一、使用SpringBoot创建web
1、简介
1)创建SpringBoot应用,选中我们需要的模块(比如:web模块,sql模块)
2)SpringBoot已经默认将这些场景配置好了,只需要在配置文件中指定少量配置就可以运行起来
3)自己编写业务代码
自动配置原理?
每引入一个场景,SpringBoot帮我们配置了什么?能不能修改配置?能修改那些配置?能不能扩展配置?等等等
xxxAutoConfiguration:帮我们给容器中自动配置组件
xxxProperties:配置类来封装配置文件的内容
比如web场景的配置:
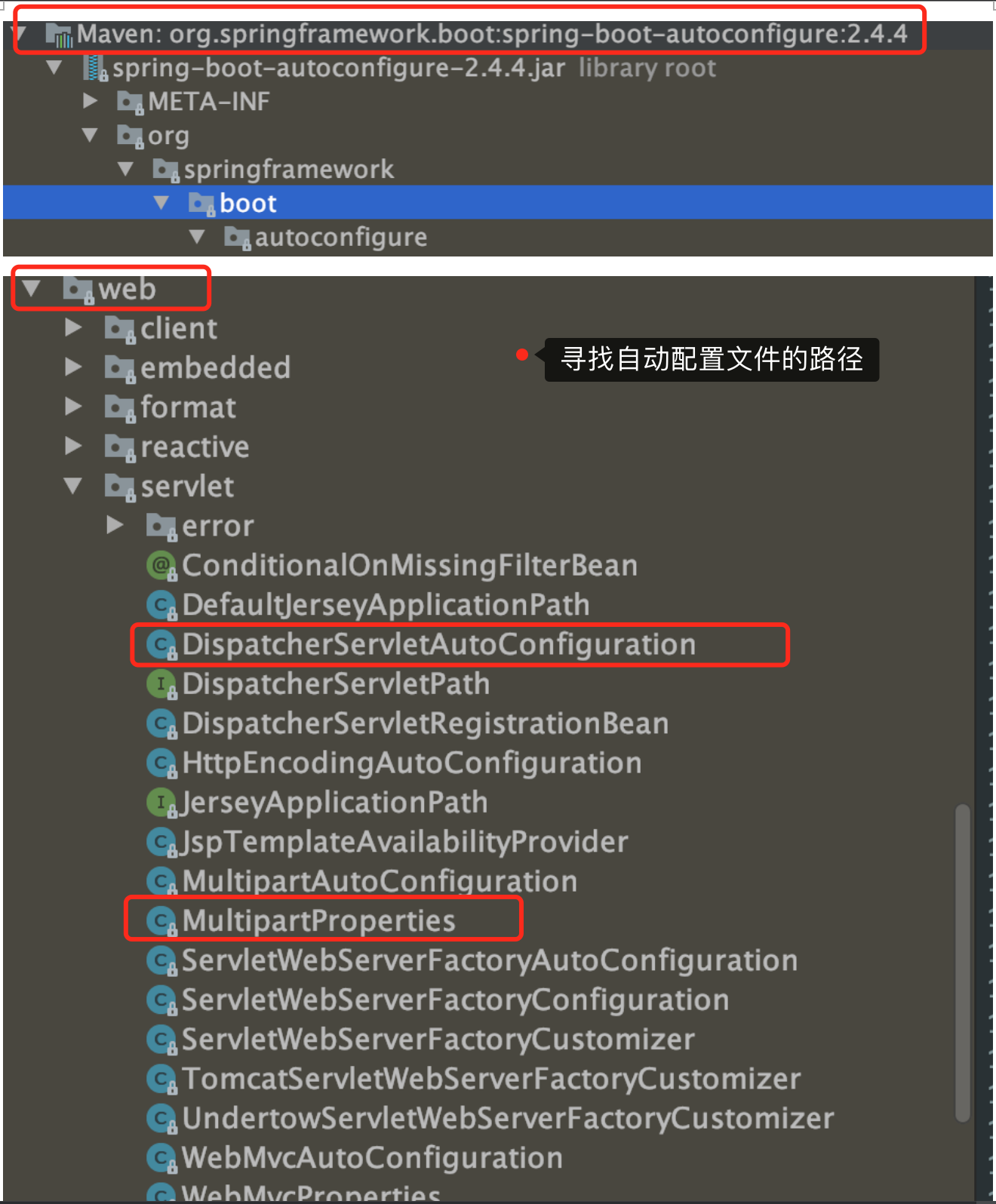
2、SpringBoot对静态资源的映射规则
WebMvcAutoConfigration.class文件
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) { super.addResourceHandlers(registry); if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled"); } else { ServletContext servletContext = this.getServletContext();
//第一种映射:在本类路径下的META-INF/resources/webjars/"找静态资源 this.addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**", "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
//第二种映射:静态资源文件夹映射 this.addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> { registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()); if (servletContext != null) { registration.addResourceLocations(new Resource[]{new ServletContextResource(servletContext, "/")}); } }); } }
1)所有的/webjars/**,都去classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"找资源
|-- webjars:以jar包的方式引入静态资源(webjars官网:https://www.webjars.org/)
|-- webjars的作用:将前端的一些jquery等以maven,lvy的形式展示
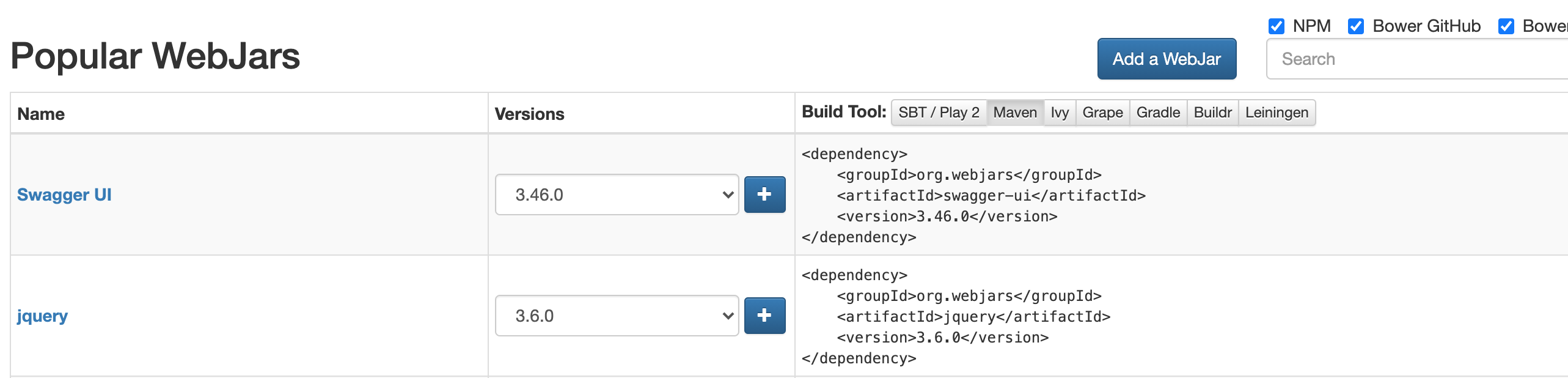
|-- 用这些文件,只需要在pom文件引入jquery的jar包
<!--引入jquery-webjars 在访问的时候只需要写webjars下面的资源名即可--> <dependency> <groupId>org.webjars</groupId> <artifactId>jquery</artifactId> <version>3.6.0</version> </dependency>
引入的webjars目录如下:
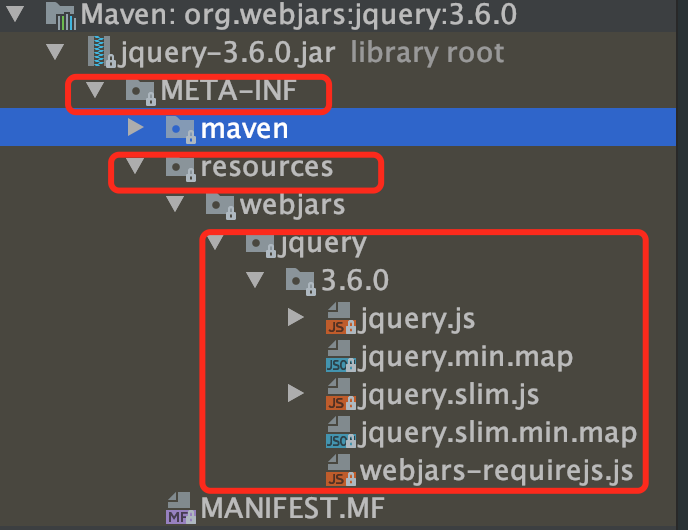
|-- 验证能不能在/META-INF/resources/webjars/路径下找到jquery
http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js 验证可以访问
2)ResourceProperties可以设置和静态资源相关的参数,缓存时间等
