题目描述
Description
给定由 n 个点 m 条边组成的无向连通图,保证没有重边和自环。
你需要找出所有边,满足这些边恰好存在于一个简单环中。一个环被称为简单环,当且仅当它包含的所有点都只在这个环中被经过了一次。
注意到这些边可能有很多条,你只需要输出他们编号的异或和即可。
Input
第一行两个数 n, m。
接下来 m 行,每行两个数 ai , bi,表示第 i 条边连接了 ai , bi。
Output
输出一个数,表示所有满足条件的边的编号的异或和。
Sample Input
Sample Input1
4 4
1 2
2 4
4 3
3 2
Sample Input2
4 5
1 2
1 3
2 4
4 3
3 2
Sample Output
Sample Output2
5
Sample Output2
0
对于第一个样例,2,3,4 满足要求。
对于第二个样例,所有边都不满足要求。
Data Constraint
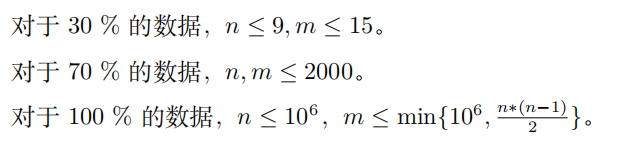
题解
复习求点双
先拓扑去掉树边,剩下的是若干个相连的点双,Tarjan即可
一些注意事项:
1、栈存的是边
2、求边双or点双时的low要做完之后再赋值(或者在返祖边时把dfn赋过去)
3、记录点双中的边:
只需要记录向下的边和向上的返祖边(不能直接指向父亲)即可,弹栈时一直弹到当前的t
如果相邻两点不在同一个点双中,那么显然栈顶的边是父亲-->儿子,可以直接弹
code
有重边所以打表
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#define fo(a,b,c) for (a=b; a<=c; a++)
#define fd(a,b,c) for (a=b; a>=c; a--)
#define min(a,b) (a<b?a:b)
#define max(a,b) (a>b?a:b)
using namespace std;
int a[2000002][2];
int ls[2000002];
int d[2000002];
int D[2000002];
int d2[2000002][2];
int d3[2000002];
bool BZ[2000002];
bool bz[2000002];
bool Bz[2000002];
int dfn[2000002];
int low[2000002];
int n,m,root,i,j,k,l,len,h,t,ans,tot,sum,s1,s2,T;
void New(int x,int y)
{
++len;
a[len][0]=y;
a[len][1]=ls[x];
ls[x]=len;
}
void dfs2(int Fa,int t)
{
int i;
Bz[t]=1;
for (i=ls[t]; i; i=a[i][1])
if (!bz[i] && a[i][0]!=Fa && !Bz[a[i][0]])
{
dfs2(t,a[i][0]);
tot+=t==root;
}
}
void work()
{
sum^=d2[l][1]/2;
++s1;
if (!BZ[d2[l][0]])
{
++s2;
BZ[d2[l][0]]=1;
d3[++T]=d2[l][0];
}
--l;
}
void pop(int t)
{
int i;
sum=0;s1=0;s2=0;T=0;
while (d2[l][0]!=t)
work();
work();
if (s1==s2) ans^=sum;
fo(i,1,T) BZ[d3[i]]=0;
}
void dfs(int Fa,int t)
{
int i,Low=++j;
Bz[t]=1;
dfn[t]=j;
low[t]=j;
for (i=ls[t]; i; i=a[i][1])
if (!bz[i] && a[i][0]!=Fa)
{
if (!Bz[a[i][0]] || dfn[a[i][0]]<dfn[t])
{
++l;
d2[l][0]=t;
d2[l][1]=i;
}
if (!Bz[a[i][0]])
{
dfs(t,a[i][0]);
if ((t!=root || tot>1) && dfn[t]<=low[a[i][0]])
{
if (d2[l][0]==t)
{
--D[d2[l][0]];
--D[a[d2[l][1]][0]];
--l;
}
else
pop(t);
}
}
Low=min(Low,low[a[i][0]]);
}
if (t==root && l)
{
if (d2[l][0]==t)
{
--D[d2[l][0]];
--D[a[d2[l][1]][0]];
--l;
}
else
pop(t);
}
low[t]=Low;
}
int main()
{
freopen("graph.in","r",stdin);
freopen("graph.out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
if (n==9 && m==12) //chongbian
{
printf("0
");
return 0;
}
len=1;
fo(i,1,m)
{
scanf("%d%d",&j,&k);
New(j,k);
New(k,j);
++D[j];++D[k];
}
h=0;
fo(i,1,n)
if (D[i]==1)
d[++t]=i;
while (h<t)
{
for (i=ls[d[++h]]; i; i=a[i][1])
if (!bz[i])
{
bz[i]=1;
bz[i^1]=1;
--D[d[h]];
--D[a[i][0]];
if (D[a[i][0]]==1)
d[++t]=a[i][0];
}
}
fo(i,1,n)
if (D[i])
{
root=i;
dfs2(0,root);
j=0;
l=0;
memset(Bz,0,sizeof(Bz));
dfs(0,root);
break;
}
printf("%d
",ans);
fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);
return 0;
}