1、原生form表单
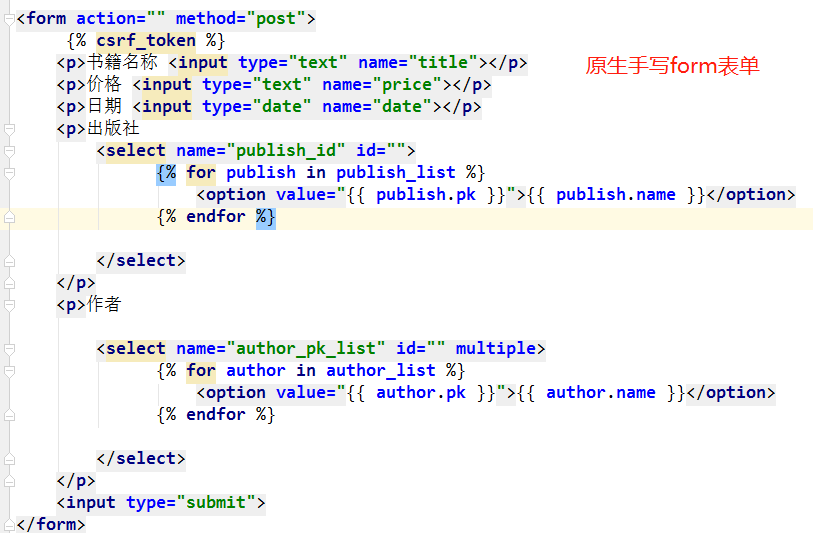
步骤:
1.models.py
makemigrations
migrate
2.createsuperuser
yuan yuan1234
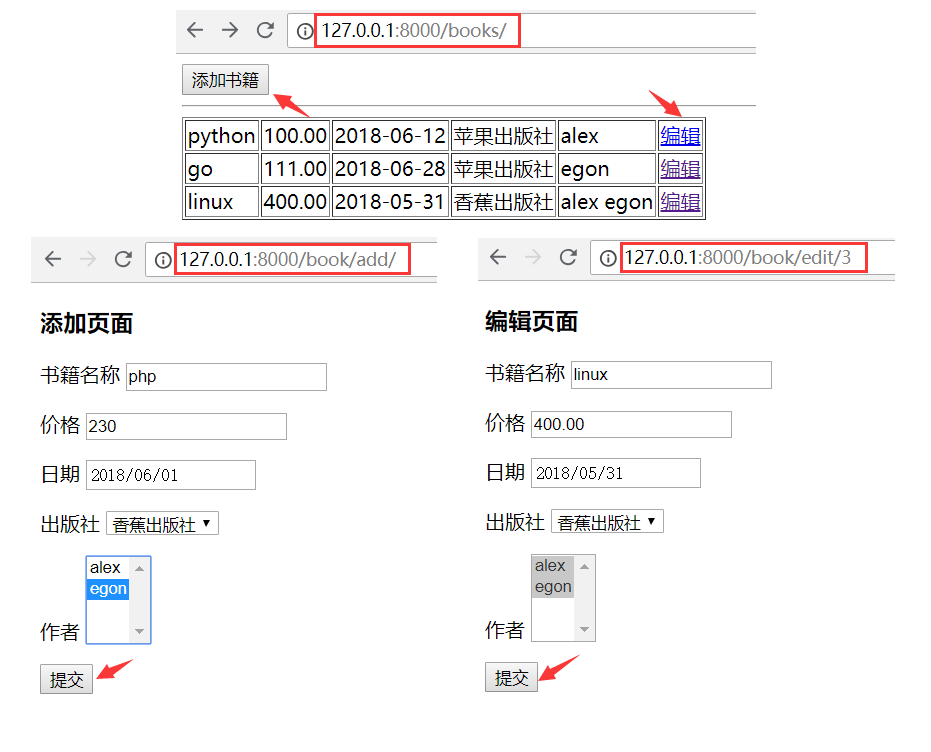
1.addbook:(getlist)
...
publish_id = request.POST.get('publish_id') auhtor_pk_list = request.POST.getlist('auhtor_pk_list') # ['1', '2'] book_obj = Book.objects.create(title=title,price=price,date=date,publish_id=publish_id) book_obj.authors.add(*auhtor_pk_list)
2.editbook:(set)
...
<p>价格 <input type="text" name="price" value="{{ edit_book.price }}"></p> {% if author in edit_book.authors.all %} <option selected value="{{ author.pk }}">{{ author.name }}</option> {% else %} <option value="{{ author.pk }}">{{ author.name }}</option> {% endif %} ... ret = Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).update(title=title, price=price, date=date, publish_id=publish_id) print('ret---', ret) # 1 book_obj = Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).first() print('book_obj---', book_obj) # 对象 book_obj.authors.set(auhtor_pk_list)
code代码
models

from django.db import models # Create your models here. class Book(models.Model): title=models.CharField(max_length=32) price=models.DecimalField(max_digits=8,decimal_places=2) # 999999.99 date=models.DateField() publish=models.ForeignKey(to="Publish",on_delete=True) authors=models.ManyToManyField("Author") def __str__(self): return self.title class Publish(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_length=32) def __str__(self): return self.name class Author(models.Model): name=models.CharField(max_length=32) def __str__(self): return self.name
urls

