| 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。

事件处理机制分为单点触屏,多点触屏,加速度事件,键盘事件和鼠标事件。在现在的智能手机中,触屏的应用比较的广泛,尤其是多点触屏事件的技术,使很多触屏事件操作在游戏中更泛的应用,使得操作更加的丰富。
单点触屏事件:
1.单点触屏事件
Touch的重要方法:
cocos2d::Vec2 getLocation() const;
//获得GL坐标
cocos2d::Vec2 getLocationInView() const;
//获得屏幕的坐标点
2. 监听器: EventListenerTouchOneByOne
事件方法:
1 virtual bool onTouchBegan(cocos2d::Touch* touch, cocos2d::Event* unused_event); 2 触摸开始,返回true可以使得该触摸点属于该函数的目标对象,该点的变化只会影响该目标对象函数的调用,不会影响其他对象 3 virtual bool onTouchMoved(cocos2d::Touch* touch, cocos2d::Event* unused_event); 4 触摸点移动 5 virtual bool onTouchEnded(cocos2d::Touch* touch, cocos2d::Event* unused_event); 6 触摸动作结束 7 virtual bool onTouchCancelled(cocos2d::Touch* touch, cocos2d::Event* unused_event); 8 系统中断通知需要取消触摸事件的时候会调用此函数,这个中断往往是因为应用时间没有响应或者当前视图从系统的顶层上移除
*.如果在onTouchBegan中返回的为false,则onTouchMoved,onTouchEnded,onTouchCancelled这几个方法均不会执行。如果返回的是true的话,则这几个方法会执行
3. 注册监听器
auto listener = EventListenerTouchOneByOne::create();
listener->onTouchBegan = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onTouchBegan, this);
listener->onTouchMoved = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onTouchMoved, this);
listener->onTouchEnded = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onTouchEnded, this);
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener,this);
实例:
.h files
#ifndef _ONETOUCHTEST_SCENE_H_
#define _ONETOUCHTEST_SCENE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
class touchTest : public cocos2d::Layer
{
private:
cocos2d::Size visible;
cocos2d::Vec2 origin;
public:
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
virtual bool onTouchBegan(cocos2d::Touch *touch, cocos2d::Event *unused_event);
virtual void onTouchMoved(cocos2d::Touch *touch, cocos2d::Event *unused_event);
virtual void onTouchEnded(cocos2d::Touch *touch, cocos2d::Event *unused_event);
CREATE_FUNC(touchTest);
};
#endif // _ONETOUCHTEST_SCENE_H_
.cpp files
#include "OneTouchTest.h"
USING_NS_CC;
Scene* touchTest::createScene()
{
auto scene = Scene::create();
auto layer = touchTest::create();
scene->addChild(layer);
return scene;
