对于Spring Boot整个的启动,“SpringBoot源码分析之SpringBoot的启动过程”这篇文章分析得很详细所以一懒就不想写了~这里主要想讨论下Spring Boot里内嵌Tomcat的启动。
主要的入口是“createApplicationContext()”方法,目前看很多书和文章都是提到的“AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext”类,但是查源码的时候发现这个类只在Spring boot 1.x版本中有,应该是2.x版本有所调整。
这里先梳理一下逻辑:
Spring Boot项目的启动是从“SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);”这句开始的,而这一句定位到代码中,实际会执行的代码如下:
1 /** 2 * Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new 3 * {@link ApplicationContext}. 4 * @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method) 5 * @return a running {@link ApplicationContext} 6 */ 7 public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) { 8 StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch(); 9 stopWatch.start(); 10 ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null; 11 Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>(); 12 configureHeadlessProperty(); 13 SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args); 14 listeners.starting(); 15 try { 16 ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args); 17 ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments); 18 configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment); 19 Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment); 20 context = createApplicationContext(); 21 exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, 22 new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context); 23 prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner); 24 refreshContext(context); 25 afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments); 26 stopWatch.stop(); 27 if (this.logStartupInfo) { 28 new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch); 29 } 30 listeners.started(context); 31 callRunners(context, applicationArguments); 32 } 33 catch (Throwable ex) { 34 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners); 35 throw new IllegalStateException(ex); 36 } 37 38 try { 39 listeners.running(context); 40 } 41 catch (Throwable ex) { 42 handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null); 43 throw new IllegalStateException(ex); 44 } 45 return context; 46 }
这里我们只点进20行继续跟踪,可以看到:
1 /** 2 * Strategy method used to create the {@link ApplicationContext}. By default this 3 * method will respect any explicitly set application context or application context 4 * class before falling back to a suitable default. 5 * @return the application context (not yet refreshed) 6 * @see #setApplicationContextClass(Class) 7 */ 8 protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() { 9 Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass; 10 if (contextClass == null) { 11 try { 12 switch (this.webApplicationType) { 13 case SERVLET: 14 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); 15 break; 16 case REACTIVE: 17 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS); 18 break; 19 default: 20 contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS); 21 } 22 } 23 catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { 24 throw new IllegalStateException( 25 "Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex); 26 } 27 } 28 return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass); 29 }
