3.1 robotic mapping
3.1.1 Introduction
3.1.2 Introduction to mapping
Map and Mapping
(1) map is a spatial model of robot's environment
(2) mapping is a process for building a map
(3) consideration for mapping
- map representation
- avalable sensors
- purpose of mapping
Type of map:
(1) metric map : a localization is represented as a coordinate
(2) topological : Locations are represented as nodes and their connectivity as arcs. Only the connectivity between nodes matter. Graph representation is useful for path planning.
(3) semantic map : semantic map is a map with labels.
What make it challengin?
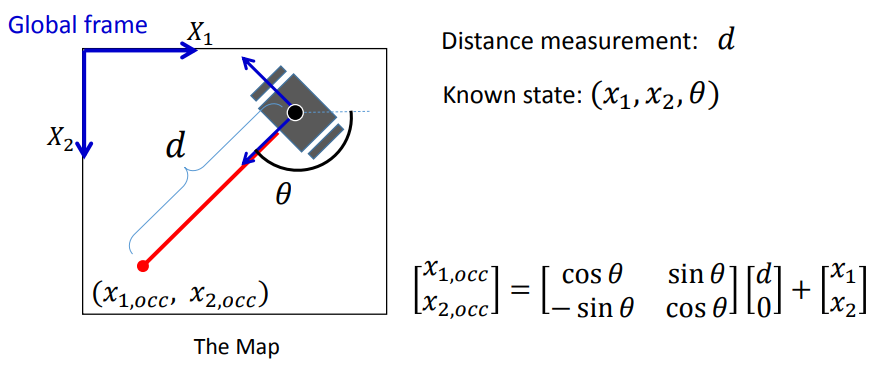
- Noisy measurement in local coordinate
- Motion involved
- Change over time
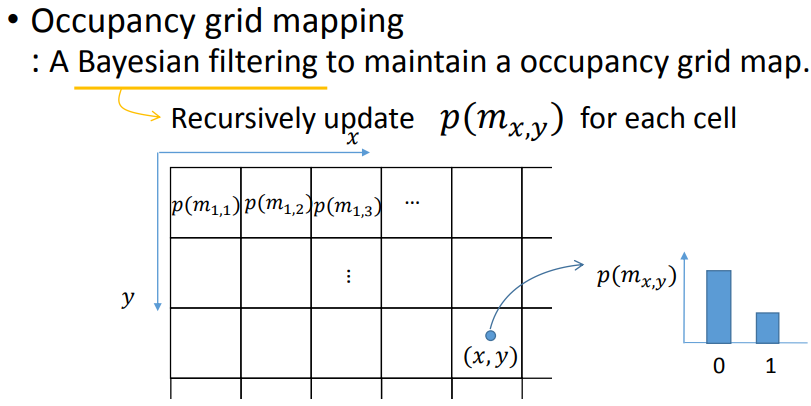
3.2 occupancy grid mapping
3.2.1 occupancy grid map