"""formsDemo URL Configuration The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/http/urls/ Examples: Function views 1. Add an import: from my_app import views 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', views.home, name='home') Class-based views 1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', Home.as_view(), name='home') Including another URLconf 1. Import the include() function: from django.conf.urls import url, include 2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls')) """ from django.conf.urls import url from django.contrib import admin from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls), url(r'^books/', views.books), url(r'^book/add', views.addbook), url(r'^book/edit/(d+)', views.editbook), ]
views

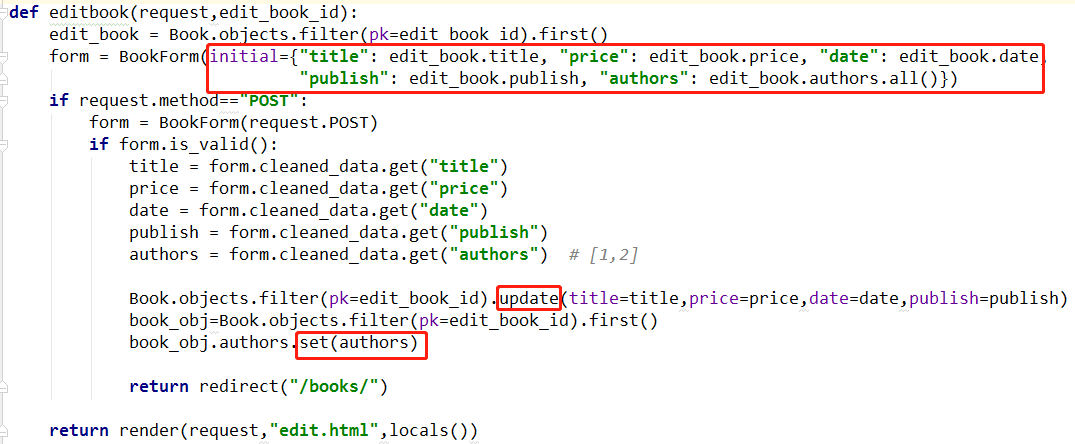
from django.shortcuts import render,redirect # Create your views here. from .models import * def books(request): book_list=Book.objects.all() return render(request,"books.html",locals()) def addbook(request): if request.method=="POST": title=request.POST.get("title") price=request.POST.get("price") date=request.POST.get("date") publish_id=request.POST.get("publish_id") author_pk_list=request.POST.getlist("author_pk_list") # [1,2] book_obj=Book.objects.create(title=title,price=price,date=date,publish_id=publish_id) book_obj.authors.add(*author_pk_list) return redirect("/books/") publish_list=Publish.objects.all() author_list=Author.objects.all() return render(request,"add.html",locals()) def editbook(request,edit_book_id): if request.method=="POST": title=request.POST.get("title") price=request.POST.get("price") date=request.POST.get("date") publish_id=request.POST.get("publish_id") author_pk_list=request.POST.getlist("author_pk_list") # [1,2] Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).update(title=title,price=price,date=date,publish_id=publish_id) book_obj=Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).first() book_obj.authors.set(author_pk_list) return redirect("/books/") edit_book=Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).first() publish_list = Publish.objects.all() author_list = Author.objects.all() return render(request,"edit.html",locals())
books.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> </head> <body> <a href="/book/add"><button>添加书籍</button></a> <hr> <table border="1"> {% for book in book_list %} <tr> <td>{{ book.title }}</td> <td>{{ book.price }}</td> <td>{{ book.date|date:"Y-m-d" }}</td> <td>{{ book.publish.name }}</td> <td>{{ book.authors.all }}</td> <td><a href="/book/edit/{{book.pk}}"><button>编辑</button></a></td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table> </body> </html>
add.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> </head> <body> <h3>添加页面</h3> <form action="" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <p>书籍名称 <input type="text" name="title"></p> <p>价格 <input type="text" name="price"></p> <p>日期 <input type="date" name="date"></p> <p>出版社 <select name="publish_id" id=""> {% for publish in publish_list %} <option value="{{ publish.pk }}">{{ publish.name }}</option> {% endfor %} </select> </p> <p>作者 <select name="author_pk_list" id="" multiple> {% for author in author_list %} <option value="{{ author.pk }}">{{ author.name }}</option> {% endfor %} </select> </p> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
edit.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> </head> <body> <h3>编辑页面</h3> <form action="" method="post"> {% csrf_token %} <p>书籍名称 <input type="text" name="title" value="{{ edit_book.title }}"></p> <p>价格 <input type="text" name="price" value="{{ edit_book.price }}"></p> <p>日期 <input type="date" name="date" value="{{ edit_book.date|date:'Y-m-d' }}"></p> <p>出版社 <select name="publish_id" id=""> {% for publish in publish_list %} {% if edit_book.publish == publish %} <option selected value="{{ publish.pk }}">{{ publish.name }}</option> {% else %} <option value="{{ publish.pk }}">{{ publish.name }}</option> {% endif %} {% endfor %} </select> </p> <p>作者 <select name="author_pk_list" id="" multiple> {% for author in author_list %} {% if author in edit_book.authors.all %} <option selected value="{{ author.pk }}">{{ author.name }}</option> {% else %} <option value="{{ author.pk }}">{{ author.name }}</option> {% endif %} {% endfor %} </select> </p> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
2、forms组件
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/7614921.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/wupeiqi/articles/6144178.html
1、针对form表单设计form组件
forms组件:
#三个渲染出来的都是select框
forms.ChoiceField(Field) #这个使用的是choice=数据
forms.ModelChoiceField(ChoiceField) #这个使用是queryset=数据,单选框
forms.ModelMultipleChoiceField(ModelChoiceField) #这个也是queryset=数据,多选框
编辑功能不好实现。(将循环的结果放到input内)
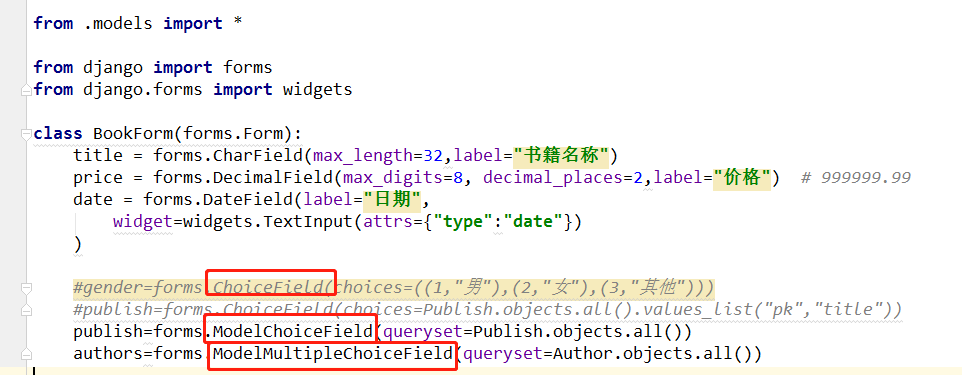
2、form组件能做的事情:
form组件能做的事情:
1.能渲染页面
2.能做校验用
3.拿到错误信息显示
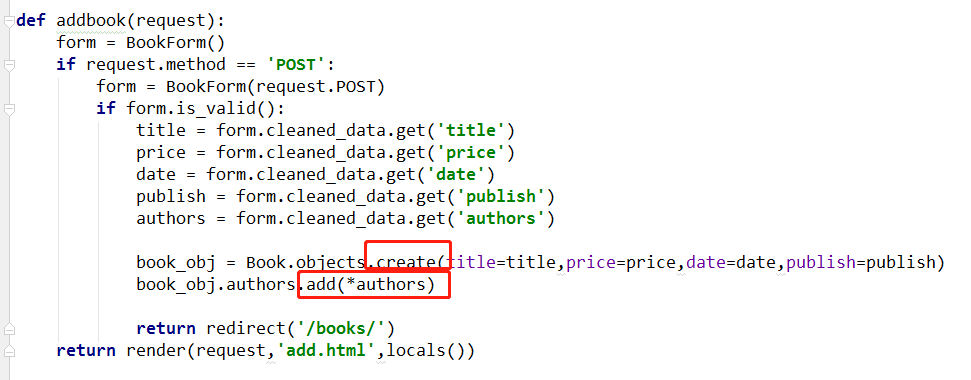

