一.单分支结构
if [ 条件表达式 ];then
command
fi
或
if [ 条件表达式 ]
then
command
fi
或
[ 条件表达式 ] && command
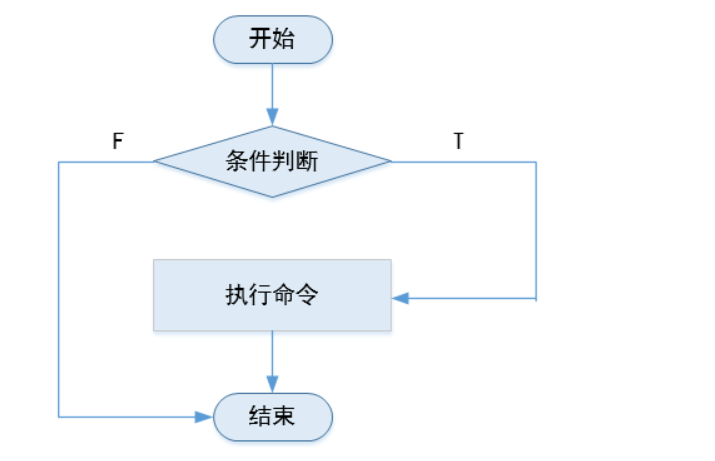
执行逻辑如下图
二.双分支结构
if [ 条件表达式 ];then
command1
else
command2
fi
或
if [ 条件表达式 ]
then
command1
else
command2
fi
或
[ 条件 ] && 命令1 || 命令2
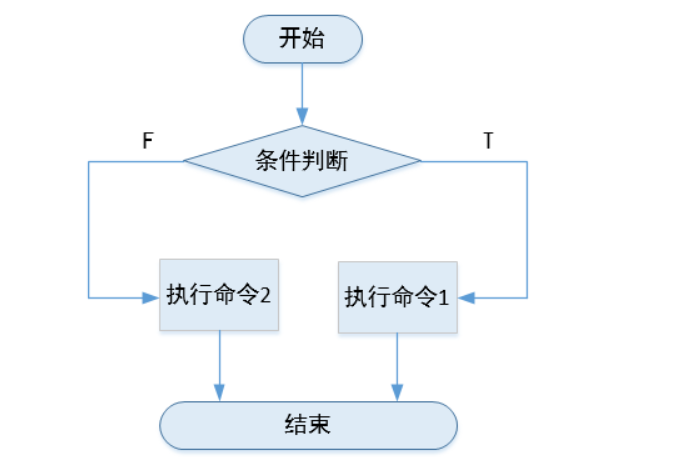
执行逻辑如下图
三.多分支结构
if [ 条件表达式1 ];then
command1
elif [ 条件表达式2 ];then
command2
else
command3
fi
或
if [ 条件表达式1 ]
then
command1
elif [ 条件表达式2 ]
then
command2
else
command3
fi
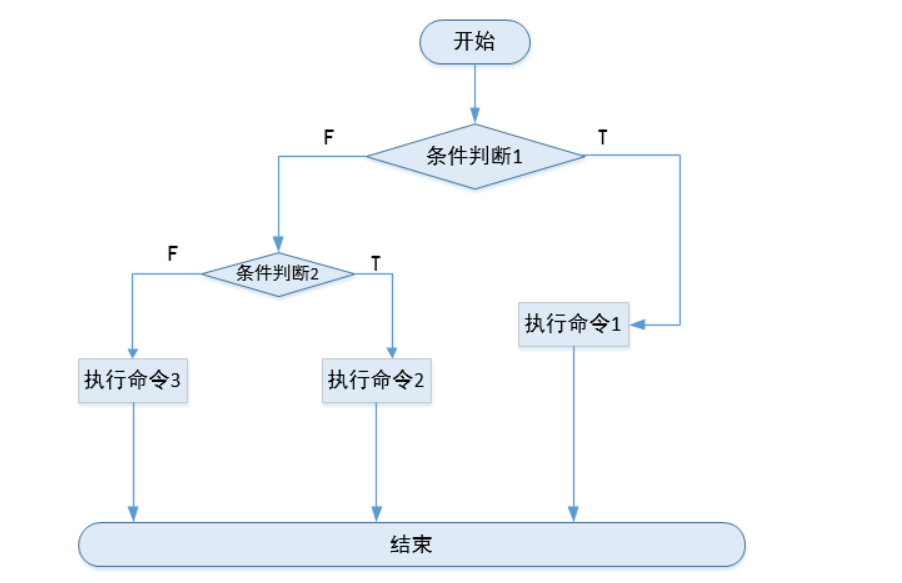
执行逻辑:
如果条件1满足,执行命令1后结束;
如果条件1不满足,再看条件2,如果条件2满足执行命令2后结束;
如果条件1和条件2都不满足执行命令3结束.
