XGBoost API
参数
可以参考官方文档,比较清晰,多做几个demo,应该就记住了,
分类问题
这个demo是datacamp上面的使用的不是原生xgb而是sklearn接口的xgb,目前很多人是推荐使用接口的
我 先来看一下原生的和使用接口的有什么区别
使用逻辑回归
# Import xgboost
import xgboost as xgb
# Create arrays for the features and the target: X, y
#备注一下这个X是从第一列到倒数第二列,y是最后一列,哈哈,因为原来对slice的概念没熟透
X, y = churn_data.iloc[:,:-1], churn_data.iloc[:,-1]
# Create the training and test sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test= train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=123)
# Instantiate the XGBClassifier: xg_cl
#以逻辑回归定义损失函数
xg_cl = xgb.XGBClassifier(objective='binary:logistic', n_estimators=10, seed=123)
# Fit the classifier to the training set
xg_cl.fit(X_train,y_train)
# Predict the labels of the test set: preds
preds = xg_cl.predict(X_test)
# Compute the accuracy: accuracy
#做的是样本精度评估
accuracy = float(np.sum(preds==y_test))/y_test.shape[0]
print("accuracy: %f" % (accuracy))
<script.py> output:
accuracy: 0.743300
使用交叉验证划分数据集
# Create arrays for the features and the target: X, y
X, y = churn_data.iloc[:,:-1], churn_data.iloc[:,-1]
# Create the DMatrix from X and y: churn_dmatrix
churn_dmatrix = xgb.DMatrix(data=X, label=y)
# Create the parameter dictionary: params
params = {"objective":"reg:logistic", "max_depth":3}
# Perform cross-validation: cv_results
cv_results = xgb.cv(dtrain=churn_dmatrix, params=params,
nfold=3, num_boost_round=5,
metrics="error", as_pandas=True, seed=123)
# Print cv_results
print(cv_results)
# Print the accuracy
print(((1-cv_results["test-error-mean"]).iloc[-1]))
<script.py> output:
train-error-mean train-error-std test-error-mean test-error-std
0 0.28232 0.002366 0.28378 0.001932
1 0.26951 0.001855 0.27190 0.001932
2 0.25605 0.003213 0.25798 0.003963
3 0.25090 0.001845 0.25434 0.003827
4 0.24654 0.001981 0.24852 0.000934
0.75148
使用AUC评价分类效果
# Perform cross_validation: cv_results
cv_results = xgb.cv(dtrain=churn_dmatrix, params=params,
nfold=3, num_boost_round=5,
metrics="auc", as_pandas=True, seed=123)
# Print cv_results
print(cv_results)
# Print the AUC
print((cv_results["test-auc-mean"]).iloc[-1])
<script.py> output:
train-auc-mean train-auc-std test-auc-mean test-auc-std
0 0.768893 0.001544 0.767863 0.002820
1 0.790864 0.006758 0.789157 0.006846
2 0.815872 0.003900 0.814476 0.005997
3 0.822959 0.002018 0.821682 0.003912
4 0.827528 0.000769 0.826191 0.001937
0.826191
分类问题一般都是测试结果的准确程度
回归问题一般是用mse,rmse测试结果的误差
回归问题
线性分类器liner
# Create the training and test sets
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X,y, test_size=0.2, random_state=123)
# Instantiate the XGBRegressor: xg_reg
xg_reg = xgb.XGBRegressor(objective="reg:linear",n_estimators=10,booster="gbtree",seed=123)
# Fit the regressor to the training set
xg_reg.fit(X_train,y_train)
# Predict the labels of the test set: preds
preds = xg_reg.predict(X_test)
# Compute the rmse: rmse
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test, preds))
print("RMSE: %f" % (rmse))
<script.py> output:
[08:39:03] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
RMSE: 78847.401758
# Convert the training and testing sets into DMatrixes: DM_train, DM_test
DM_train = xgb.DMatrix(data=X_train, label=y_train)
DM_test = xgb.DMatrix(data=X_test, label=y_test)
# Create the parameter dictionary: params
params = {"booster":"gblinear", "objective":"reg:linear"}
# Train the model: xg_reg
xg_reg = xgb.train(params = params, dtrain=DM_train, num_boost_round=5)
# Predict the labels of the test set: preds
preds = xg_reg.predict(DM_test)
# Compute and print the RMSE
rmse = np.sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_test,preds))
print("RMSE: %f" % (rmse))
<script.py> output:
[08:43:38] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
RMSE: 44267.430424
# Create the DMatrix: housing_dmatrix
housing_dmatrix = xgb.DMatrix(data=X,label=y)
# Create the parameter dictionary: params
params = {"objective":"reg:linear", "max_depth":4}