3、code
views

from django.shortcuts import render,redirect # Create your views here. from .models import * from django import forms from django.forms import widgets class BookForm(forms.Form): title = forms.CharField(max_length=32,label="书籍名称") price = forms.DecimalField(max_digits=8, decimal_places=2,label="价格") # 999999.99 date = forms.DateField(label="日期", widget=widgets.TextInput(attrs={"type":"date"}) ) #gender=forms.ChoiceField(choices=((1,"男"),(2,"女"),(3,"其他"))) #publish=forms.ChoiceField(choices=Publish.objects.all().values_list("pk","title")) publish=forms.ModelChoiceField(queryset=Publish.objects.all()) authors=forms.ModelMultipleChoiceField(queryset=Author.objects.all()) def books(request): book_list=Book.objects.all() return render(request,"books.html",locals()) def addbook(request): form = BookForm() if request.method == 'POST': form = BookForm(request.POST) if form.is_valid(): print(form.cleaned_data) """ clean_date: {'title': '书1', 'price': Decimal('1111'), 'date': datetime.date(2018, 6, 7), 'publish': <Publish: 香蕉出版社>, # 对象 'authors': <QuerySet [<Author: alex>, <Author: egon>]>} """ title = form.cleaned_data.get('title') price = form.cleaned_data.get('price') date = form.cleaned_data.get('date') publish = form.cleaned_data.get('publish') authors = form.cleaned_data.get('authors') book_obj = Book.objects.create(title=title,price=price,date=date,publish=publish) book_obj.authors.add(*authors) return redirect('/books/') print(form) return render(request,'add.html',locals()) def editbook(request,edit_book_id): edit_book = Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).first() form = BookForm(initial={"title": edit_book.title, "price": edit_book.price, "date": edit_book.date, "publish": edit_book.publish, "authors": edit_book.authors.all()}) if request.method=="POST": form = BookForm(request.POST) if form.is_valid(): title = form.cleaned_data.get("title") price = form.cleaned_data.get("price") date = form.cleaned_data.get("date") publish = form.cleaned_data.get("publish") authors = form.cleaned_data.get("authors") # [1,2] Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).update(title=title,price=price,date=date,publish=publish) book_obj=Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).first() book_obj.authors.set(authors) return redirect("/books/") return render(request,"edit.html",locals())
add

