最后更新: 2017-10-22
一、Python机器学习的库:scikit-learn
- 简单高效的数据挖掘和机器学习分析
- 对所有用户开放,根据不同需求高度可重用性
- 基于Numpy, SciPy和matplotlib
- 开源,商用级别:获得 BSD许可
安装 scikit-learn 自行 Google
二、实战
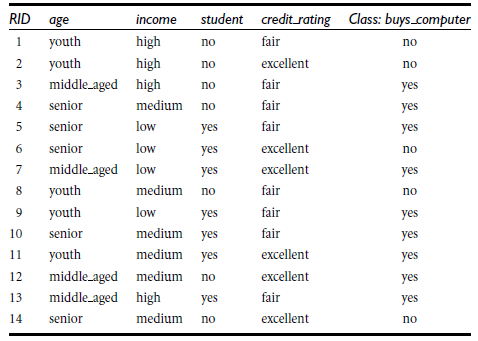
参考: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/tree.html
源码:
import csv
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn import tree
from sklearn.externals.six import StringIO
# Read in the csv file and put features into list of dict and list of class label
allElectronicsData = open('AllElectronics.csv', 'r')
reader = csv.reader(allElectronicsData)
featureList = []
labelList = []
with open('AllElectronics.csv', 'r') as csvfile:
reader = csv.reader(csvfile)
# 获得所有的头部属性
headers = next(reader)
for row in reader:
# 将每一行的结果取出来
labelList.append(row[len(row)-1])
# 将对应的属性生成字典存起来, 第一列 是 RID, 不需要
rowDict = {}
for i in range(1, len(row)-1):
rowDict[headers[i]] = row[i]
featureList.append(rowDict)
print(featureList)
# Vetorize features
vec = DictVectorizer()
dummyX = vec.fit_transform(featureList).toarray()
# 按照 get_feature_names 获取的属性去生成对应的 矩阵
# ['age=middle_aged', 'age=senior', 'age=youth', 'credit_rating=excellent', 'credit_rating=fair', 'income=high', 'income=low', 'income=medium', 'student=no', 'student=yes']
print(vec.get_feature_names())
print(dummyX)
print("labelList: " + str(labelList))
# # vectorize class labels
# 将结果集
lb = preprocessing.LabelBinarizer()
dummyY = lb.fit_transform(labelList)
print("dummyY: " + str(dummyY))
# Using decision tree for classification
# clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
# 按照什么属性来设置对对应的算法
# 可以参考: http://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/tree.html
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
clf = clf.fit(dummyX, dummyY)
print("clf: " + str(clf))
# # Visualize model
with open("allElectronicInformationGainOri.dot", 'w') as f:
f = tree.export_graphviz(clf, feature_names=vec.get_feature_names(), out_file=f)
# 修改一个值 来预测
oneRowX = dummyX[0, :]
print("oneRowX: " + str(oneRowX))
newRowX = oneRowX
newRowX[0] = 1
newRowX[2] = 0
print("newRowX: " + str(newRowX))
predictedY = clf.predict([newRowX])
print("predictedY: " + str(predictedY))