python常用模块之time
1. python中三种时间格式
在Python中,通常有这三种方式来表示时间:时间戳、元组(struct_time)、格式化的时间字符串
时间戳是计算机能够识别的时间;时间字符串是人能够看懂的时间;元组则是用来操作时间的
1.1. 时间戳
时间戳(timestamp) :通常来说,时间戳表示的是从1970年1月1日00:00:00开始按秒计算的偏移量。我们运行“type(time.time())”,返回的是float类型。
# 1- 时间戳时间的开始为 英国伦敦时间 1970 1 1 0 0 0 # 相当于 北京时间 1970 1 8 0 0 0 import time print(time.time()) # 1525680508.1982615
1.2. 时间元组
元组(struct_time):struct_time元组共有9个元素:(年、月、日、时、分、秒、一年中的第几天、是否为夏令时间等)
import time print(time.localtime()) # time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=5, tm_mday=7, tm_hour=16, tm_min=28, tm_sec=46, tm_wday=0, tm_yday=127, tm_isdst=0) # 索引(Index) 属性(Attribute) 值(Values) # 0 tm_year (年) 比如2011 # 1 tm_mon (月) 1 - 12 # 2 tm_mday (日) 1 - 31 # 3 tm_hour (时) 0 - 23 # 4 tm_min (分) 0 - 59 # 5 tm_sec (秒) 0 - 60 # 6 tm_wday (weekday) 0 - 6(0表示周一) # 7 tm_yday (一年中的第几天) 1 - 366 # 8 tm_isdst (是否是夏令时) 默认为0
1.3. 格式化的时间字符串(format string)
# 2- 格式化时间 用字符串表示的时间
# str-format-time
print(time.strftime('%H:%M:%S'))
# 16:10:03
print(time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S'))
# 2018-05-07 16:10:55
# %y 两位数的年份表示(00-99)
print(time.strftime('%y'))
# 18
# %Y 四位数的年份表示(000-9999)
print(time.strftime('%Y'))
# 2018
# %m 月份(01-12)
print(time.strftime('%m'))
# 05
# %d 月内中的一天(0-31)
print(time.strftime('%d'))
# 07
# %H 24小时制小时数(0-23)
print(time.strftime('%H'))
# 16
# %I 12小时制小时数(01-12)
print(time.strftime('%I'))
# 04
# %M 分钟数(00=59)
print(time.strftime('%M'))
# 16
# %S 秒(00-59)
print(time.strftime('%S'))
# 55
# %a 本地简化星期名称
print(time.strftime('%a'))
# Mon
# %A 本地完整星期名称
print(time.strftime('%A'))
# Monday
# %b 本地简化的月份名称
print(time.strftime('%b'))
# May
# %B 本地完整的月份名称
print(time.strftime('%B'))
# May
# %c 本地相应的日期表示和时间表示
print(time.strftime('%c'))
# Mon May 7 16:18:08 2018
# %j 年内的一天(001-366)
print(time.strftime('%j'))
# 127
# %p 本地A.M.或P.M.的等价符
print(time.strftime('%p'))
# PM
# %U 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期天为星期的开始
print(time.strftime('%U'))
# 18
# %w 星期(0-6),星期天为星期的开始
print(time.strftime('%w'))
# 1
# %W 一年中的星期数(00-53)星期一为星期的开始
print(time.strftime('%W'))
# 19
# %x 本地相应的日期表示
print(time.strftime('%x'))
# 05/07/18
# %X 本地相应的时间表示
print(time.strftime('%X'))
# 16:20:13
# %Z 当前时区的名称
print(time.strftime('%Z'))
# %% %号本身
print(time.strftime('%%'))
# % 没有其他输出,只打印%
2. 常见时间格式之间的转化
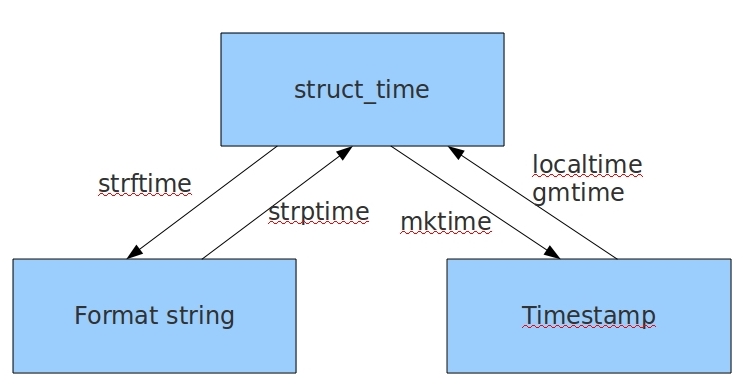
2.1. 时间戳与时间元组之间的转化
import time # 打印时间戳时间 stamp_time = time.time() print(stamp_time) print(type(stamp_time)) # 1584701718.5006225 # <class 'float'> # 打印时间元组