}
bool touchTest::init()
{
if (!Layer::init())
{
return false;
}
//第一步创建一个监听器listener
auto listener = EventListenerTouchOneByOne::create();
//注册监听器
listener->onTouchBegan = CC_CALLBACK_2(touchTest::onTouchBegan, this);
listener->onTouchMoved = CC_CALLBACK_2(touchTest::onTouchMoved, this);
listener->onTouchEnded = CC_CALLBACK_2(touchTest::onTouchEnded, this);
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
return true;
}
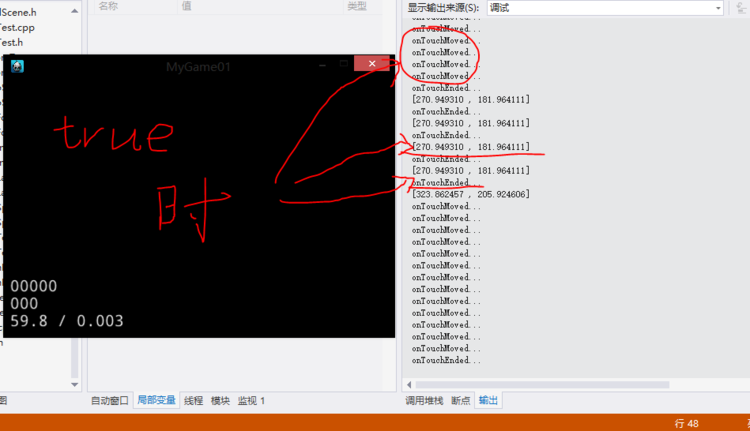
bool touchTest::onTouchBegan(cocos2d::Touch *touch, cocos2d::Event *unused_event)
{
//取得单击屏幕处那个位置的点
origin = touch->getLocationInView();
//转换成GL坐标
origin = Director::getInstance()->convertToGL(origin);
CCLOG("[%f , %f]", origin.x, origin.y);
//return true;
return false;
}
void touchTest::onTouchMoved(cocos2d::Touch *touch, cocos2d::Event *unused_event)
{
CCLOG("onTouchMoved...");
}
void touchTest::onTouchEnded(cocos2d::Touch *touch, cocos2d::Event *unused_event)
{
CCLOG("onTouchEnded...");
}

多点触屏事件:
1. 多点触屏事件
Touch重要方法
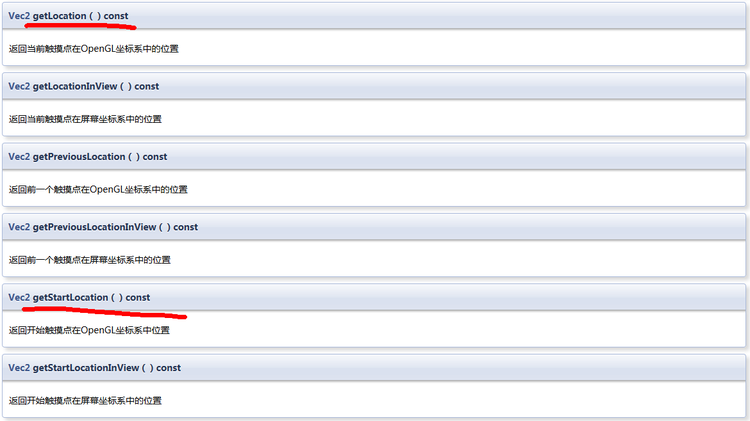
cocos2d::Vec2 getLocation() const;
//获得GL坐标
cocos2d::Vec2 getLocationInView() const;
//获得屏幕坐标点
2. 监听器: EventListenerTouchAllAtOnce
事件方法:
1 virtual void onTouchesBegan(const std::vector<Touch*>& touches, Event* unused_envent); 2 触摸开始,与单点触屏不同的是,多点触屏事件的返回不是bool类型,而是void类型 3 virtual void onTouchesMoved(const std::vector<Touch*>& touches, Event* unused_envent); 4 触摸点移动 5 virtual void onTouchesEnded(const std::vector<Touch*>& touches, Event* unused_envent); 6 触摸动作结束 7 virtual void onTouchesCancelled(const std::vector<Touch*>& touches, Event* unused_envent); 8 系统中断通知需要取消触摸事件的时候调用此函数
实例:
.h files
#ifndef _MOSTTOUCHTEST_SCENE_H_
#define _MOSTTOUCHTEST_SCENE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
class mostTouch : public cocos2d::Layer
{
private:
cocos2d::Vec2 origin;
public:
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
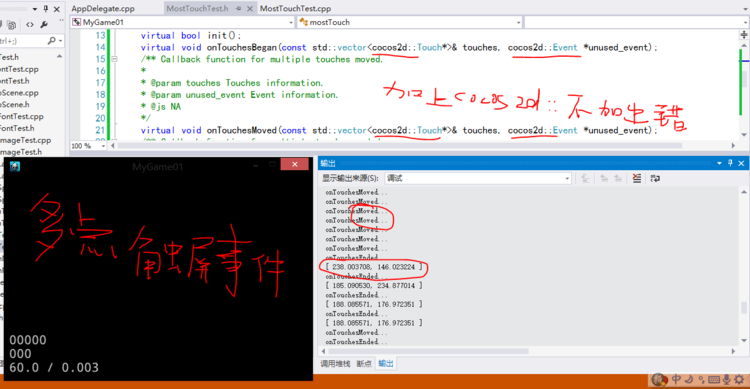
virtual void onTouchesBegan(const std::vector<cocos2d::Touch*>& touches, cocos2d::Event *unused_event);
/** Callback function for multiple touches moved.