public static class Resources { private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"}; private String[] staticLocations; private boolean addMappings; private boolean customized; private final WebProperties.Resources.Chain chain; private final WebProperties.Resources.Cache cache;
3)"/**"访问当前项目的任何资源,都去(静态资源的文件夹)找映射
点击this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()的getStaticPathPattern()方法,查看具体方法内的元素
---> public String getStaticPathPattern() { return this.staticPathPattern; } ---> private String staticPathPattern;public WebMvcProperties() {this.staticPathPattern = "/**";
"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", 类路径下的/META-INF/resources/ 其中java文件和resources文件都是类路径,所以resources、static、public文件夹都可以在他两下面创建 "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"
"/" 当前项目的根路径
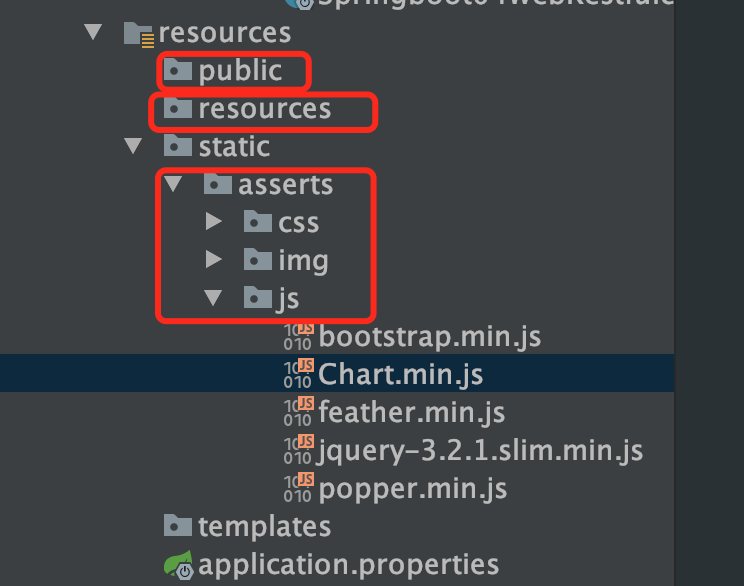
|-- 验证能不能在/META-INF/resources/路径下找到js静态文件
http://localhost:8080/asserts/js/Chart.min.js
4)欢迎页:静态资源文件夹下所有的index.html页面,被“/**”映射
WebMvcAutoConfigration.class文件 //配置欢迎页映射 @Bean public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext, FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) { WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern()); welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider)); welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(this.getCorsConfigurations()); return welcomePageHandlerMapping; }
http://localhost:8080/ 找首页
5)所有的 **/favicon.ico都是在静态资源文件下找
以上几种情况都是SpringBoot找静态资源的方式
3、模板引擎
常见模板引擎:JSP、Velocity、Freemarker、Thymeleaf
模板引擎的作用
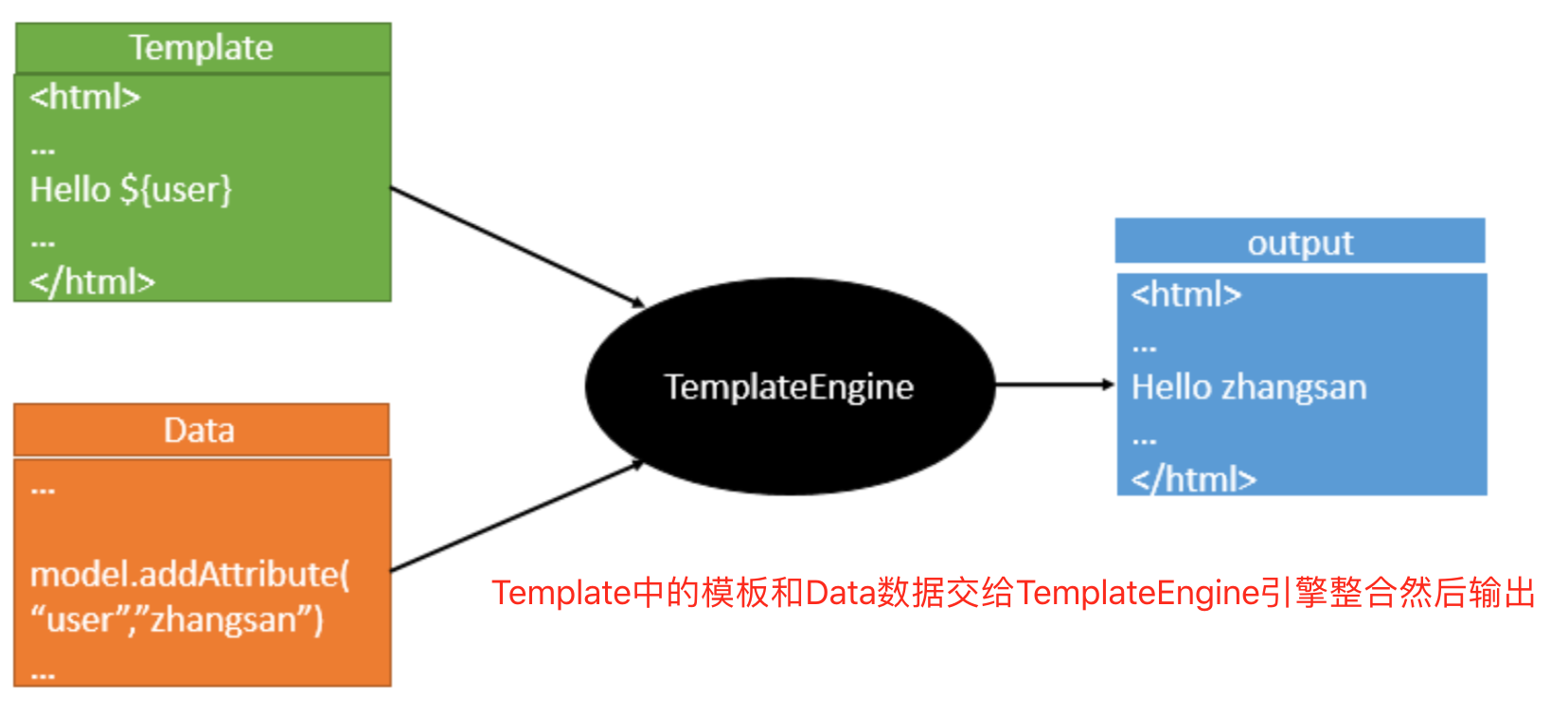
SpringBoot推荐的Thymeleaf引擎。
如何使用Thymeleaf
1)引入Thymeleaf
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId> </dependency>
2)Thymeleaf的使用及语法
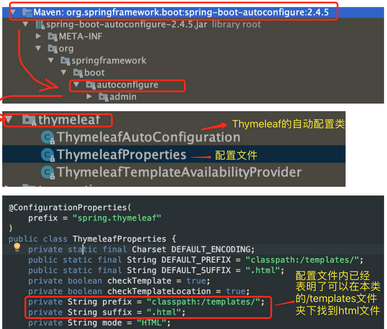
只要我们把html页面放到classpath:/templates/,thymeleaf就能渲染
|-- thymeleaf的使用
举例演示:查出业务类的一些数据,然后在页面上展示