# 根据本地时间获取时间元组 tuple_time = time.localtime() print(tuple_time) print(type(tuple_time)) # time.struct_time(tm_year=2020, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=18, tm_min=56, tm_sec=46, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=80, tm_isdst=0) # <class 'time.struct_time'>
# 根据格林威治时间获取时间元组
tuple_time = time.gmtime()
print(tuple_time)
print(type(tuple_time))
# time.struct_time(tm_year=2020, tm_mon=3, tm_mday=20, tm_hour=11, tm_min=47, tm_sec=38, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=80, tm_isdst=0)
# <class 'time.struct_time'>
# 时间元组 --> 时间戳
print(time.mktime(tuple_time)) # 1584702781.0
转化使用方法
time - 返回当前时间的时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。
Help on built-in function time in module time:
time(...)
time() -> floating point number
Return the current time in seconds since the Epoch.
Fractions of a second may be present if the system clock provides them.
None
localtime - 打印当前时间元组
Help on built-in function localtime in module time:
localtime(...)
localtime([seconds]) -> (tm_year,tm_mon,tm_mday,tm_hour,tm_min,
tm_sec,tm_wday,tm_yday,tm_isdst)
Convert seconds since the Epoch to a time tuple expressing local time.
When 'seconds' is not passed in, convert the current time instead.
None
gmtime - 接收时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)并返回格林威治天文时间下的时间元组t。注:t.tm_isdst始终为0
Help on built-in function gmtime in module time:
gmtime(...)
gmtime([seconds]) -> (tm_year, tm_mon, tm_mday, tm_hour, tm_min,
tm_sec, tm_wday, tm_yday, tm_isdst)
Convert seconds since the Epoch to a time tuple expressing UTC (a.k.a.
GMT). When 'seconds' is not passed in, convert the current time instead.
If the platform supports the tm_gmtoff and tm_zone, they are available as
attributes only.
None
mktime - 接受时间元组并返回时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。
Help on built-in function mktime in module time:
mktime(...)
mktime(tuple) -> floating point number
Convert a time tuple in local time to seconds since the Epoch.
Note that mktime(gmtime(0)) will not generally return zero for most
time zones; instead the returned value will either be equal to that
of the timezone or altzone attributes on the time module.
None
2.2. 时间元组与时间字符串之间的转化
# 时间元组 --> 时间字符串
time_stamp = time.time()
# 获取时间元组
time_tuple = time.localtime(time_stamp)
# 时间元组转化成时间字符串
time_str = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X', time_tuple)
print(time_str)
# 时间字符串 --> 时间元组
time_str = '2020-03-20 19:38:00'
# 时间字符串转化成时间元组
time_tuple = time.strptime(time_str, '%Y-%m-%d %X')
print(time_tuple)
转化使用方法
strftime - 接收以时间元组,并返回以可读字符串表示的当地时间,格式由fmt决定。
Help on built-in function strftime in module time:
strftime(...)
strftime(format[, tuple]) -> string
Convert a time tuple to a string according to a format specification.
