DZY loves chemistry, and he enjoys mixing chemicals.
DZY has n chemicals, and m pairs of them will react. He wants to pour these chemicals into a test tube, and he needs to pour them in one by one, in any order.
Let's consider the danger of a test tube. Danger of an empty test tube is 1. And every time when DZY pours a chemical, if there are already one or more chemicals in the test tube that can react with it, the danger of the test tube will be multiplied by 2. Otherwise the danger remains as it is.
Find the maximum possible danger after pouring all the chemicals one by one in optimal order.
The first line contains two space-separated integers n and m 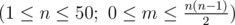 .
.
Each of the next m lines contains two space-separated integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi < yi ≤ n). These integers mean that the chemical xi will react with the chemical yi. Each pair of chemicals will appear at most once in the input.
Consider all the chemicals numbered from 1 to n in some order.
Print a single integer — the maximum possible danger.
1 0
1
2 1 1 2
2
3 2 1 2 2 3
4
In the first sample, there's only one way to pour, and the danger won't increase.
In the second sample, no matter we pour the 1st chemical first, or pour the 2nd chemical first, the answer is always 2.
In the third sample, there are four ways to achieve the maximum possible danger: 2-1-3, 2-3-1, 1-2-3 and 3-2-1 (that is the numbers of the chemicals in order of pouring).
建图,n个化学试剂为点,会反应的连边
非常easy发现,同一连通块。必定存在方案:除了第一个,剩下的都于已取的点的连边
易证该方案最优
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<functional>
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<cctype>
#include<ctime>
using namespace std;
#define For(i,n) for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
#define Fork(i,k,n) for(int i=k;i<=n;i++)
#define Rep(i,n) for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
#define ForD(i,n) for(int i=n;i;i--)
#define RepD(i,n) for(int i=n;i>=0;i--)
#define Forp(x) for(int p=pre[x];p;p=next[p])
#define Lson (x<<1)
#define Rson ((x<<1)+1)
#define MEM(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
#define MEMI(a) memset(a,127,sizeof(a));
#define MEMi(a) memset(a,128,sizeof(a));
#define INF (2139062143)
#define F (100000007)
#define MAXN (50+10)
#define MAXM (MAXN*MAXN+10)
long long mul(long long a,long long b){return (a*b)%F;}
long long add(long long a,long long b){return (a+b)%F;}
long long sub(long long a,long long b){return (a-b+(a-b)/F*F+F)%F;}
typedef long long ll;
int n,m;
int edge[MAXM],next[MAXM],pre[MAXM],siz=1;;
void addedge(int u,int v){edge[++siz]=v;next[siz]=pre[u];pre[u]=siz;}
void addedge2(int u,int v){addedge(u,v);addedge(v,u);}
bool b[MAXN]={0};
int tot=0;
void dfs(int x)
{
tot++;b[x]=1;
Forp(x)
{
int v=edge[p];
if (!b[v]) dfs(v);
}
}
ll ans=1;
int main()
{
// freopen("Chemistry.in","r",stdin);
// freopen(".out","w",stdout);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
For(i,m)
{
int x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&x,&y);
addedge2(x,y);
}
For(i,n)
if (!b[i])
{
tot=0;
dfs(i);
while (tot>1) ans*=2,tot--;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}