*
* @param touches Touches information.
* @param unused_event Event information.
* @js NA
*/
virtual void onTouchesMoved(const std::vector<cocos2d::Touch*>& touches, cocos2d::Event *unused_event);
/** Callback function for multiple touches ended.
*
* @param touches Touches information.
* @param unused_event Event information.
* @js NA
*/
virtual void onTouchesEnded(const std::vector<cocos2d::Touch*>& touches, cocos2d::Event *unused_event);
/** Callback function for multiple touches cancelled.
*
* @param touches Touches information.
* @param unused_event Event information.
* @js NA
*/
CREATE_FUNC(mostTouch);
};
#endif // _MOSTTOUCHTEST_SCENE_H_
.cpp files
#include "MostTouchTest.h"
USING_NS_CC;
Scene* mostTouch::createScene()
{
auto scene = Scene::create();
auto layer = mostTouch::create();
scene->addChild(layer);
return scene;
}
bool mostTouch::init()
{
if (!Layer::init())
{
return false;
}
//设置监听器
auto listener = EventListenerTouchAllAtOnce::create();
listener->onTouchesBegan = CC_CALLBACK_2(mostTouch::onTouchesBegan, this);
listener->onTouchesMoved = CC_CALLBACK_2(mostTouch::onTouchesMoved, this);
listener->onTouchesEnded = CC_CALLBACK_2(mostTouch::onTouchesEnded, this);
//注册监听器
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
return true;
}
void mostTouch::onTouchesBegan(const std::vector<cocos2d::Touch*>& touches, cocos2d::Event *unused_event)
{
//首先设置屏幕上取一个点,[n]表示取得多个点
Touch* touch = touches[0];
//取得这个点在屏幕上的位置
origin = touch->getLocationInView();
//再将这个点转换成坐标表示
origin = Director::getInstance()->convertToGL(origin);
//输出这个点
CCLOG("[ %f, %f ]", origin.x, origin.y);
}
void mostTouch::onTouchesMoved(const std::vector<cocos2d::Touch*>& touches, cocos2d::Event *unused_event)
{
CCLOG("onTouchesMoved...");
}
void mostTouch::onTouchesEnded(const std::vector<cocos2d::Touch*>& touches, cocos2d::Event *unused_event)
{
CCLOG("onTouchesEnded...");
}
一些重要的函数及功能
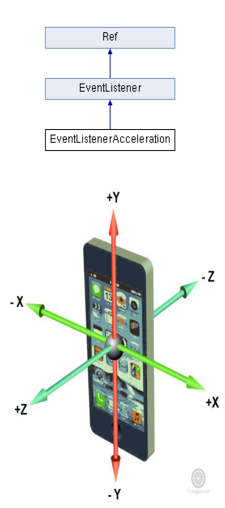
加速度事件:
移动设备上一个很重要的输入源是设备的方向,大多数设备都配备了加速计,用于测量设备静止或匀速运动时所受到的重力方向。重力感应来自移动设备的加速计,通常支持X、Y和Z三个方向的加速度感应,又称为三向加速计。实际应用中,可以根据三个方向的力度大小来计算手机倾斜的角度和方向。3.0机制中,我们只需要创建一个加速计监听器EventListenerAcceleration,实现响应的回调函数,在回调函数中实现相应的游戏逻辑即可,最后把创建的监听器注册到事件分发器_eventDispatcher中即可。
1. 加速度事件简介
virtual void onAcceleration(Acceleration* acc,
Event* unused_event);
class Acceleration
{
public:
double x;
double y;
double z;
double timestamp;
Acceleration():x(0),y(0),z(0),timestamp(0){}
};
2. 注册事件
Device::setAccelerometerEnabled(true);
auto listener =
EventListenerAcceleration::create(CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onAcceleration,
this));
_eventDispather->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
实例:
.h files
#ifndef _ACCELERATIONTEST_SCENE_H_
#define _ACCELERATIONTEST_SCENE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
class accelerationTest : public cocos2d::Layer
{
private:
public:
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
virtual void onAcceleration(cocos2d::Acceleration* acc, cocos2d::Event* unused_event);
/** If isTouchEnabled, this method is called onEnter. Override it to change the
way Layer receives touch events.
