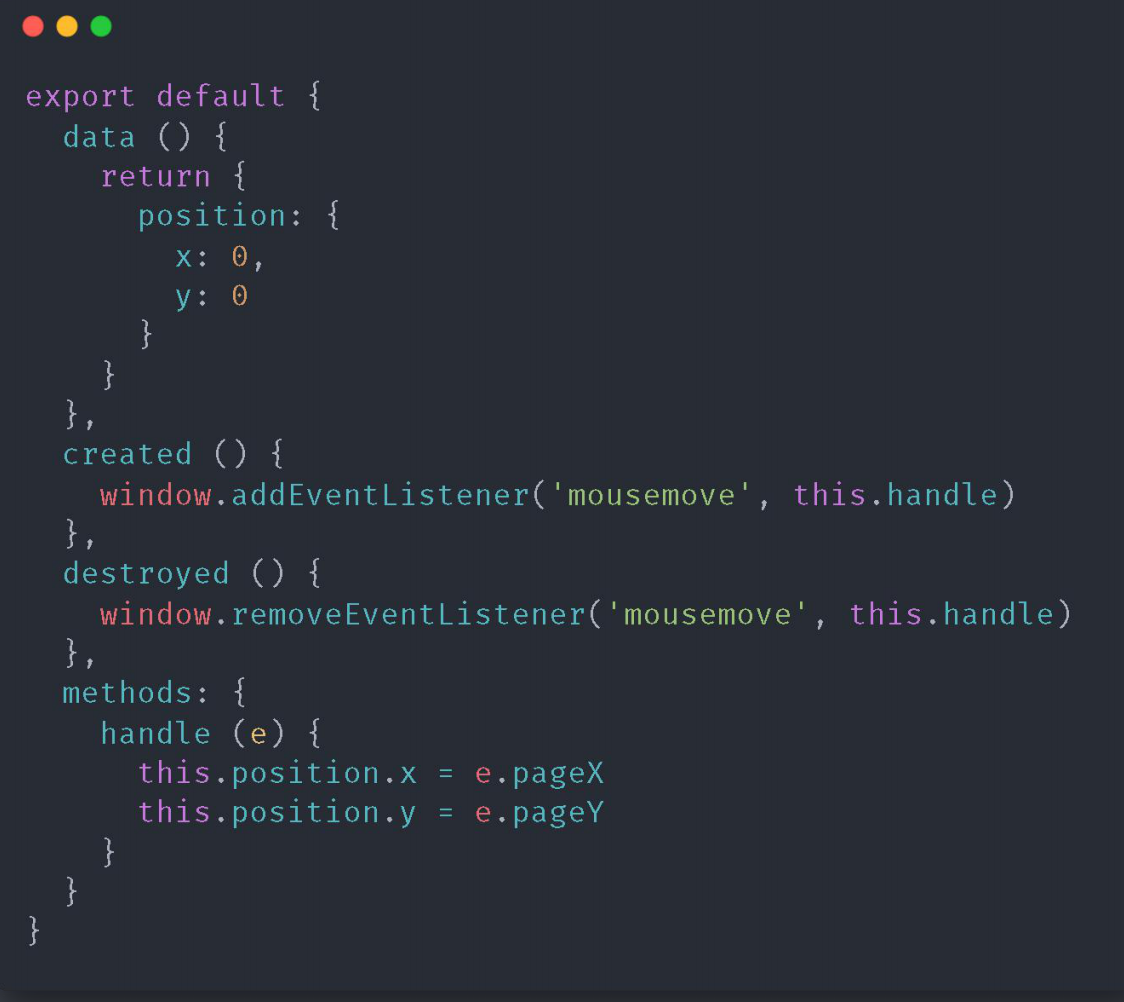
2. Options Demo
三、Composition API
1. 设计动机
- Vue.js 3.0 新增的一组 API
- 一组基于函数的 API
- 可以更灵活的组织组件的逻辑
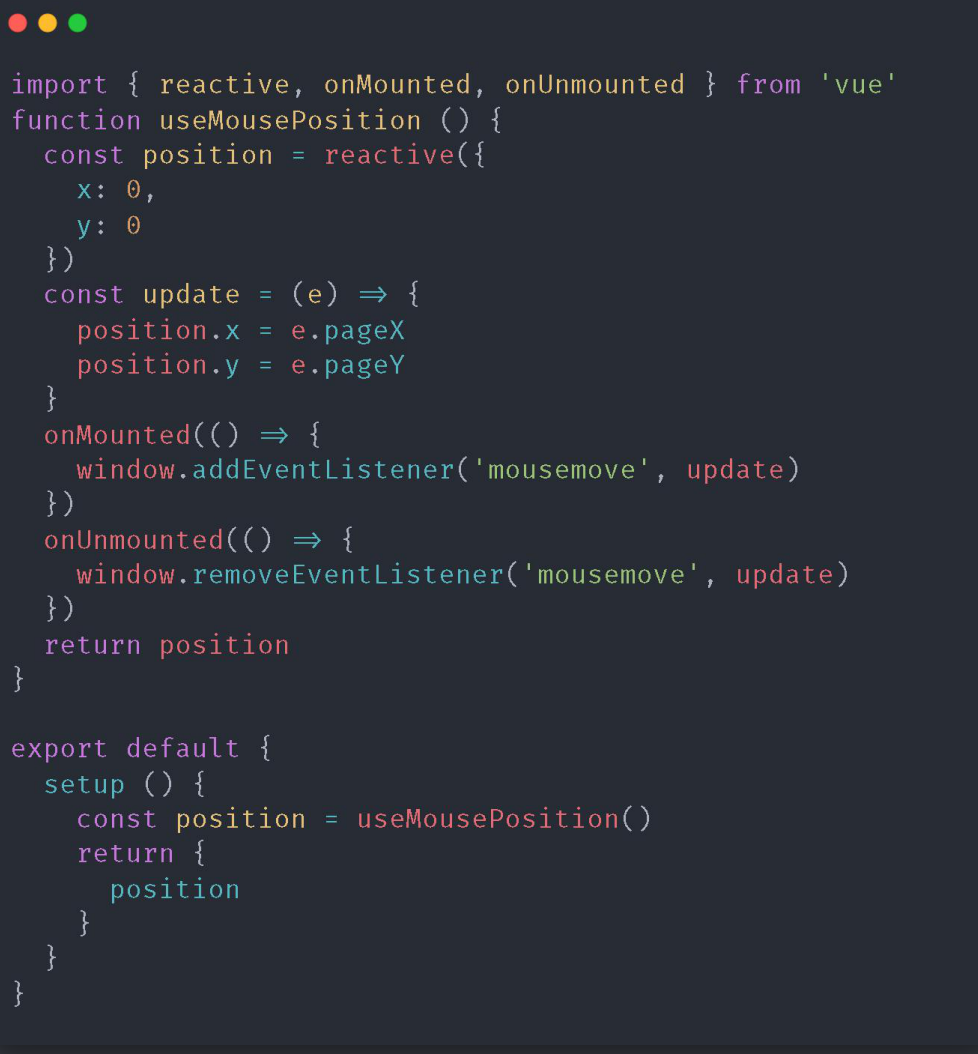
2. Composition API Demo
四、Options API VS Composition API
1. 入口对比
Vue2.x: 每个 Vue 应用都是通过用 Vue 函数创建一个新的 Vue 实例开始的:
var vm = new Vue({
// 选项
})
Vue3.x: Vue.js的核心是一个系统,通过 createApp 创建系统,并通过 mount 绑定首页,该系统使我们能够使用简单的模板语法声明性地将数据呈现到DOM:
Vue.createApp({}).mount('#counter')
2. 方法 对比
Vue 2.x : data, methods, props, mounted, components, computed, watch 等
Vue3.x : setup, reactive, onMounted, onUnmounted, toRefs, Ref, computed,watch,watchEffect 等
3. 生命周期钩子-对比
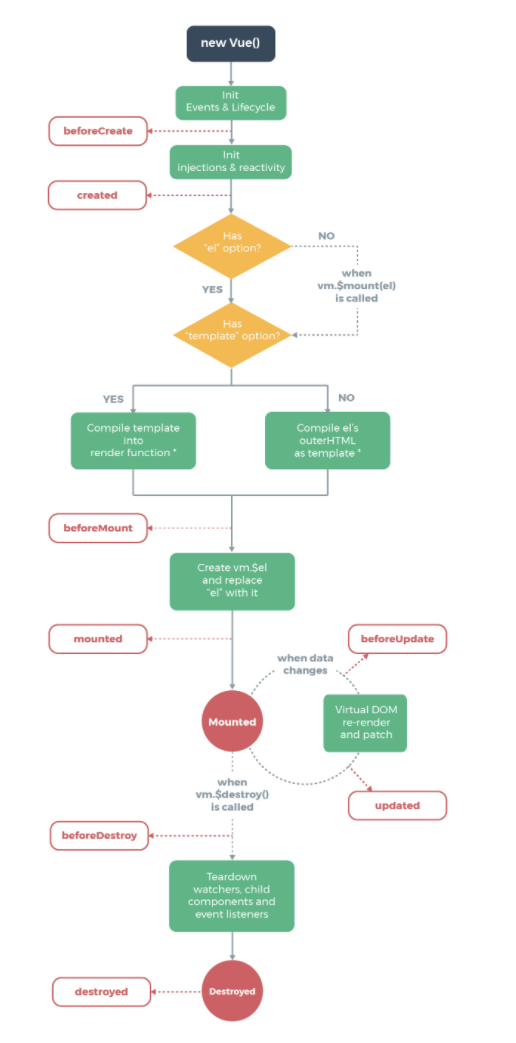
Vue2.x 生命周期图示
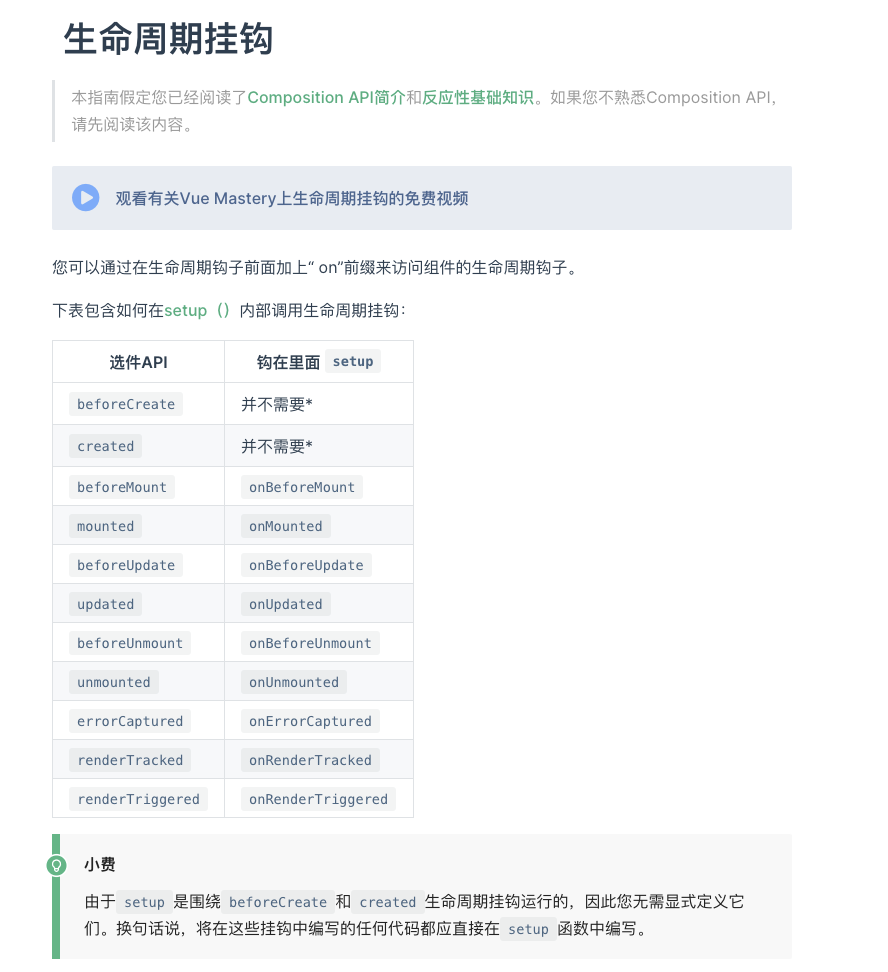
Vue3.x 生命周期挂钩
4. Demo 对比

5. 逻辑模块拆分
Vue2.x: 不具备
Vue3.x: 通过setup 将逻辑拆分
6. 举例说明 逻辑拆分
查看以下代码,我们会看到,我们可以将一个逻辑通过函数的形式进行包裹,分逻辑拆分,每个逻辑部分互相独立,不受影响,其中每个函数都可使用生命周期钩子进行组合,因为函数可以以方法的形式去重用和共享