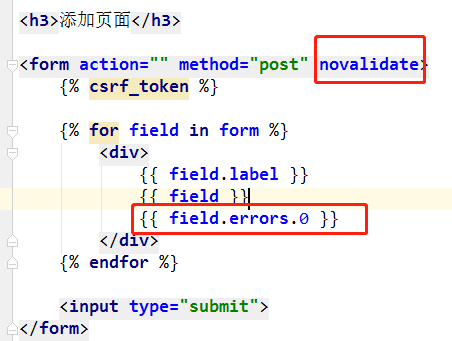
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> </head> <body> <h3>添加页面</h3> <form action="" method="post" novalidate> {% csrf_token %} {% for field in form %} <div> {{ field.label }} {{ field }} {{ field.errors.0 }} </div> {% endfor %} <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
edit

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-CN"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> </head> <body> <h3>编辑页面</h3> <form action="" method="post" novalidate> {% csrf_token %} {% for field in form %} <div> {{ field.label }} {{ field }} {{ field.errors.0 }} </div> {% endfor %} <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
4、form组件补充
1、Django内置字段如下:

Field required=True, 是否允许为空 widget=None, HTML插件 label=None, 用于生成Label标签或显示内容 initial=None, 初始值 help_text='', 帮助信息(在标签旁边显示) error_messages=None, 错误信息 {'required': '不能为空', 'invalid': '格式错误'} show_hidden_initial=False, 是否在当前插件后面再加一个隐藏的且具有默认值的插件(可用于检验两次输入是否一直) validators=[], 自定义验证规则 localize=False, 是否支持本地化 disabled=False, 是否可以编辑 label_suffix=None Label内容后缀 CharField(Field) max_length=None, 最大长度 min_length=None, 最小长度 strip=True 是否移除用户输入空白 IntegerField(Field) max_value=None, 最大值 min_value=None, 最小值 FloatField(IntegerField) ... DecimalField(IntegerField) max_value=None, 最大值 min_value=None, 最小值 max_digits=None, 总长度 decimal_places=None, 小数位长度 BaseTemporalField(Field) input_formats=None 时间格式化 DateField(BaseTemporalField) 格式:2015-09-01 TimeField(BaseTemporalField) 格式:11:12 DateTimeField(BaseTemporalField)格式:2015-09-01 11:12 DurationField(Field) 时间间隔:%d %H:%M:%S.%f ... RegexField(CharField) regex, 自定制正则表达式 max_length=None, 最大长度 min_length=None, 最小长度 error_message=None, 忽略,错误信息使用 error_messages={'invalid': '...'} EmailField(CharField) ... FileField(Field) allow_empty_file=False 是否允许空文件 ImageField(FileField) ... 注:需要PIL模块,pip3 install Pillow 以上两个字典使用时,需要注意两点: - form表单中 enctype="multipart/form-data" - view函数中 obj = MyForm(request.POST, request.FILES) URLField(Field) ... BooleanField(Field) ... NullBooleanField(BooleanField) ... ChoiceField(Field) ... choices=(), 选项,如:choices = ((0,'上海'),(1,'北京'),) required=True, 是否必填 widget=None, 插件,默认select插件 label=None, Label内容 initial=None, 初始值 help_text='', 帮助提示 ModelChoiceField(ChoiceField) ... django.forms.models.ModelChoiceField queryset, # 查询数据库中的数据 empty_label="---------", # 默认空显示内容 to_field_name=None, # HTML中value的值对应的字段 limit_choices_to=None # ModelForm中对queryset二次筛选 ModelMultipleChoiceField(ModelChoiceField) ... django.forms.models.ModelMultipleChoiceField TypedChoiceField(ChoiceField) coerce = lambda val: val 对选中的值进行一次转换 empty_value= '' 空值的默认值 MultipleChoiceField(ChoiceField) ... TypedMultipleChoiceField(MultipleChoiceField) coerce = lambda val: val 对选中的每一个值进行一次转换 empty_value= '' 空值的默认值 ComboField(Field) fields=() 使用多个验证,如下:即验证最大长度20,又验证邮箱格式 fields.ComboField(fields=[fields.CharField(max_length=20), fields.EmailField(),]) MultiValueField(Field) PS: 抽象类,子类中可以实现聚合多个字典去匹配一个值,要配合MultiWidget使用 SplitDateTimeField(MultiValueField) input_date_formats=None, 格式列表:['%Y--%m--%d', '%m%d/%Y', '%m/%d/%y'] input_time_formats=None 格式列表:['%H:%M:%S', '%H:%M:%S.%f', '%H:%M'] FilePathField(ChoiceField) 文件选项,目录下文件显示在页面中 path, 文件夹路径 match=None, 正则匹配 recursive=False, 递归下面的文件夹 allow_files=True, 允许文件 allow_folders=False, 允许文件夹 required=True, widget=None, label=None, initial=None, help_text='' GenericIPAddressField protocol='both', both,ipv4,ipv6支持的IP格式 unpack_ipv4=False 解析ipv4地址,如果是::ffff:192.0.2.1时候,可解析为192.0.2.1, PS:protocol必须为both才能启用 SlugField(CharField) 数字,字母,下划线,减号(连字符) ... UUIDField(CharField) uuid类型 ...
2、Django内置插件:

TextInput(Input)
NumberInput(TextInput)
EmailInput(TextInput)
URLInput(TextInput)
PasswordInput(TextInput)
HiddenInput(TextInput)
Textarea(Widget)
DateInput(DateTimeBaseInput)
DateTimeInput(DateTimeBaseInput)
TimeInput(DateTimeBaseInput)
CheckboxInput
Select
NullBooleanSelect
SelectMultiple
RadioSelect
CheckboxSelectMultiple
FileInput
ClearableFileInput
MultipleHiddenInput
SplitDateTimeWidget
SplitHiddenDateTimeWidget
SelectDateWidget
3、常用选择插件:

# 单radio,值为字符串 # user = fields.CharField( # initial=2, # widget=widgets.RadioSelect(choices=((1,'上海'),(2,'北京'),)) # ) # 单radio,值为字符串 # user = fields.ChoiceField( # choices=((1, '上海'), (2, '北京'),), # initial=2, # widget=widgets.RadioSelect # ) # 单select,值为字符串 # user = fields.CharField( # initial=2, # widget=widgets.Select(choices=((1,'上海'),(2,'北京'),)) # ) # 单select,值为字符串 # user = fields.ChoiceField( # choices=((1, '上海'), (2, '北京'),), # initial=2, # widget=widgets.Select # ) # 多选select,值为列表 # user = fields.MultipleChoiceField( # choices=((1,'上海'),(2,'北京'),), # initial=[1,], # widget=widgets.SelectMultiple # ) # 单checkbox # user = fields.CharField( # widget=widgets.CheckboxInput() # ) # 多选checkbox,值为列表 # user = fields.MultipleChoiceField( # initial=[2, ], # choices=((1, '上海'), (2, '北京'),), # widget=widgets.CheckboxSelectMultiple # )
form组件补充:
get请求的时候,render的时候可以自己渲染,也可以用form组件渲染,只要input的name属性值和form组件的字段值一致性就可以。在post请求的时候,把对应字段上传到
后端,也就是把request.POST这个参数传给form=BookForm(request.POST),这样的就拿到了数据,无论你上传了多少数据,(包含CSRF_TOKEN),form都不管,只拿对应
字段的值匹配,只要全部取到并且通过了自定义的验证规则就是干净数据(cleaned_data),如果少了一个字段或者规则没有校验过去,那么就是errors信息。
3、modleForm组件(主题来了)
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/7614921.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/8034442.html
1、modleform组件
使用modelform组件,相比于form组件功能更加的强大。
1.modelform 组件
中间转换的组件, 不用自己去写form组件。
将模型表转换成, 具体的form组件。
注意:这里只需要告诉这个组件,你要对哪张表做一个form验证,然后field可以校验的字段。
labels,widgets,error_message等都可以进行添加。form有的modelForm组件都有。
modelform
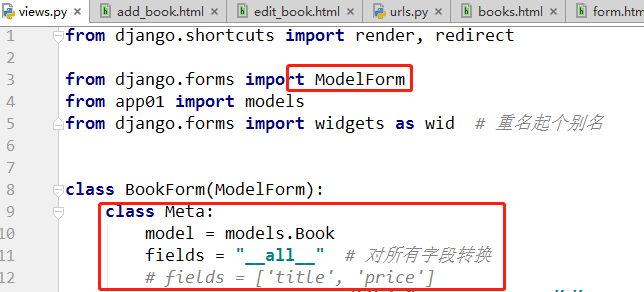
class BookForm(ModelForm): class Meta: model=models.Book fields="__all__" labels={ "title":"书籍名称", "price":"价格", "date":"日期", "publish":"出版社", "authors":"作者", } widgets={ "title":wid.TextInput(attrs={"class":"form-control"}), "price": wid.TextInput(attrs={"class": "form-control"}), "date": wid.TextInput(attrs={"class": "form-control"}), }
2.fields
3.一对多,多对多,不用考虑! form.save()
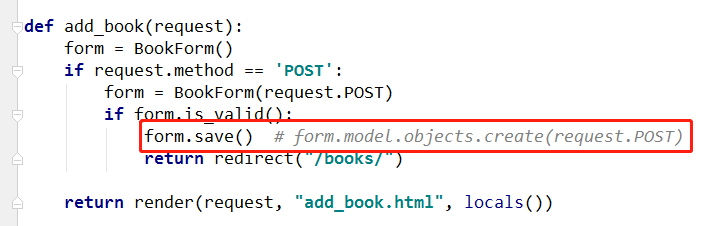
4.BookForm(instance=edit_book) # 接收一个对象
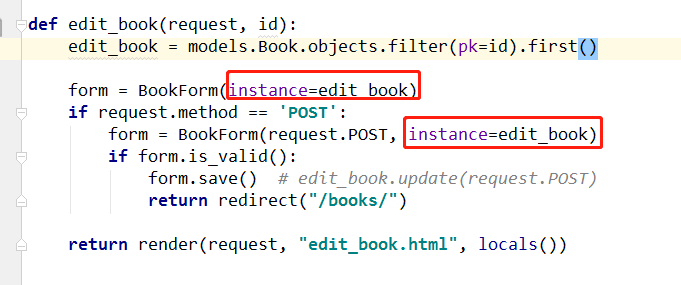
5、 {{ field.label }}{{ field }} {{ field.errors.0 }}
6、扩展modleform
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/8034442.html