--> resources--tempplates文件夹下新建success.html-- 导入thymeleaf的名称空间并编写文本数据
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"> <head> <title>Title</title> </head> <body> <h1>成功</h1> <div th:text="${hello}">这是显示欢迎信息</div> <!--这里的${hello}取的是HelloController类的map.put("hello","你好")中的key --> </body> </html>
-->在java.com.wufq.springboot04webrestfulcrud包下新建--controller包--HelloController类--编写内容如下:
@Controller public class HelloController { // 查出一些数据,在页面显示 @RequestMapping("/success") public String sucess(Map<String,Object> map){ map.put("hello","你好"); return "success"; } }
--> 通过页面验证

3)语法规则
|-- th:text 改变当前元素里面的文本内容
th:任意html属性,来替换原生属性的值,比如:
<div id=1001 class="mykey" th:id="${hello}" th:class="${hello}" th:text="${hello}"> th:id,th.class动态修改原生的id和class属性,
其他的th语法

|-- 表达式
Simple expressions:(表达式语法) Variable Expressions: ${...}:获取变量值;OGNL; 1)、获取对象的属性、调用方法 2)、使用内置的基本对象: #ctx : the context object. #vars: the context variables. #locale : the context locale. #request : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletRequest object. #response : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpServletResponse object. #session : (only in Web Contexts) the HttpSession object. #servletContext : (only in Web Contexts) the ServletContext object. ${session.foo} 3)、内置的一些工具对象: #execInfo : information about the template being processed. #messages : methods for obtaining externalized messages inside variables expressions, in the same way as they would be obtained using #{…} syntax. #uris : methods for escaping parts of URLs/URIs #conversions : methods for executing the configured conversion service (if any). #dates : methods for java.util.Date objects: formatting, component extraction, etc. #calendars : analogous to #dates , but for java.util.Calendar