( Default: TouchDispatcher::sharedDispatcher()->addStandardDelegate(this,0); )
Example:
void Layer::registerWithTouchDispatcher()
{
TouchDispatcher::sharedDispatcher()->addTargetedDelegate(this,INT_MIN+1,true);
}
@since v0.8.0
@js NA
*/
CREATE_FUNC(accelerationTest);
};
#endif // _ACCELERATIONTEST_SCENE_H_
.cpp files
#include "AccelerationTest.h"
USING_NS_CC;
Scene* accelerationTest::createScene()
{
auto scene = Scene::create();
auto layer = accelerationTest::create();
scene->addChild(layer);
return scene;
}
bool accelerationTest::init()
{
if (!Layer::init())
{
return false;
}
Device::setAccelerometerEnabled(true);
auto listener = EventListenerAcceleration::create(CC_CALLBACK_2(accelerationTest::onAcceleration, this));
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
return true;
}
void accelerationTest::onAcceleration(cocos2d::Acceleration* acc, cocos2d::Event* unused_event)
{
float x = acc->x;
float y = acc->y;
float z = acc->z;
//一些加速度事件的操作
//.....
CCLOG("[%f, %f, %f]", x, y, z);
}

键盘事件:
1. 键盘事件:
EventKeyboard::KeyCode
重要常量(键盘按键常量a~z,0~9...);
KEY_0 ='0'
KEY_1 ='1'
KEY_2 ='2'
KEY_3 ='3'
KEY_4 ='4'
KEY_5 ='5'
KEY_6 ='6'
....
2. 监听器: EventListenerKeyboard
事件方法:
1 //按下 2 virtual void onKeyPressed(EventKeyboard::KeyCode keycode, Event* event); 3 //抬起 4 virtual void onKeyReleased(EventKeyboard::KeyCode keycode, Event* event);
3. 注册监听器
auto listener =
EventListenerKeyboard::create();
listener->onKeyPressed = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onKeyPressed, this);
listener->onKeyReleased = CC_CALLBACK_2(HelloWorld::onKeyReleased, this);
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
实例:
.h files
#ifndef _ONKEYBOARDTEST_SCENE_H_
#define _ONKEYBOARDTEST_SCENE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
class KeyBoardTest : cocos2d::Layer
{
private:
public:
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
virtual void onKeyPressed(cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode keyCode, cocos2d::Event* event);
/** Callback function for key released.
* @param keyCode KeyCode information.
* @param event Event information.