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect from django.forms import ModelForm # Create your views here. from app01 import models def test(request): # model_form = models.Student model_form = models.Student.objects.all() return render(request,'test.html',{'model_form':model_form}) class StudentList(ModelForm): class Meta: model = models.Student #对应的Model中的类 fields = "__all__" #字段,如果是__all__,就是表示列出所有的字段 exclude = None #排除的字段 labels = None #提示信息 help_texts = None #帮助提示信息 widgets = None #自定义插件 error_messages = None #自定义错误信息 #error_messages用法: error_messages = { 'name':{'required':"用户名不能为空",}, 'age':{'required':"年龄不能为空",}, } #widgets用法,比如把输入用户名的input框给为Textarea #首先得导入模块 from django.forms import widgets as wid #因为重名,所以起个别名 widgets = { "name":wid.Textarea } #labels,自定义在前端显示的名字 labels= { "name":"用户名" } def student(request): if request.method == 'GET': student_list = StudentList() return render(request,'student.html',{'student_list':student_list}) else: student_list = StudentList(request.POST) if student_list.is_valid(): student_list.save() return render(request,'student.html',{'student_list':student_list}) def student_edit(request,pk): obj = models.Student.objects.filter(pk=pk).first() if not obj: return redirect('test') if request.method == "GET": student_list = StudentList(instance=obj) return render(request,'student_edit.html',{'student_list':student_list}) else: student_list = StudentList(request.POST,instance=obj) if student_list.is_valid(): student_list.save() return render(request,'student_edit.html',{'student_list':student_list}) 扩展 modelform
7、modle.EmialField()
models.CharFiled()
models.EmailField() # 为什么,不写charField? 因为在使用 modelForm 时,可以校验!!这时EmailField才有意义!
eg:
models.URLField
models.UUIDField
这里对用法具体做一些注释
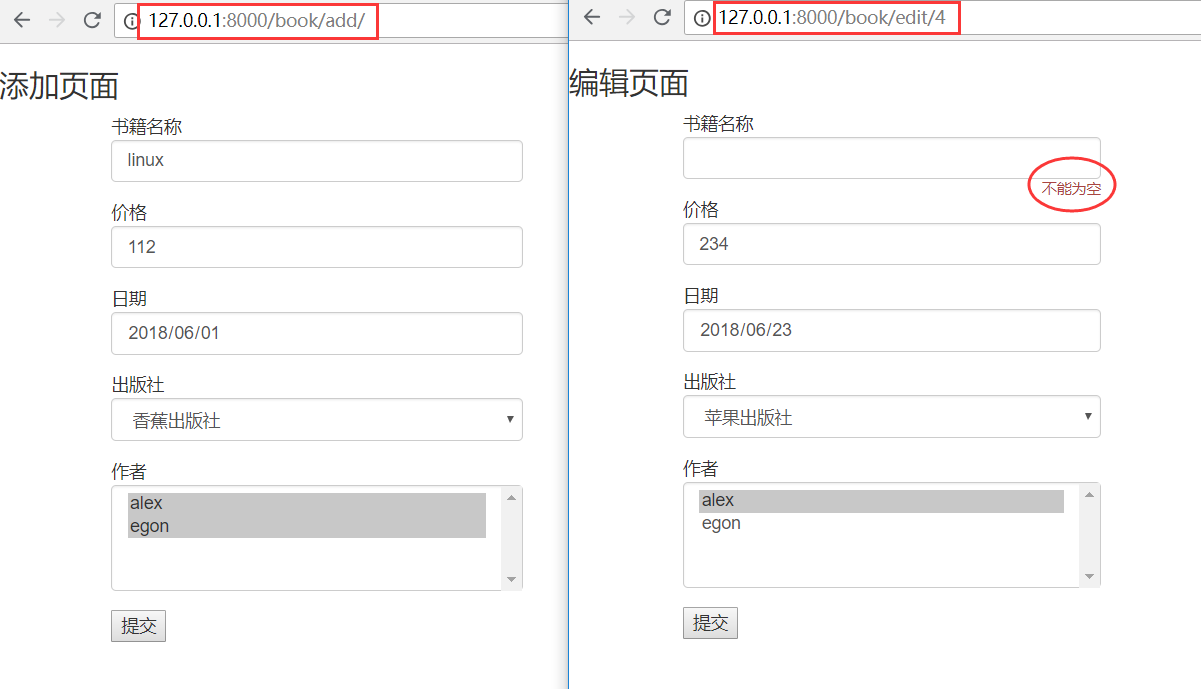
def book(request): book_list=models.Book.objects.all() return render(request,"books.html",locals()) def addbook(request): if request.method == "POST": form=BookForm(request.POST) if form.is_valid(): #通过验证直接form.save()就可以进行添加了。 form.save() return redirect("/books/") form = BookForm() return render(request,"add.html",locals())
如果是编辑的话:
def editbook(request,edit_book_id): edit_book = models.Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).first() print(edit_book) if request.method == "POST": #这里进行编辑的时候需要注意的是需要加一个参数instance=编辑对象 #告诉modelForm 对哪张表进行一个修改,不加这个参数就会变成添加而不是修改。 form=BookForm(request.POST,instance=edit_book) if form.is_valid(): form.save() return redirect("/books/") #这里加这个参数的意思是取到对应编辑对象的值放到input框内。 form=BookForm(instance=edit_book) return render(request,"edit.html",locals())
最后就是一个简单的删除
def delbook(request,del_book_id): models.Book.objects.filter(id=del_book_id).delete() return redirect("/books/")
8、code
views

