原题链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3278
算法:bfs+队列+STL(C++)
PS:bfs入门题目,好高兴啊,终于会用bfs了。
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 32679 | Accepted: 10060 |
Description
Farmer John has been informed of the location of a fugitive cow and wants to catch her immediately. He starts at a point N (0 ≤ N ≤ 100,000) on a number line and the cow is at a point K (0 ≤ K ≤ 100,000) on the same number line. Farmer John has two modes of transportation: walking and teleporting.
* Walking: FJ can move from any point X to the points X - 1 or X + 1 in a single minute
* Teleporting: FJ can move from any point X to the point 2 × X in a single minute.
If the cow, unaware of its pursuit, does not move at all, how long does it take for Farmer John to retrieve it?
Input
Output
Sample Input
5 17
Sample Output
4
Hint
Source
FJ要抓奶牛。
开始输入N(FJ的位置)K(奶牛的位置)。
FJ有三种移动方法:1、向前走一步,耗时一分钟。
2、向后走一步,耗时一分钟。
3、向前移动到当前位置的两倍N*2,耗时一分钟。
问FJ抓到奶牛的最少时间。PS:奶牛是不会动的。
思路:1、如果FJ不在奶牛后面,那么他只有一步步往后移动到奶牛位置了,即N>=K时,输出N-K即可。
2、否则bfs+队列查找(具体见下面的分析&&代码区)
相关算法:
1、STL中的队列。(PS:周四才在数据结构上了解bfs的真正思想,惭愧啊!)
需要的头文件:STL是C++中的 #include<iostream>
using namespace std;
queue队列容器的头文件 #include<queue>
queue队列的相关用法:先进先出(FIFO)
入队push() //即插入元素
出队pop() //即删除元素
front() //读取队首元素
back() //读取队尾元素
empty() //判断队列是否为空
size() //读取队列当前元素的个数
2、bfs思想:节点进行广度优先搜索的顺序。
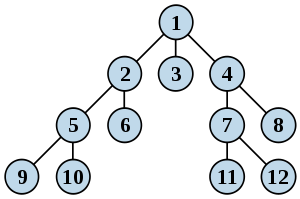
搜索实现方法(非递归):
算法思想:1.设置一个队列Q,从顶点出发,遍历该顶点后让其进队;
2.出队一个顶点元素,求该顶点的所有邻接点(对应于此题即FJ的三种走法),
对于没有遍历过的邻接点遍历之,并 让其进队;
3.若队空停止,队不空时继续第2步。
关于bfs数据结构思想的详细介绍:http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/BFS
看了牛人博客后的代码,总算了解bfs了,Orz
代码一:C++STL&&bfs版本:
//Accepted 984K 79MS C++ 1128B 2012-11-10 00:44:26
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=100001;
bool vis[maxn];//标记数组
int step[maxn];//记录到了每一位置所走的步数
queue <int> q;//定义队列
int bfs(int n,int k)
{
int head,next;
q.push(n); //开始FJ在n位置,n入队
step[n]=0;
vis[n]=true; //标记已访问
while(!q.empty()) //当队列非空
{
head=q.front(); //取队首
q.pop(); //弹出对首
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) //FJ的三种走法
{
if(i==0) next=head-1;
else if(i==1) next=head+1;
else next=head*2;
if(next<0 || next>=maxn) continue; //排除出界情况
if(!vis[next]) //如果next位置未被访问
{
q.push(next); //入队
step[next]=step[head]+1; //步数+1
vis[next]=true; //标记已访问
}
if(next==k) return step[next]; //当遍历到结果,返回步数
}
}
}
int main()
{
int n,k;
while(cin>>n>>k)
{
memset(step,0,sizeof(step));
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
if(n>=k) printf("%d\n",n-k);
else printf("%d\n",bfs(n,k));
}
return 0;
}
代码二:C语言+bfs+模拟队列版本
//Accepted 736K 0MS C++ 1017B 2012-11-10 04:24:09
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
const int maxn=100001;
bool vis[maxn];
int n,k;
struct Node
{
int x,step;
};
Node q[maxn];
int bfs()
{
int i;
Node now,next;
int head,tail;
head=tail=0;
q[tail].x=n;
q[tail].step=0;tail++;
vis[n]=true;
while(head<tail)
{
now=q[head];//取队首
head++;//弹出对首
for(i=0;i<3;i++)
{
if(i==0) next.x=now.x-1;
else if(i==1) next.x=now.x+1;
else next.x=2*now.x;
if(next.x<0 || next.x>=maxn) continue;//剪枝、排除越界
if(!vis[next.x])
{
vis[next.x]=true;
next.step=now.step+1;
q[tail].x=next.x;q[tail].step=next.step;tail++;
if(next.x==k) return next.step;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)!=EOF)
{
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
if(n>=k) printf("%d\n",n-k);
else printf("%d\n",bfs());
}
return 0;
}