关键字:SQL树查询(参考:树遍历)
1.CTE的通用形式
WITH temp_name as
(
CTE查询结果集
)
释义:
(1)with/as :关键字
(2)temp_name:为CTE临时使用名称,可以看初学者做是一个临时表
(3)():查询结果集主体
2.CTE的递归查询
介绍:其实CTE最强大的地方就是在于其递归查询
举例1:使用CTE递归获取某年的1-12月份
--获取2018年的1-12月份(可以用来做外连接和分组) ;with date_test as ( select cast('20180101 00:00:00' as datetime) as 'date' union all select dateadd(mm,1,cast([date] as datetime)) as 'date' from date_test where [date] < cast('20181201' as datetime) ) select date date from date_test --select convert(char(7),date,120) date from date_test 获取其年号与月号
执行结果如图:

举例2:递归快速构建1~100(再大也可以用这个办法快速构建)
with t as (select 1 as dt union all select dt+1 from t where dt+1<=100 ) select dt from t -- option(maxrecursion 0) ;
结果如图:篇幅太长看下面的行数即可

举例3:经典树形结构查询
IF OBJECT_ID('TEST106') IS NOT NULL
BEGIN
drop table test106
END
--建表
create table test106(
id int,
name varchar(20),
parent int,
description varchar(20)
)
--建造数据
insert into test106 values
(1,'A',0,'总经理'),
(2,'B',1,'开发部经理'),
(3,'C',2,'JAVA小组长'),
(4,'guo',3,'苦逼的开发'),
(5,'li',3,'苦逼的开发'),
(6,'zhao',3,'安静的测试'),
(7,'wang',3,'暴躁的测试'),
(8,'D',2,'JAVA测试小组长')
--1.从上往下查,我要查开发部经理B下的所有下属
--2.从下往上查也一样(只是稍作修改),这里就不作演示了
with tree_test(id,name,parent,description) as
(
select id,name,parent,description from test106
where id=2
union all
select t1.id,t1.name,t1.parent,t1.description from test106 t1 join tree_test t2 on t1.parent = t2.id --这里不做表关联用exists也是不错的选择
)
select * from tree_test
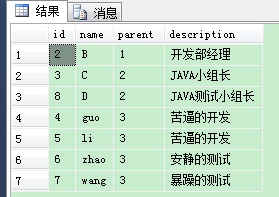
结果如图:
举例4:CTE实现instr功能
if object_id('tempdb..#T') is not null drop table #T create table #T ( source_string nvarchar(4000) ) insert into #T values (N'我们我们') insert into #T values (N'我我哦我') declare @sub_string nvarchar(1024) declare @nth int set @sub_string = N'我们' set @nth = 2 ;with T(source_string, starts, pos, nth) as ( select source_string, 1, charindex(@sub_string, source_string), 1 from #t union all select source_string, pos + 1, charindex(@sub_string, source_string, pos + 1), nth+1 from T where pos > 0 ) select source_string, pos, nth from T where pos <> 0 and nth = @nth order by source_string, starts --source_string pos nth --我们我们 3 2
检索字符改成我,试试。

3.CTE的CUR(R上面1-2已经描述过了,这里不再赘述)
这里使用2中的例3中的数据
insert into test106 values
(1,'A',0,'总经理'),
(2,'B',1,'开发部经理'),
(3,'C',2,'JAVA小组长'),
(4,'guo',3,'苦逼的开发'),
(5,'li',3,'苦逼的开发'),
(6,'zhao',3,'安静的测试'),
(7,'wang',3,'暴躁的测试'),
(8,'D',2,'JAVA测试小组长')
(1)delete示例
select * from test106 --用CTE筛选出id<=3的数据 ;with temp_delete as ( select * from test106 where id <=3 ) delete from temp_delete select * from test106;
结果如下:

(2)update
与(1)一样没什么区别
做好with temp_name as ()之后,直接就update语句from temp_name 即可,这里不再演示。
(3)insert
同(1)、(2),直接insert into select temp_name即可
4.CTE的总结与分析
(1)递归CTE的执行过程

(2)CTE的注意事项
【1】在cte使用之前如果有有语句运行,必须加';'分号,如3中的delete示例中一样。否则可以不加。

【2】在cte中可以定义多个temp_name,但不可重复,只能后者调用先定义的

【3】CTE只在定以后第一条语句使用,并且可以重复在第一条语句使用其temp_name表

【4】CTE定义好后,使用的时候temp_name如果和现有表同名,则CTE下第一条语句使用的是temp_name表

【5】同一个CTE定义过程中不可有同名的temp_name

【6】CTE中不可嵌套CTE,这个不演示了,有意者可以自己去。