from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse,redirect # Create your views here. from .models import * from django.forms import ModelForm from django.forms import widgets as wid # 因为重名,所以起个别名! wid_text = wid.TextInput(attrs={'class':'form-control'}) required_msg = {'required':'不能为空'} class BookForm(ModelForm): class Meta: model = Book fields = "__all__" # 对所有字段转换 # fields = ['title','price'] labels = {"title":"书籍名称","price":"价格","date":"日期","publish":"出版社","authors":"作者"} widgets = { 'title':wid_text, 'price':wid_text, 'date':wid.TextInput(attrs={'class':'form-control','type':'date'}), 'publish':wid.Select(attrs={'class':'form-control'}), 'authors':wid.SelectMultiple(attrs={'class':'form-control'}) } error_messages = { 'title':required_msg, 'price':required_msg, 'date':{'required':'不能为空','invalid':'格式错误'}, 'publish':required_msg, 'authors':required_msg, } def books(request): book_list = Book.objects.all() return render(request,'books.html',locals()) def addbook(request): form = BookForm() if request.method == 'POST': form = BookForm(request.POST) if form.is_valid(): form.save() # form.model.objects.create(request.POST) return redirect('/books/') return render(request,'add.html',locals()) def editbook(request, edit_book_id): edit_book = Book.objects.filter(pk=edit_book_id).first() form = BookForm(instance=edit_book) if request.method == 'POST': form = BookForm(request.POST,instance=edit_book) if form.is_valid(): form.save() # edit_book.update(request.POST) return redirect('/books/') return render(request, 'edit.html', locals())
add.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!-- 最新版本的 Bootstrap 核心 CSS 文件 --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-BVYiiSIFeK1dGmJRAkycuHAHRg32OmUcww7on3RYdg4Va+PmSTsz/K68vbdEjh4u" crossorigin="anonymous"> </head> <body> <h3>添加页面</h3> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-1"> {% include 'form.html' %} </div> </div> </body> </html> add.html
edit

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <!-- 最新版本的 Bootstrap 核心 CSS 文件 --> <link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-BVYiiSIFeK1dGmJRAkycuHAHRg32OmUcww7on3RYdg4Va+PmSTsz/K68vbdEjh4u" crossorigin="anonymous"> </head> <body> <h3>编辑页面</h3> <div class="row"> <div class="col-md-4 col-md-offset-1"> {% include 'form.html' %} </div> </div> </body> </html>
form.html

<form action="" method="post" novalidate> {% csrf_token %} {% for field in form %} <p> {{ field.label }} {{ field }} <small><span class="pull-right text-danger has-error">{{ field.errors.0 }}</span></small> </p> {% endfor %} <input type="submit"> </form>
4、前端form表单,后台form组件(可以没有数据库)
前端手写一个form表单,后台使用form组件,进行校验,也是可以的!!
注意: <p>名称 <input type="text" name="title"></p> 和 title = forms.CharField()
name和title对应
view.py

from django import forms class BookForms(forms.Form): title = forms.CharField() price = forms.FloatField() def addbook(request): form = BookForms() if request.method == 'POST': form = BookForms(request.POST) # form = BookForm({'title':'php','price':111,'xxx':'egon'}) if form.is_valid(): print('clean_data',form.cleaned_data) # clean_data {'title': '水浒传', 'price': 123.0} else: print('error',form.errors) return render(request,'addbook.html',locals())
addbook.html

