
awk '/REG/{action} ' file
/REG/为正则表达式,可以将$0 ($0代表每一行)中,满足条件的记录送入到:action 进行处理
[root@Gin scripts]# awk '/root/{print $0}' passwd ##匹配所有包含root的行
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
[root@Gin scripts]# awk -F: '$5~/root/{print $0}' passwd ## 以分号作为分隔符,匹配第5个字段是root的行
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
布尔表达式
awk '布尔表达式{action}' file 仅当对前面的布尔表达式求值为真时, awk 才执行代码块。
[root@Gin scripts]# awk -F: '$1=="root"{print $0}' passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
[root@Gin scripts]# awk -F: '($1=="root")&&($5=="root") {print $0}' passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
awk 的 if、循环和数组
[root@zhangchao ~]# cat zc.log
root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin
[root@zhangchao ~]# cat awk.txt
#!/bin/awk
BEGIN {
FS=":"
}
{
if($1=="root")
{
print "Yes"
}
else if($1=="bar")
{
print "No"
}
else
{
print "Defailed"
}
}
[root@zhangchao ~]# awk -f awk.txt zc.log
Yes
Defailed
使用 if 语句还可以将代码:
1
! /matchme/ { print $1 $3 $4 }
转换成:
{
if ( $0 !~ /matchme/ ) {
print $1 $3 $4
}
}
循环结构
我们已经看到了 awk 的 while 循环结构,它等同于相应的 C 语言 while 循环。 awk 还有"do...while"循环,它在代码块结尾处对条件求值,而不像标准 while 循环那样在开始处求值。
它类似于其它语言中的"repeat...until"循环。以下是一个示例:
do...while 示例
{
count=1do {
print "I get printed at least once no matter what"
} while ( count !=1 )
}
与一般的 while 循环不同,由于在代码块之后对条件求值, "do...while"循环永远都至少执行一次。换句话说,当第一次遇到普通 while 循环时,如果条件为假,将永远不执行该循环。
for 循环
awk 允许创建 for 循环,它就象 while 循环,也等同于 C 语言的 for 循环:
for ( initial assignment; comparison; increment ) {
code block
}
以下是一个简短示例:
for ( x=1;x<=4;x++ ) {
print "iteration", x
}
此段代码将打印:
iteration1
iteration2
iteration3
iteration4
break 和 continue
此外,如同 C 语言一样, awk 提供了 break 和 continue 语句。使用这些语句可以更好地控制 awk 的循环结构。以下是迫切需要 break 语句的代码片断:
while 死循环
while (1) {
print "forever and ever..."
}
while 死循环 1 永远代表是真,这个 while 循环将永远运行下去。
以下是一个只执行十次的循环:
#break 语句示例
x=1
while(1) {
print "iteration", x
if ( x==10 ) {
break
}
x++
}
这里, break 语句用于“逃出”最深层的循环。 "break"使循环立即终止,并继续执行循环代码块后面的语句。
continue 语句补充了 break,其作用如下:
x=1while (1) {
if ( x==4 ) {
x++
continue
}
print "iteration", x
if ( x>20 ) {
break
}
x++
}
这段代码打印"iteration1"到"iteration21", "iteration4"除外。如果迭代等于 4,则增加 x并调用 continue 语句,该语句立即使 awk 开始执行下一个循环迭代,而不执行代码块的其余部分。如同 break 一样,
continue 语句适合各种 awk 迭代循环。在 for 循环主体中使用时, continue 将使循环控制变量自动增加。以下是一个等价循环:
for ( x=1;x<=21;x++ ) {
if ( x==4 ) {
continue
}
print "iteration", x
}
在while 循环中时,在调用 continue 之前没有必要增加 x,因为 for 循环会自动增加 x。
数组
for…in 输出,因为数组是关联数组,默认是无序的。所以通过 for…in 得到是无序的数组。如果需要得到有序数组,需要通过下标获得。
[root@zhangchao ~]# cat ws.txt
I am Zhang Chao, I am from Num 20.