继续~注意第14行,不难找到“DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS”的值为:
"org.springframework.boot."
+ "web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext"
然后我们再来看看相关的类图:
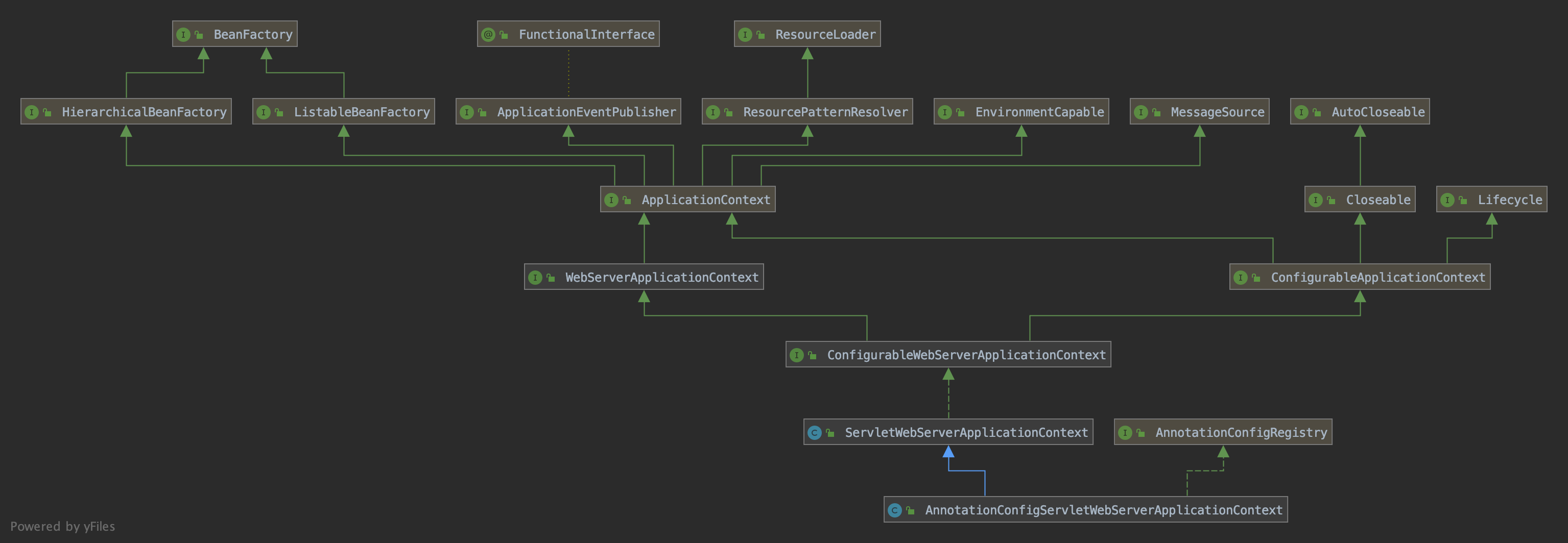
类太多不要紧,我们只需要重点关注上面的几个类:
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext(也就是我们刚刚说的类),ServletWebServerApplicationContext,AbstractApplicationContext。
AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext继承自ServletWebServerApplicationContext,而ServletWebServerApplicationContext则重写了AbstractApplicationContext中refresh()方法中提到的提供给子类来重写的onRefresh()方法。(接下来继续一步一步跟踪下方标红的代码)
1 @Override 2 protected void onRefresh() { 3 super.onRefresh(); 4 try { 5 createWebServer(); 6 } 7 catch (Throwable ex) { 8 throw new ApplicationContextException("Unable to start web server", ex); 9 } 10 }
1 private void createWebServer() { 2 WebServer webServer = this.webServer; 3 ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); 4 if (webServer == null && servletContext == null) { 5 ServletWebServerFactory factory = getWebServerFactory(); 6 this.webServer = factory.getWebServer(getSelfInitializer()); 7 getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerGracefulShutdown", 8 new WebServerGracefulShutdownLifecycle(this.webServer)); 9 getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("webServerStartStop", 10 new WebServerStartStopLifecycle(this, this.webServer)); 11 } 12 else if (servletContext != null) { 13 try { 14 getSelfInitializer().onStartup(servletContext); 15 } 16 catch (ServletException ex) { 17 throw new ApplicationContextException("Cannot initialize servlet context", ex); 18 } 19 } 20 initPropertySources(); }

然后我们点进TomcatServletWebServerFactory可以看到具体的实现:
1 @Override 2 public WebServer getWebServer(ServletContextInitializer... initializers) { 3 if (this.disableMBeanRegistry) { 4 Registry.disableRegistry(); 5 } 6 Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat(); 7 File baseDir = (this.baseDirectory != null) ? this.baseDirectory : createTempDir("tomcat"); 8 tomcat.setBaseDir(baseDir.getAbsolutePath()); 9 Connector connector = new Connector(this.protocol); 10 connector.setThrowOnFailure(true); 11 tomcat.getService().addConnector(connector); 12 customizeConnector(connector); 13 tomcat.setConnector(connector); 14 tomcat.getHost().setAutoDeploy(false); 15 configureEngine(tomcat.getEngine()); 16 for (Connector additionalConnector : this.additionalTomcatConnectors) { 17 tomcat.getService().addConnector(additionalConnector); 18 } 19 prepareContext(tomcat.getHost(), initializers); 20 return getTomcatWebServer(tomcat); 21 }