objects. #numbers : methods for formatting numeric objects. #strings : methods for String objects: contains, startsWith, prepending/appending, etc. #objects : methods for objects in general. #bools : methods for boolean evaluation. #arrays : methods for arrays. #lists : methods for lists. #sets : methods for sets. #maps : methods for maps. #aggregates : methods for creating aggregates on arrays or collections. #ids : methods for dealing with id attributes that might be repeated (for example, as a result of an iteration). Selection Variable Expressions: *{...}:选择表达式:和${}在功能上是一样; 补充:配合 th:object="${session.user}: <div th:object="${session.user}"> <p>Name: <span th:text="*{firstName}">Sebastian</span>.</p> <p>Surname: <span th:text="*{lastName}">Pepper</span>.</p> <p>Nationality: <span th:text="*{nationality}">Saturn</span>.</p> </div> Message Expressions: #{...}:获取国际化内容 Link URL Expressions: @{...}:定义URL; @{/order/process(execId=${execId},execType='FAST')} Fragment Expressions: ~{...}:片段引用表达式 <div th:insert="~{commons :: main}">...</div> Literals(字面量) Text literals: 'one text' , 'Another one!' ,… Number literals: 0 , 34 , 3.0 , 12.3 ,… Boolean literals: true , false Null literal: null Literal tokens: one , sometext , main ,… Text operations:(文本操作) String concatenation: + Literal substitutions: |The name is ${name}| Arithmetic operations:(数学运算) Binary operators: + , - , * , / , % Minus sign (unary operator): - Boolean operations:(布尔运算) Binary operators: and , or Boolean negation (unary operator): ! , not Comparisons and equality:(比较运算) Comparators: > , < , >= , <= ( gt , lt , ge , le ) Equality operators: == , != ( eq , ne ) Conditional operators:条件运算(三元运算符) If-then: (if) ? (then) If-then-else: (if) ? (then) : (else) Default: (value) ?: (defaultvalue) Special tokens: No-Operation: _
