融合动态障碍物
简介:考虑怎样把其他节点发布的动态障碍物考虑进来
1.本部分演示了动态障碍物该如何被包含到teb_local_planner中。
2.写一个简单的动态障碍物的发布器publish_dynamic_obstacles.py

#!/usr/bin/env python 2 3 import rospy, math, tf 4 from costmap_converter.msg import ObstacleArrayMsg, ObstacleMsg 5 from geometry_msgs.msg import Point32, QuaternionStamped, Quaternion, TwistWithCovariance 6 from tf.transformations import quaternion_from_euler 7 8 9 def publish_obstacle_msg(): 10 pub = rospy.Publisher('/test_optim_node/obstacles', ObstacleArrayMsg, queue_size=1) 11 rospy.init_node("test_obstacle_msg") 12 13 y_0 = -3.0 14 vel_x = 0.0 15 vel_y = 0.3 16 range_y = 6.0 17 18 obstacle_msg = ObstacleArrayMsg() 19 obstacle_msg.header.stamp = rospy.Time.now() 20 obstacle_msg.header.frame_id = "odom" # CHANGE HERE: odom/map 21 22 # Add point obstacle 23 obstacle_msg.obstacles.append(ObstacleMsg()) 24 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].id = 99 25 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].polygon.points = [Point32()] 26 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].polygon.points[0].x = -1.5 27 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].polygon.points[0].y = 0 28 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].polygon.points[0].z = 0 29 30 yaw = math.atan2(vel_y, vel_x) 31 q = tf.transformations.quaternion_from_euler(0,0,yaw) 32 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].orientation = Quaternion(*q) 33 34 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].velocities.twist.linear.x = vel_x 35 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].velocities.twist.linear.y = vel_y 36 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].velocities.twist.linear.z = 0 37 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].velocities.twist.angular.x = 0 38 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].velocities.twist.angular.y = 0 39 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].velocities.twist.angular.z = 0 40 41 r = rospy.Rate(10) # 10hz 42 t = 0.0 43 while not rospy.is_shutdown(): 44 45 # Vary y component of the point obstacle 46 if (vel_y >= 0): 47 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].polygon.points[0].y = y_0 + (vel_y*t)%range_y 48 else: 49 obstacle_msg.obstacles[0].polygon.points[0].y = y_0 + (vel_y*t)%range_y - range_y 50 51 t = t + 0.1 52 53 pub.publish(obstacle_msg) 54 55 r.sleep() 56 57 58 if __name__ == '__main__': 59 try: 60 publish_obstacle_msg() 61 except rospy.ROSInterruptException: 62 pass
运行:
roslaunch teb_local_planner test_optim_node.launch
roslaunch mypublisher publish_dynamic_obstacles.py
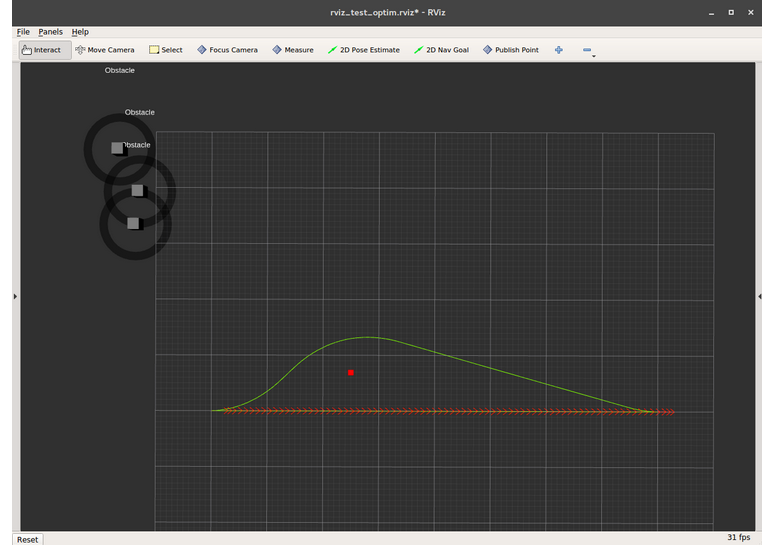
3.设置规划器来考虑动态障碍物
启动rosrun rqt_reconfigure rqt_reconfigure;选中参数include_dynamic_obstacles,teb local planner使用一个常速度模型来预测障碍物将来的行为。现在的轨迹是根据时间和空间来避免障碍物而不是仅仅考当前障碍物的位置来避免。对于速度模型的估计精确性是很重要的,常速度假设是合理且满足的。

如果调节参数visualize_with_time_as_z_axis,可以可视化规划的和预测的速度的时间变化。设置该参数值为0.1。在rviz中的z轴被解释为时间轴,且可被扩展。也可以看到homotopy-class-planning把动态障碍物的预测考虑进去。
相关的参数

~<name>/min_obstacle_dist: Desired minimal distance from (static and dynamic) obstacles ~<name>/inflation_dist: Non-zero cost region around (static) obstacles ~<name>/include_dynamic_obstacles: Specify whether the motion of dynamic obstacles should be included (constant-velocity-model) or not. ~<name>/dynamic_obstacle_inflation_dist: Non-zero cost region around (dynamic) obstacles ~<name>/include_costmap_obstacles: Deactivate costmap obstacles completely ~<name>/costmap_obstacles_behind_robot_dist: Maximum distance behind the robot searched for occupied costmap cells. ~<name>/obstacle_poses_affected: Specify how many trajectory configurations/poses should be taken into account next to the closest one. ~<name>/weight_obstacle: Optimization weight for keeping a distance to static obstacles. ~<name>/weight_inflation: Optimization weight for inflation costs of static obstacles. ~<name>/weight_dynamic_obstacle: Optimization weight for keeping a distance to dynamic obstacles. ~<name>/weight_dynamic_obstacle_inflation: Optimization weight for inflation costs of dynamic obstacles. ~<name>/footprint_model: The robot footprint model