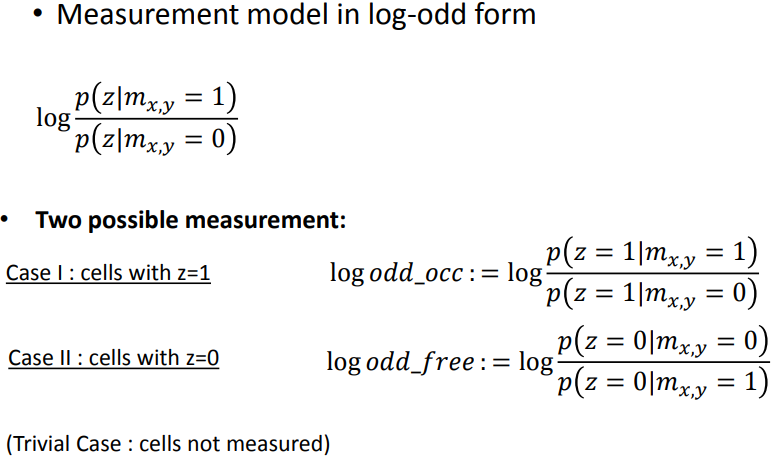
3.2.2 log-odd update
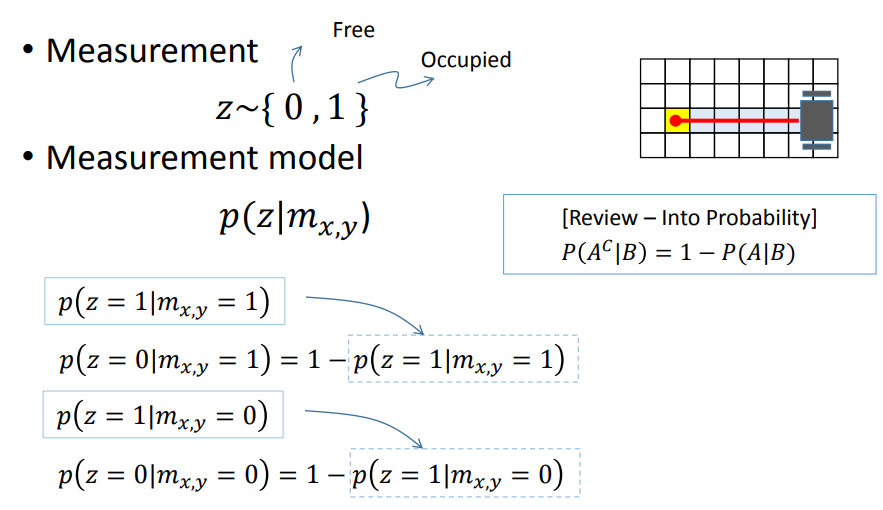
在贝叶斯框架下根据观测模型直接更新每个珊格的占据概率是困难的,引入一个新的变量Odd,赢率,其含义为某件事发生的概率与不发生的概率之比。