<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h3>添加书籍</h3> <form action="" method="post" novalidate> {% csrf_token %} <p>名称 <input type="text" name="title"></p> <p>价格 <input type="text" name="price"></p> <p>xxx <input type="text" name="xxx"></p> <input type="submit"> </form> <form action="" method="post" novalidate> {% csrf_token %} {{ form.as_p }} {{ form.as_table }} {{ form.as_ul }} <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>
5、django补充 - 请求流程
说明:
django 请求流程图--流程最重要!
http协议
请求协议:请求首行,请求头,请求体!
响应协议: 响应首行,响应头,响应体!
我们发给浏览器的响应体(html)是一堆 str 浏览器解析(html)才能看到数据!
render 对templates 模板渲染!
没有模板 就 httpresponse 返回str
打开文件 捕获是否模板语法,嵌入{{}} 数据 返回 html(str) response
只要到了 中间件 交给浏览器的 一定已经是一些 html(str)
1、什么是WSGI?什么是wsgiref?
WSGI(Web Server Common Interface)是专门为Python语言制定的web服务器与应用程序之间的网关接口规范,通俗的来说,只要一个服务器拥有一个实现了WSGI标准规范的模块(例如apache的mod_wsgi模块),那么任意的实现了WSGI规范的应用程序都能与它进行交互。因此,WSGI也主要分为两个程序部分:服务器部分和应用程序部分。
wsgiref则是官方给出的一个实现了WSGI标准用于演示用的简单Python内置库,它实现了一个简单的WSGI Server和WSGI Application(在simple_server模块中),主要分为五个模块:simple_server, util, headers, handlers, validate。
wsgiref源码地址:https://pypi.python.org/pypi/wsgiref
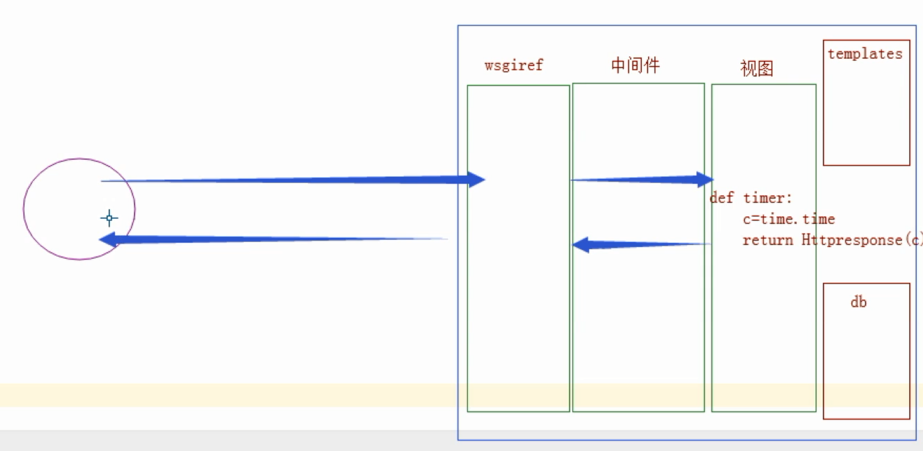
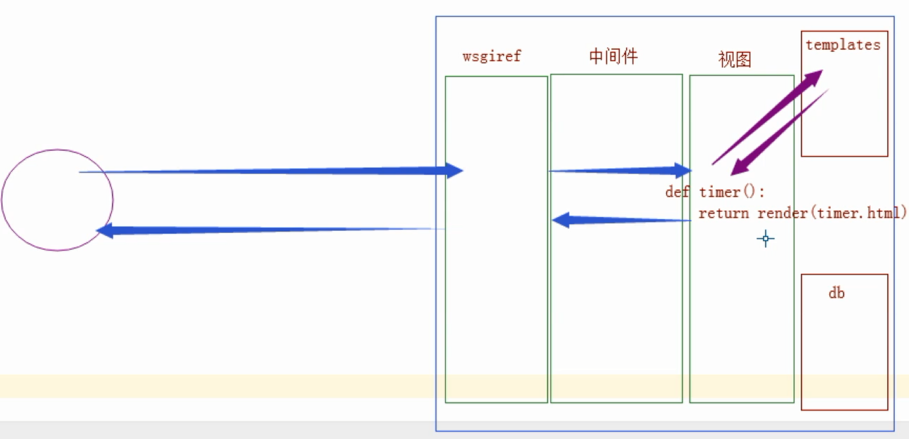
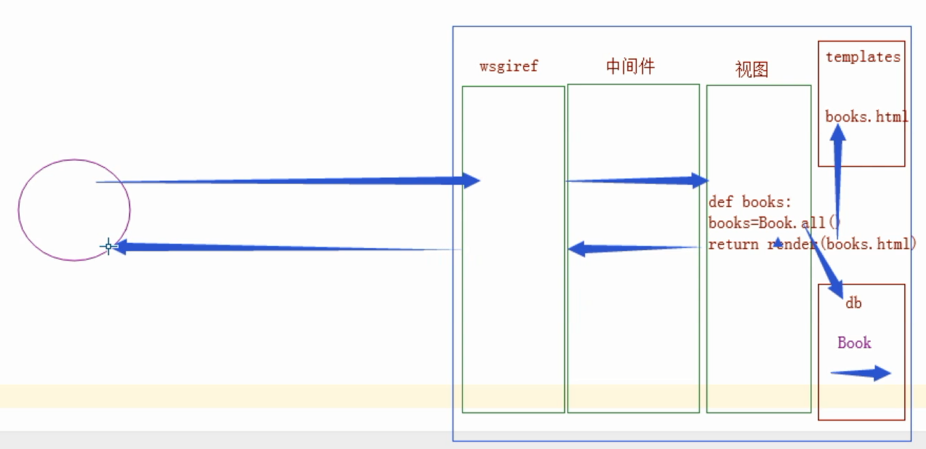
django(render深层原理)
Httprespone方法就相当于把return的字符串给了wsgi,封装成一堆标签字符串,然后返回给浏览器解析。
而render方法,是从template中取到标签字符串,把里面的{{}} ,{% %},这些的模板语法等解析好
变成一个个标签后,然后通过HttpResponse把这堆标签字符串通过wSGI封装好给了浏览器,浏览器只渲染标签语言。{{}},{% %}这些是在后端完成的渲染。
如果跟数据库结合的话,就是视图从数据库取到数据,从模板语言拿到标签字符串,进行一个解析结合。形成一个完整的HTML(处理模板语法),最后把这个还是返回给浏览器。