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
x: {{ x }} <br>
y: {{ y }}
</div>
<script type="module">
import { createApp, onMounted, onUnmounted, reactive, toRefs, ref, computed, watch, watchEffect } from './node_modules/vue/dist/vue.esm-browser.js'
/** reactive */
function useMousePosition() {
// 第一个参数 props
// 第二个参数 context,attrs、emit、slots
const position = reactive({
x: 0,
y: 0
})
const update = e => {
position.x = e.pageX
position.y = e.pageY
}
onMounted(() => {
window.addEventListener('mousemove', update)
})
onUnmounted(() => {
window.removeEventListener('mousemove', update)
})
return toRefs(position)
}
/** ref */
function useCount() {
const count = ref(0)
return {
count,
increase: () => {
count.value++
}
}
}
/** computed */
function todosFun() {
const todos = reactive(data)
const activeCount = computed(() => {
return todos.filter(item => !item.completed).length
})
return {
activeCount,
push: () => {
todos.push({
text: '开会',
completed: false
})
}
}
}
/** watch */
function answerFun(params) {
const question = ref('')
const answer = ref('')
watch(question, async (newValue, oldValue) => {
const response = await fetch('https://www.yesno.wtf/api')
const data = await response.json()
answer.value = data.answer
})
return {
question,
answer
}
}
/** watchEffect */
function countFun(params) {
const counts = ref(0)
const stops = watchEffect(() => {
console.log(count.value)
})
return {
counts,
stops,
increases: () => {
count.value++
}
}
}
const app = createApp({
setup() {
const { x, y } = useMousePosition()
return {
x,
y,
...useCount(),
...todosFun(),
...answerFun(),
...countFun()
}
}
})
app.mount('#app')
</script>
</body>
</html>
五、参考文献
2. Vue2 生命周期
4. Vue 3 生命周期