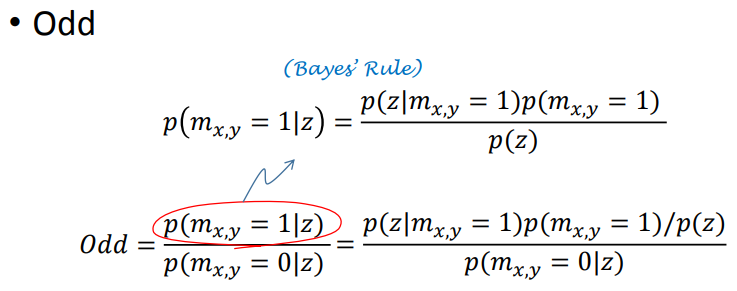
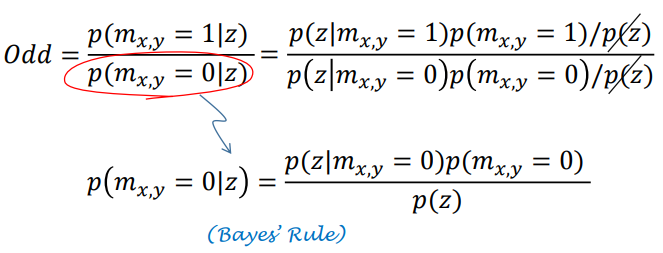
取对数,获得odd的更新方法,即每次观测后都更新先验地图,获得的后验地图将作为下一时刻的先验地图,以此方式不断迭代。
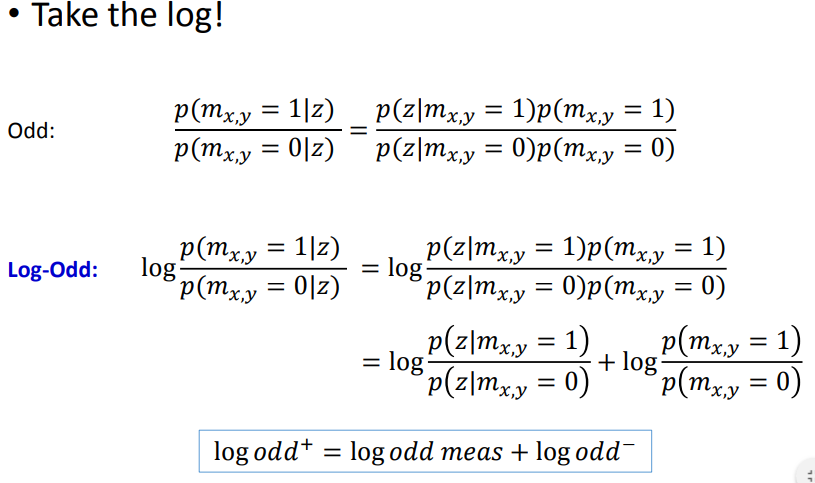
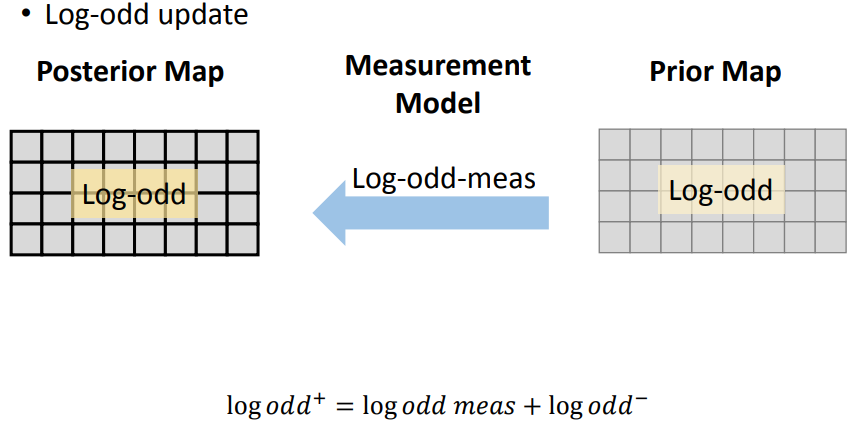
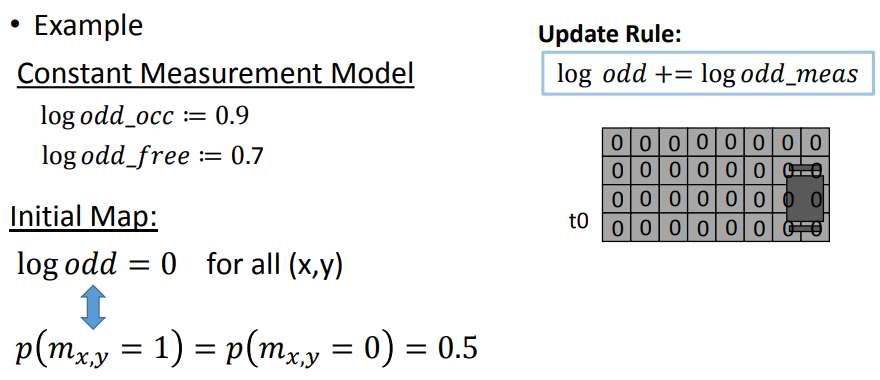
例题:

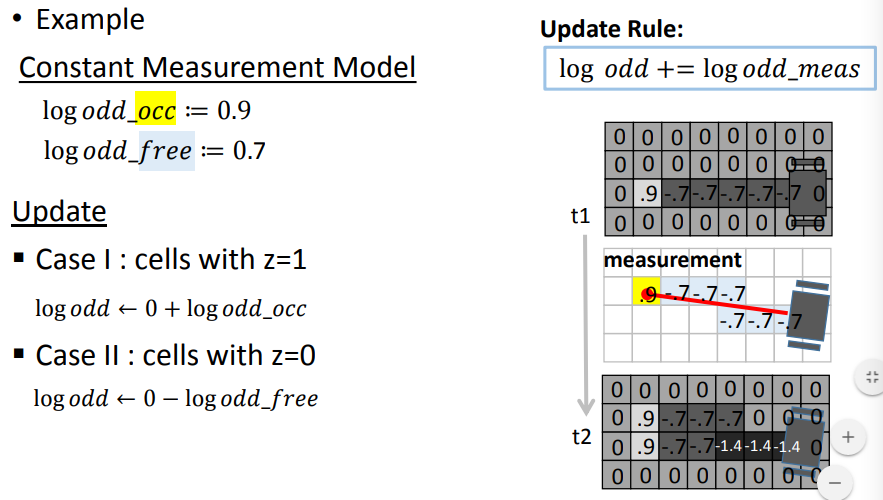
3.2.3 handling range sensor

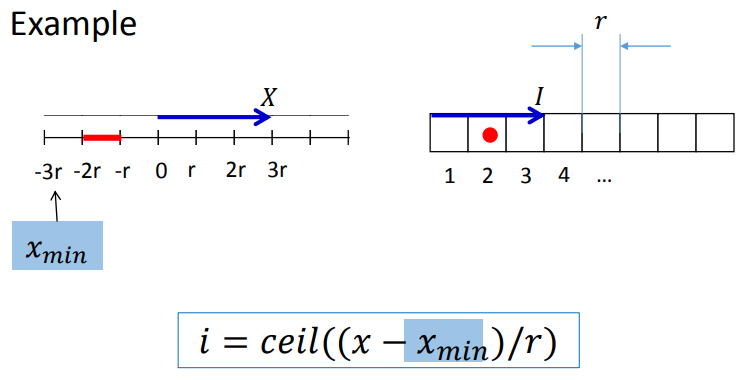
注意,我觉得[2,2]矩阵里面的sin前面不应该加负号

采用Bresenham算法搜寻所有被激光穿过的珊格。
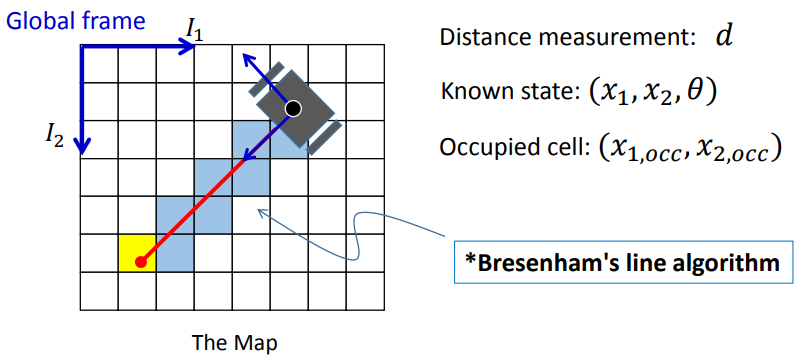
对于多束激光的场景
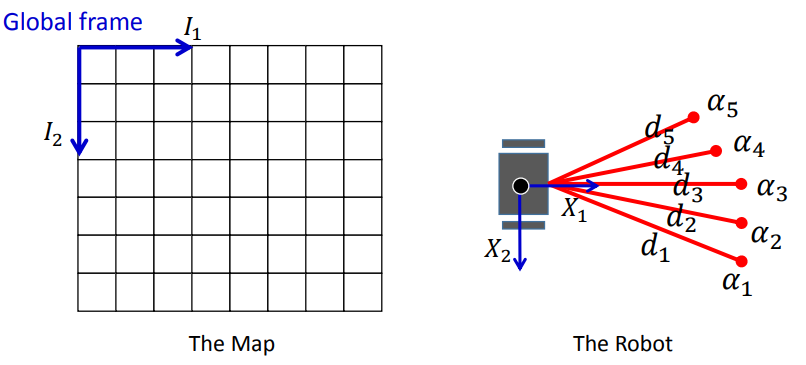

3.2.4 2D occupancy grid mapping
3.3 3D mapping
The pros and cons of map representations
珊格地图的优点是查找方便,计算复杂度小。每次添加新的测量数据,可以计算出新数据所对应的珊格,按珊格索引添加到珊格地图中。