4、SpringMVC自动配置原理
Spring boot参考指南:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.10.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#boot-features-developing-web-applications
1)Spring MVC auto-configuration
SpringBoot自动配置好了SpringMVC
以下是SpringBoot对SpringMVC的默认配置:(WebMvcAutoConfiguration)
-
Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans(包含ContentNegotiatingViewResolver和BeanNameViewResolver bean)- 自动配置了ViewResolver(视图解析器:根据方法的返回值得到视图对象(View),视图对象决定如何渲染(转发?重定向?))
- ContentNegotiatingViewResolver:组合所有的视图解析器的;
- ==如何定制:我们可以自己给容器中添加一个视图解析器;自动的将其组合进来;==
-
Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (see below).(支持提供静态资源,包括支持webjars)
-
Static
index.htmlsupport. (支持静态首页访问) -
Custom
Faviconsupport (see below). (支持favicon.ico) -
自动注册了 of
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatterbeans.- Converter:转换器; public String hello(User user):类型转换使用Converter
Formatter格式化器; 2017.12.17===Date;
@Bean @ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc", name = "date-format")//在文件中配置日期格式化的规则 public Formatter<Date> dateFormatter() { return new DateFormatter(this.mvcProperties.getDateFormat());//日期格式化组件 }
自己添加的格式化器转换器,我们只需要放在容器中即可==
-
Support for
HttpMessageConverters(see below).-
HttpMessageConverter:SpringMVC用来转换Http请求和响应的;User---Json;
-
HttpMessageConverters是从容器中确定;获取所有的HttpMessageConverter;==自己给容器中添加HttpMessageConverter,只需要将自己的组件注册容器中(@Bean,@Component)==
-
-
Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(see below).定义错误代码生成规则 -
Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (see below).==我们可以配置一个ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer来替换默认的;(添加到容器)==
初始化WebDataBinder;
请求数据=====JavaBean;
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc.