[root@zhangchao ~]# cat awk.txt
#!/bin/awk
{
A[1]="beijing"
A[2]="shanghai"
A["three"]="shenzhen"
A["4"]="guangzhou"
for(a in A){
print A[a]
}
print "
"
print A[1]
print A[2]
print A["three"]
print A["4"]
}
[root@zhangchao ~]# awk -f awk.txt ws.txt
guangzhou
shenzhen
beijing
shanghai
beijing
shanghai
shenzhen
guangzhou
awk -F: '{print NF}' /etc/passwd //显示每行有多少字段;显示每行的字段数量;
awk -F: '{print $NF}' /etc/passwd //将每行第NF个字段的值打印出来;将每行最后一个字段的内容打印出来
s是数组,$NF是s数组的下标,s[$NF]是数组元素(类似于s[2]);只不过下标可以是字符串;
/^tcp/匹配没有tcp的行;
++s[$NF]数组元素加1;
[root@zhangchao ~]# netstat -an|awk '/^tcp/{++s[$NF];print $NF,s[$NF]}END{for(a in s)print a,s[a]}'
LISTEN 1
LISTEN 2
LISTEN 3
LISTEN 4
ESTABLISHED 1
LISTEN 5
LISTEN 6
LISTEN 7
LISTEN 7
ESTABLISHED 1
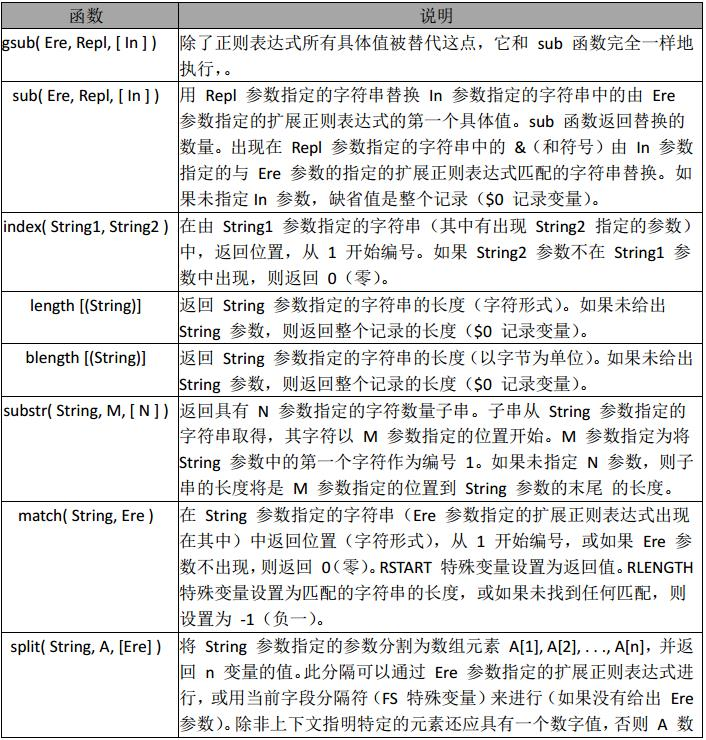
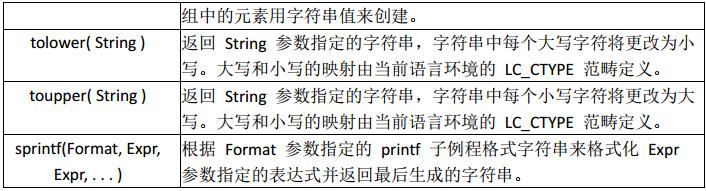
字符串函数的应用
替换
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";gsub(/[0-9]+/,"!",info);print info}' this is a test!test!
在 info 中查找满足正则表达式, /[0-9]+/ 用”!”替换,并且替换后的值,赋值给 info 未
给 info 值,默认是$0
查找
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";print index(info,"test")?"ok":"no found";}'
ok #未找到,返回 0
匹配查找
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";print match(info,/[0-9]+/)?"ok":"no found";}'
ok #如果查找到数字则匹配成功返回 ok,否则失败,返回未找到
截取
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test2010test!";print substr(info,4,10);}'
s is a tes #从第 4 个 字符开始,截取 10 个长度字符串
分割
awk 'BEGIN{info="this is a test";split(info,tA," ");print length(tA);for(k in tA){print k,tA[k];}}' 4
4 test 1 this 2 is 3 a
#分割 info,动态创建数组 tA,awk for …in 循环,是一个无序的循环。 并不是从数组下标
1…n 开始