See the library reference manual for formatting codes. When the time tuple
is not present, current time as returned by localtime() is used.
Commonly used format codes:
%Y Year with century as a decimal number.
%m Month as a decimal number [01,12].
%d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31].
%H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23].
%M Minute as a decimal number [00,59].
%S Second as a decimal number [00,61].
%z Time zone offset from UTC.
%a Locale's abbreviated weekday name.
%A Locale's full weekday name.
%b Locale's abbreviated month name.
%B Locale's full month name.
%c Locale's appropriate date and time representation.
%I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12].
%p Locale's equivalent of either AM or PM.
Other codes may be available on your platform. See documentation for
the C library strftime function.
None
strptime - 根据fmt的格式把一个时间字符串解析为时间元组。
Help on built-in function strptime in module time:
strptime(...)
strptime(string, format) -> struct_time
Parse a string to a time tuple according to a format specification.
See the library reference manual for formatting codes (same as
strftime()).
Commonly used format codes:
%Y Year with century as a decimal number.
%m Month as a decimal number [01,12].
%d Day of the month as a decimal number [01,31].
%H Hour (24-hour clock) as a decimal number [00,23].
%M Minute as a decimal number [00,59].
%S Second as a decimal number [00,61].
%z Time zone offset from UTC.
%a Locale's abbreviated weekday name.
%A Locale's full weekday name.
%b Locale's abbreviated month name.
%B Locale's full month name.
%c Locale's appropriate date and time representation.
%I Hour (12-hour clock) as a decimal number [01,12].
%p Locale's equivalent of either AM or PM.
Other codes may be available on your platform. See documentation for
the C library strftime function.
None
2.3. 时间戳与时间字符串之间的转化
# 时间戳、时间字符串之间的转化
import time
# 时间字符串 --> 时间元组 --> 时间戳
time_str = '2018-05-07 17:00:15'
time_tuple = time.strptime(time_str, '%Y-%m-%d %X')
time_stamp = time.mktime(time_tuple)
print(time_stamp)
# 1525683615.0
# 时间戳 --> 时间元组 --> 时间字符串
time_stamp = 1525683615.0
time_tuple = time.localtime(time_stamp)
time_str = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %X', time_tuple)
print(time_str)
# 2018-05-07 17:00:15
3. 其他方法
| 序号 | 函数及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | time.altzone 返回格林威治西部的夏令时地区的偏移秒数。如果该地区在格林威治东部会返回负值(如西欧,包括英国)。对夏令时启用地区才能使用。 |
| 2 | time.asctime([tupletime]) 接受时间元组并返回一个可读的形式为"Tue Dec 11 18:07:14 2008"(2008年12月11日 周二18时07分14秒)的24个字符的字符串。 |
| 3 | time.clock( ) 用以浮点数计算的秒数返回当前的CPU时间。用来衡量不同程序的耗时,比time.time()更有用。 |
| 4 | time.ctime([secs]) 作用相当于asctime(localtime(secs)),未给参数相当于asctime() |
| 5 | time.gmtime([secs]) 接收时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)并返回格林威治天文时间下的时间元组t。注:t.tm_isdst始终为0 |
| 6 | time.localtime([secs]) 接收时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)并返回当地时间下的时间元组t(t.tm_isdst可取0或1,取决于当地当时是不是夏令时)。 |
| 7 | time.mktime(tupletime) 接受时间元组并返回时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。 |
| 8 | time.sleep(secs) 推迟调用线程的运行,secs指秒数。 |
| 9 | time.strftime(fmt[,tupletime]) 接收以时间元组,并返回以可读字符串表示的当地时间,格式由fmt决定。 |
| 10 | time.strptime(str,fmt='%a %b %d %H:%M:%S %Y') 根据fmt的格式把一个时间字符串解析为时间元组。 |
| 11 | time.time( ) 返回当前时间的时间戳(1970纪元后经过的浮点秒数)。 |
| 12 | time.tzset() 根据环境变量TZ重新初始化时间相关设置。 |