Peter's Hobby
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 56 Accepted Submission(s): 17
Problem Description
Recently, Peter likes to measure the humidity of leaves. He recorded a leaf humidity every day. There are four types of leaves wetness: Dry , Dryish , Damp and Soggy. As we know, the humidity of leaves is affected by the weather. And there are only three kinds
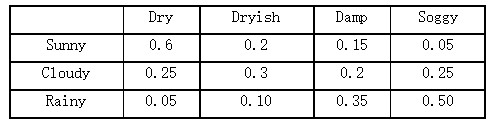
of weather: Sunny, Cloudy and Rainy.For example, under Sunny conditions, the possibility of leaves are dry is 0.6.
Give you the possibility list of weather to the humidity of leaves.
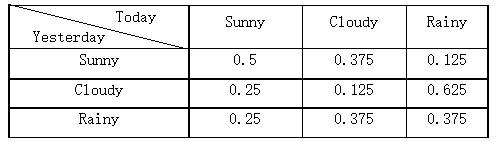
The weather today is affected by the weather yesterday. For example, if yesterday is Sunny, the possibility of today cloudy is 0.375.
The relationship between weather today and weather yesterday is following by table:
Now,Peter has some recodes of the humidity of leaves in N days.And we know the weather conditons on the first day : the probability of sunny is 0.63,the probability of cloudy is 0.17,the probability of rainny is 0.2.Could you know the weathers of these days most probably like in order?
Give you the possibility list of weather to the humidity of leaves.

The weather today is affected by the weather yesterday. For example, if yesterday is Sunny, the possibility of today cloudy is 0.375.
The relationship between weather today and weather yesterday is following by table:

Now,Peter has some recodes of the humidity of leaves in N days.And we know the weather conditons on the first day : the probability of sunny is 0.63,the probability of cloudy is 0.17,the probability of rainny is 0.2.Could you know the weathers of these days most probably like in order?
Input
The first line is T, means the number of cases, then the followings are T cases. for each case:
The first line is a integer n(n<=50),means the number of days, and the next n lines, each line is a string shows the humidity of leaves (Dry, Dryish, Damp, Soggy)
The first line is a integer n(n<=50),means the number of days, and the next n lines, each line is a string shows the humidity of leaves (Dry, Dryish, Damp, Soggy)
Output
For each test case, print the case number on its own line. Then is the most possible weather sequence.( We guarantee that the data has a unique solution)
Sample Input
1 3 Dry Damp Soggy
Sample Output
Case #1: Sunny Cloudy RainyHintLog is useful.
Source
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define N 100
double leave[3][4]={0.6, 0.2, 0.15, 0.05, 0.25, 0.3, 0.2, 0.25, 0.05, 0.10, 0.35, 0.50};
double yt[3][3]={0.5, 0.375, 0.125, 0.25, 0.125, 0.625, 0.25, 0.375, 0.375};
double dp[N][N];
int mark[N][N],ans[N],a[N];
void solve(int x,int y)
{
int i,u;
double max,b;
max=-1;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
b=dp[x-1][i]*yt[i][y]*leave[y][a[x]];
if(b>max)
{
max=b;
u=i;
}
}
dp[x][y]=max;
mark[x][y]=u;
}
void print(int n)
{
int i,x,k;
x=0; k=0;
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
if(dp[n][i]>dp[n][x])
x=i;
}
ans[k++]=x;
for(i=n-1;i>=1;i--)
{
x=mark[i+1][x];
ans[k++]=x;
}
for(i=k-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if(ans[i]==0)
printf("Sunny
");
else if(ans[i]==1)
printf("Cloudy
");
else if(ans[i]==2)
printf("Rainy
");
}
}
int main()
{
int t,cnt=1,i,j,n;
char str[N];
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%s",str);
if(strcmp(str,"Dry")==0)
a[i]=0;
else if(strcmp(str,"Dryish")==0)
a[i]=1;
else if(strcmp(str,"Damp")==0)
a[i]=2;
else
a[i]=3;
}//dp[i][j]表示的是第i天天气是j的概率最大值
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dp[1][0]=0.63*leave[0][a[1]];
dp[1][1]=0.17*leave[1][a[1]];
dp[1][2]=0.2*leave[2][a[1]];
for(i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
solve(i,j);
}
printf("Case #%d:
",cnt++);
print(n);
}
return 0;
}