* @js NA
*/
virtual void onKeyReleased(cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode keyCode, cocos2d::Event* event);
CREATE_FUNC(KeyBoardTest);
};
//KeyBoard
#endif // _ONKEYBOARDTEST_SCENE_H_
.cpp files
#include "onKeyBoardTest.h"
USING_NS_CC;
Scene* KeyBoardTest::createScene()
{
auto scene = Scene::create();
auto layer = KeyBoardTest::create();
scene->addChild(layer);
return scene;
}
bool KeyBoardTest::init()
{
if (!Layer::init())
{
return false;
}
//设置键盘事件的监听器
auto listener = EventListenerKeyboard::create();
//设置监听的对象,按下对象和抬起状态
listener->onKeyPressed = CC_CALLBACK_2(KeyBoardTest::onKeyPressed, this);
listener->onKeyReleased = CC_CALLBACK_2(KeyBoardTest::onKeyReleased, this);
//注册监听器
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
return true;
}
void KeyBoardTest::onKeyPressed(cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode keyCode, cocos2d::Event* event)
{
switch (keyCode)
{
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_0:
CCLOG("Pressed key = '0'");
break;
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_1:
CCLOG("Pressed key = '1'");
break;
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_2:
CCLOG("Pressed key = '2'");
break;
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_3:
CCLOG("Pressed key = '3'");
break;
default:
CCLOG("Pressed other Key...");
break;
}
}
void KeyBoardTest::onKeyReleased(cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode keyCode, cocos2d::Event* event)
{
switch (keyCode)
{
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_0:
CCLOG("Released key = '0'");
break;
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_1:
CCLOG("Released key = '1'");
break;
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_2:
CCLOG("Released key = '2'");
break;
case cocos2d::EventKeyboard::KeyCode::KEY_3:
CCLOG("Released key = '3'");
break;
default:
CCLOG("Released other Key...");
break;
}
}

鼠标事件:
1.1、 事件类 EventMouse
重要属性和方法:
//事件类型
MouseEventType
_mouseEventType;
enum class MouseEventType
{
MOUSE_NONE, //无
MOUSE_DOWN, //按下,鼠标左右键
MOUSE_UP, //抬起,鼠标左右键
MOUSE_MOVE, //移动
MOUSE_SCROLL, //滚轮
};
//鼠标按键 左键:0 右键:1
int _mouseButtom;
//x坐标
float _x;
//y坐标
float _y;
//滚动坐标
float _scrollX;
float _scrollY;
1.2、 事件监听器EventListenerMouse回调方法
1 //down 2 void onMouseDown(Event* event); 3 //up 4 void onMouseUp(Event* event); 5 //move 移动 6 void onMouseMove(Event* event); 7 //scroll 滚动 8 void onMouseScroll(Event* event);
实例:
.h files
#ifndef _MOUSEEVENTTEST_SCENE_H_
#define _MOUSEEVENTTEST_SCENE_H_
#include "cocos2d.h"
class eventMouse : public cocos2d::Layer
{
private:
public:
static cocos2d::Scene* createScene();
virtual bool init();
void onMouseDown(cocos2d::Event* e);
void onMouseUp(cocos2d::Event* e);
void onMouseMove(cocos2d::Event* e);
void onMouseScroll(cocos2d::Event* e);
CREATE_FUNC(eventMouse);
};
#endif // _MOUSEEVENTTEST_SCENE_H_
.cpp files
#include "MouseEventTest.h"
USING_NS_CC;
Scene* eventMouse::createScene()
{
auto scene = Scene::create();
auto layer = eventMouse::create();
scene->addChild(layer);
return scene;
}
bool eventMouse::init()
{
if (!Layer::init())
{
return false;
}
//设置鼠标事件的监听器
auto listener = EventListenerMouse::create();
//设置监听的对象
listener->onMouseDown = CC_CALLBACK_1(eventMouse::onMouseDown, this);
listener->onMouseUp = CC_CALLBACK_1(eventMouse::onMouseUp, this);
listener->onMouseMove = CC_CALLBACK_1(eventMouse::onMouseMove, this);
listener->onMouseScroll = CC_CALLBACK_1(eventMouse::onMouseScroll, this);
//注册监听器
_eventDispatcher->addEventListenerWithSceneGraphPriority(listener, this);
return true;
}
void eventMouse::onMouseDown(cocos2d::Event* event)
{
EventMouse* elem = (EventMouse*)event;
//判断鼠标按下的是那个键
int flag = elem->getMouseButton();
CCLOG("bottom = %d", flag);
}
void eventMouse::onMouseUp(cocos2d::Event* event)
{
CCLOG("Relax buttom");
}
void eventMouse::onMouseMove(cocos2d::Event* event)
{
EventMouse* elem = (EventMouse*)event;
//取得当前鼠标位置的x,y坐标值
float x = elem->getCursorX();
float y = elem->getCursorY();
CCLOG("[%f , %f]", x, y);
}
void eventMouse::onMouseScroll(cocos2d::Event* event)
{
//取得鼠标事件
EventMouse* elem = (EventMouse*)event;
//取得滚轮滚动的值
float sx = elem->getScrollX();
float sy = elem->getScrollY();
CCLOG("[%f , %f]", sx, sy);
}