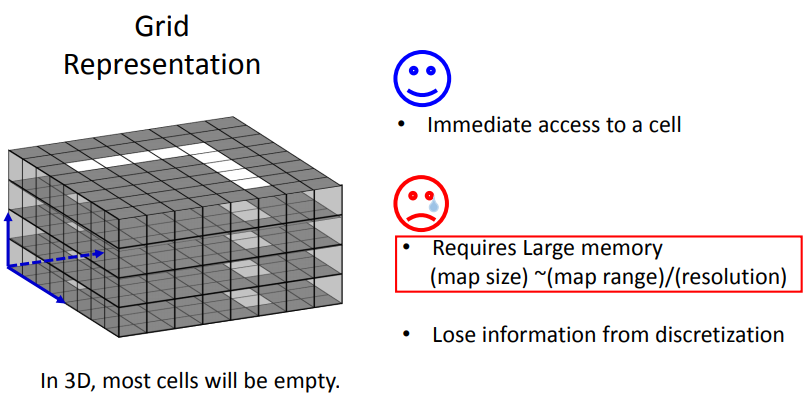
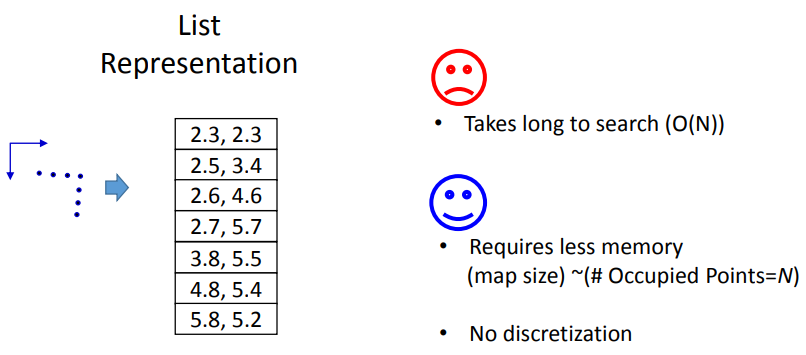

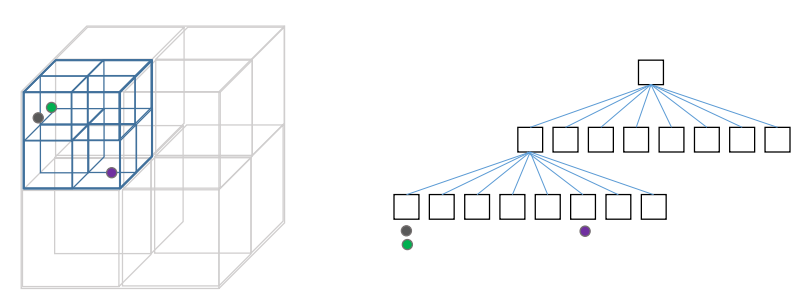
采用”树“数据结构来管理地图数据

kd-tree。视频中把kd-tree介绍的很清楚。
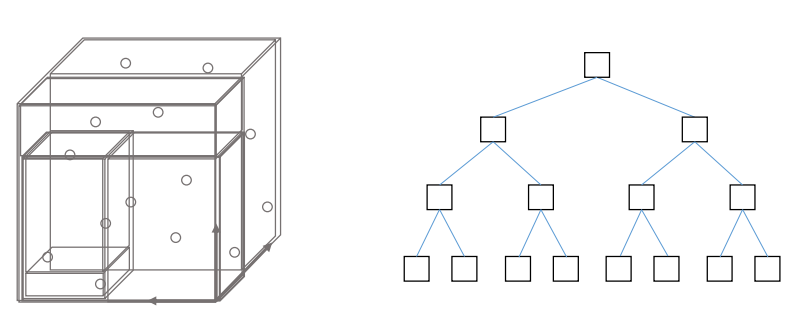
octree