流:
1、IO流是用来处理设备之间的数据传输
2、Java对数据的操作是通过流的方式
3、Java用于流的操作都在io 包
4、流按照流向分为:输入流,输出流 输入读,输出写
5、流按操作分为:
字节流:字节流可以操作任何数据,因为在计算机里面任何数据都是以字节的形式存储
字符流:字符流只能操作纯字符数据,比较方法
IO流常用的父类:
字节流的抽象父类:
InputStream,OutputStream
字符流的抽象父类:
Reader,Writer
字节流:
操作一:读取文件内容
1:创建输入字节流子类对象
2:调用read()方法一个一个字节读取内容(不推荐使用)
//1.一个一个字节的读取
public static void myRead() throws IOException{
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("F:/hello.txt");
int i;
while((i = is.read())!=-1){
System.out.println((char)i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception{
myRead();
}
3:调用read(byte[])的方法将内容读取到数组中,数组大小可以是流的.available()方法获取到的长度,但是此方法弊端是会造成内存溢出。(也不推荐使用)
//2.每次读取is.available() 可能内存溢出
//is.read(buffer) 将流的数据读到数组中
public static void myRead() throws Exception{
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("F:/hello.txt");
//2-1定义文件有效长度的一个字节数组
byte[] b = new byte [is.available()];
int i;
String str = null;
//2-2将内容读到字节数组
is.read(b);
//2-3将数组内容转化成字符串
str = new String(b);
System.out.println(str);
}
4:调用read(byte[])的方法将内容读取到数组中,数组大小可以定义成1024的倍数,(推荐使用)
//3.定义一个字节数组
//read(byte[]):从输入流读取一定数量的字节,并将其储存到缓冲区数组b中,以整数形式返回实际读取的字节数
public static void myRead() throws Exception{
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("F:/hello.txt");
int i;
String str = null;
byte[] b = new byte[4*1024];
while((i = is.read(b))!=-1){
str = new String(b,0,i);
System.out.print(str);
}
}
5:使用BufferedInputStream缓冲流进行读写
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("F:/hello.txt");
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);
byte[] b = new byte[4*1024];
int i;
String str = null;
while ((i = bis.read(b))!=-1){
str = new String(b,0,i);
}
System.out.println(str);
操作二:
将内容写入文件:创建输出流对象子类
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("F:/aaa.txt");
String str = "asdfghjkl";
byte [] b = str.getBytes();
fos.write(b);
fos.flush();
操作三:文本复制
public static void copytxt() throws Exception{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("F:/aaa.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("F:/hello.txt");
int i;
byte [] b = new byte[2*1024];
while((i = fis.read(b))!=-1){
fos.write(b);
}
}
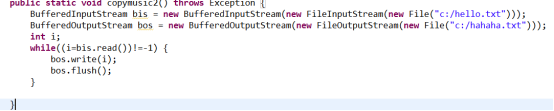
操作四:音乐拷贝,可以使用普通输入输出流,可以使用缓冲流
字符流:操作纯文本数据
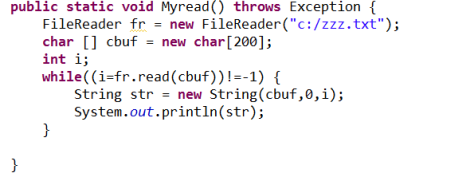
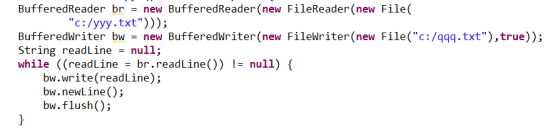
操作一:读取文件
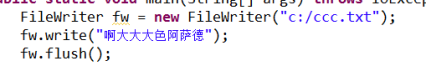
操作二:写内容到文件
操作三:文件拷贝 普通字符流

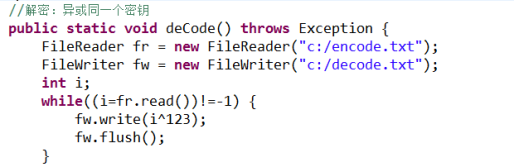
可以使用缓冲流,可以调用特有方法读取一行
操作四:对文件加密解密:原理 一个数异或同一个数两次,得到本身 3^8^8 =3