# Perform cross-validation: cv_results
cv_results = xgb.cv(dtrain=housing_dmatrix, params=params, nfold=4, num_boost_round=5, metrics="rmse", as_pandas=True, seed=123)
# Print cv_results
print(cv_results)
# Extract and print final round boosting round metric
print((cv_results["test-rmse-mean"]).tail(1))
<script.py> output:
[08:46:00] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[08:46:00] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[08:46:00] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[08:46:00] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
train-rmse-mean train-rmse-std test-rmse-mean test-rmse-std
0 141767.535156 429.442896 142980.433594 1193.789595
1 102832.541015 322.467623 104891.392578 1223.157953
2 75872.617188 266.473250 79478.937500 1601.344539
3 57245.650391 273.625907 62411.924804 2220.148314
4 44401.295899 316.422824 51348.281250 2963.379118
4 51348.28125
Name: test-rmse-mean, dtype: float64
均方误差评估模型
# Create the DMatrix: housing_dmatrix
housing_dmatrix = xgb.DMatrix(data=X,label=y)
# Create the parameter dictionary: params
params = {"objective":"reg:linear", "max_depth":4}
# Perform cross-validation: cv_results
cv_results = xgb.cv(dtrain=housing_dmatrix, params=params, nfold=4, num_boost_round=5, metrics="mae", as_pandas=True, seed=123)
# Print cv_results
print(cv_results)
# Extract and print final round boosting round metric
print((cv_results["test-mae-mean"]).tail(1))
<script.py> output:
[08:49:31] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[08:49:31] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[08:49:31] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[08:49:31] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
train-mae-mean train-mae-std test-mae-mean test-mae-std
0 127343.570313 668.341212 127633.990235 2403.991706
1 89770.056640 456.949630 90122.496093 2107.910017
2 63580.791016 263.405561 64278.561524 1887.563581
3 45633.141601 151.886070 46819.167969 1459.813514
4 33587.090821 87.001007 35670.651367 1140.608182
4 35670.651367
Name: test-mae-mean, dtype: float64
使用正则化
# Create the DMatrix: housing_dmatrix
housing_dmatrix = xgb.DMatrix(data=X, label=y)
reg_params = [1, 10, 100]
# Create the initial parameter dictionary for varying l2 strength: params
params = {"objective":"reg:linear","max_depth":3}
# Create an empty list for storing rmses as a function of l2 complexity
rmses_l2 = []
# Iterate over reg_params
for reg in reg_params:
# Update l2 strength
params["lambda"] = reg
# Pass this updated param dictionary into cv
cv_results_rmse = xgb.cv(dtrain=housing_dmatrix, params=params, nfold=2, num_boost_round=5, metrics="rmse", as_pandas=True, seed=123)
# Append best rmse (final round) to rmses_l2
rmses_l2.append(cv_results_rmse["test-rmse-mean"].tail(1).values[0])
# Look at best rmse per l2 param
print("Best rmse as a function of l2:")
print(pd.DataFrame(list(zip(reg_params, rmses_l2)), columns=["l2","rmse"]))
<script.py> output:
[09:41:04] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[09:41:04] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[09:41:04] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[09:41:04] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[09:41:04] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
[09:41:04] WARNING: /workspace/src/objective/regression_obj.cu:152: reg:linear is now deprecated in favor of reg:squarederror.
Best rmse as a function of l2:
l2 rmse
0 1 52275.357421
1 10 57746.064453
2 100 76624.628907
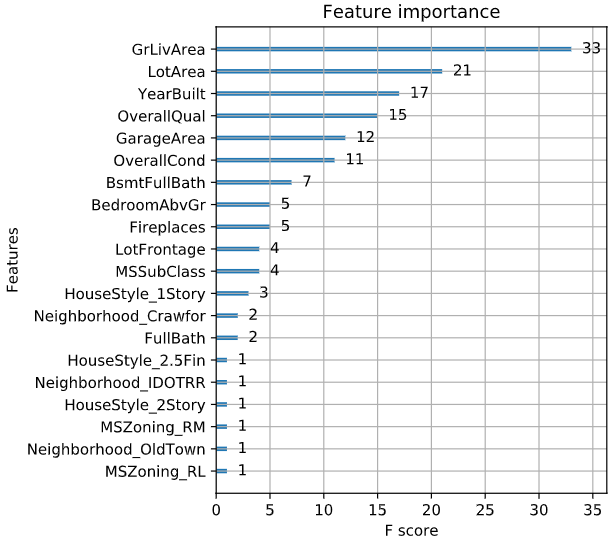
可视化
xgb.plot_tree
xgb.plot_importance
# Create the DMatrix: housing_dmatrix
housing_dmatrix = xgb.DMatrix(data=X, label=y)
# Create the parameter dictionary: params
params = {"objective":"reg:linear", "max_depth":4}
# Train the model: xg_reg
xg_reg = xgb.train(params=params, dtrain=housing_dmatrix, num_boost_round=10)
# Plot the feature importances
xgb.plot_importance(xg_reg)
plt.show()