图示如下
四.if的嵌套使用
if [ 条件1 ];then
命令1
if [ 条件2 ];then
命令2
fi
else
if [ 条件3 ];then
命令3
elif [ 条件4 ];then
命令4
else
命令5
fi
fi
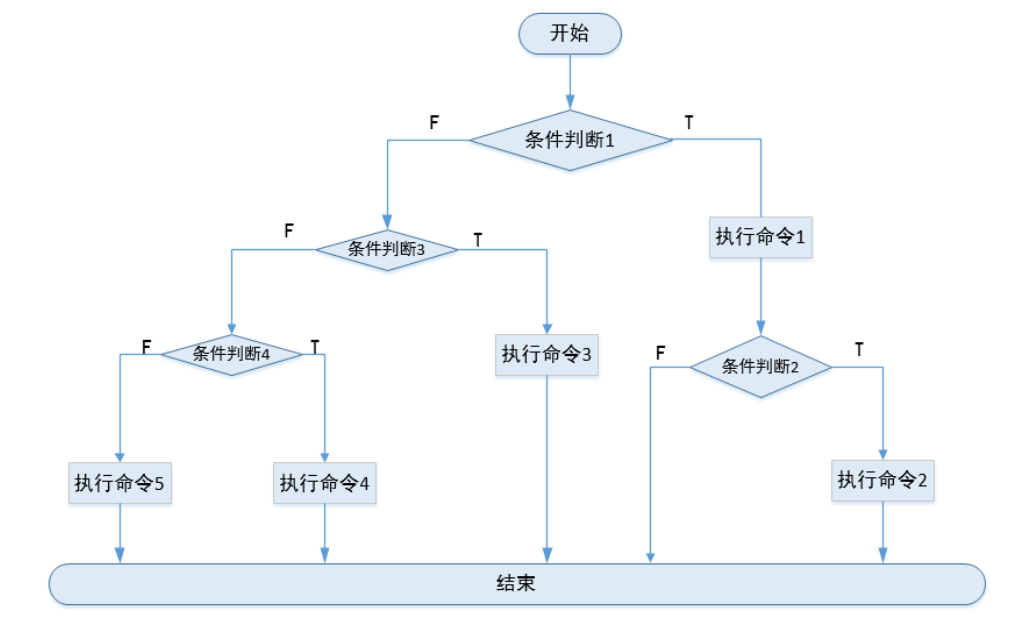
执行逻辑如下:
如果条件1满足,执行命令1;如果条件2也满足执行命令2,如果不满足就只执行命令1结束;
如果条件1不满足,不看条件2;直接看条件3,如果条件3满足执行命令3;如果不满足则看条件4,如果条件4满足执行命令4;否则执行命令5
五.相关练习
1.当内存剩余空间小于900M时,发出提示信息
[root@server shell02]# free -m total used free shared buffers cached Mem: 980 136 844 0 11 43 -/+ buffers/cache: 81 899 Swap: 1983 0 1983 [root@server shell02]# cat 7.sh #!/bin/bash free=$(free -m |grep ^Mem|tr -s " "|cut -d " " -f 4) if [ $free -le 900 ] then echo "system mem less than 900M now." fi [root@server shell02]# sh 7.sh system mem less than 900M now.
2.判断vsftp软件是否已经安装了
[root@server shell02]# cat 11.sh #!bin/bash rpm -q vsftpd &> /dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ] then echo "vsftpd software has installed." else yum -y install vsftpd &> /dev/null fi [root@server shell02]# sh 11.sh vsftpd software has installed.
3.输入一个文件路径,判断该文件是什么类型的?
[root@server shell02]# cat 10.sh #!bin/bash read -p "pls input the file path:" file_path if [ -e $file_path ] then if [ -L $file_path ] then echo "$file_path is a link file." elif [ -d $file_path ] then echo "$file_path is a directory." elif [ -f $file_path ] then echo "$file_path is a text file." elif [ -b $file_path ] then echo "$file_path is a block file." elif [ -c $file_path ] then echo "$file_path is a character file." elif [ -p $file_path ] then echo "$file_path is a pipe file." elif [ -S $file_path ] then echo "$file_path is a socket file." fi else echo "$file_path is not exist." fi [root@server shell02]# sh 10.sh pls input the file path:/tmp /tmp is a directory. [root@server shell02]# sh 10.sh pls input the file path:/etc/inittab /etc/inittab is a text file. [root@server shell02]# sh 10.sh pls input the file path:/dev/sda /dev/sda is a block file.
[root@server shell02]# cat 9.sh #!bin /bash read -p "pls input the file path:" file_path if [ -e $file_path ] then file_type=$(ls -ld $file_path|cut -c1) if [ $file_type = - ] then echo "$file_path is a text file." elif [ $file_type = d ] then echo "$file_path is a directory." elif [ $file_type = b ] then echo "$file_path is a black file." elif [ $file_type = c ] then echo "$file_path is a character file." elif [ $file_type = p ] then echo "$file_path is a pipe file." elif [ $file_type = l ] then echo "$file_path is a link file." elif [ $file_type = s ] then echo "$file_path is a socket file." fi else echo "$file_path is not exist" fi