如果你想完全控制Spring MVC,你可以添加你自己的@Configuration注解@EnableWebMvc。
2)扩展SpringMVC
如果想实现下面SpringMVC配置文件的内容
<mvc:view-controller path="/hello" view-name="success"/> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <mvc:mapping path="/hello"/> <bean></bean> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors>
可以通过编写一个配置类(@Configuration),是WebMvcConfigurerAdapter类型,不能标注@EnableWebMvc
特点:即保留了所有的自动配置,也能用我们扩展的配置
@Configuration public class MyMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { // 重写增加视图 @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { // super.addViewControllers(registry); //浏览器发送/wufq请求到success页面 registry.addViewController("/wufq").setViewName("success"); } }
原理:
|-- WebMvcConfigurerAdapter是SpringMVC的自动配置类
@Import({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class}) @EnableConfigurationProperties({WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class, WebProperties.class}) @Order(0) public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer { private final WebMvcProperties mvcProperties;
|-- 在做其他自动配置时会导入:@Import({WebMvcAutoConfiguration.EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class})
深入EnableWebMvcConfiguration类 -->父类DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
@Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) @EnableConfigurationProperties({WebProperties.class}) public static class EnableWebMvcConfiguration extends DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration implements ResourceLoaderAware { private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(WebMvcConfigurer.class); @Configuration( proxyBeanMethods = false ) public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite(); public DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration() { }
//从容器中获取所有的WebMvcConfigurer @Autowired( required = false ) public void setConfigurers(List<WebMvcConfigurer> configurers) { if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(configurers)) { this.configurers.addWebMvcConfigurers(configurers);
|--容器中所有的WebMvcConfigurer都会一起起作用
|-- 我们的配置类也会被调用
效果:SpringMVC的自动配置和我们的扩展配置都会起作用
3)全面接管SpringMVC
SpringBoot对SpringMVC的自动配置不需要了,所有都是我们的配置,所有的自动配置都会失效
我们需要在配置类上加上@EnableWebMvc
二、web开发试验
1、默认访问首页
|-- 首先引入资源(html的静态页面)

|-- 访问首页有两种方式
1)不用SpringMVC,而是采用方法找静态资源的方式
@RequestMapping({"/","/index.html"})
public String index(){
return "login";
}
2)采用SpringMVC的配置类,重写增加视图控制器方法,设置templates引擎内静态文件指定访问路径
// 所有的WebMvcConfigurerAdapter组件都会一起起作用 @Bean //将所有的组件注册到容器中 public WebMvcConfigurerAdapter webMvcConfigurerAdapter(){ //WebMvcConfigurerAdapter是一个抽象类,必须实现抽象类的方法 WebMvcConfigurerAdapter adapter = new WebMvcConfigurerAdapter(){ //重写增加视图addViewControllers方法 @Override public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) { registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("login"); registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("login"); } }; return adapter; }
注意:一定要把组件注册到容器中,否则SpringBoot找不到组件
|-- 修改页面的资源引用
修改为我们自己引入的路径
<!--修改为我们自己引入的路径 -->
<!-- Bootstrap core CSS -->
<link href="asserts/css/bootstrap.min.css" th:href="@{/webjars/bootstrap/5.0.0-beta3/css/bootstrap.css}" rel="stylesheet">
<!-- Custom styles for this template -->
<link href="asserts/css/signin.css" th.href="@{asserts/css/signin.css}" rel="stylesheet">
</head>
<body class="text-center">
<form class="form-signin" action="dashboard.html">
<img class="mb-4" th:src="@{asserts/img/bootstrap-solid.svg}"
2、实现登录功能
输入任意用户名和密码可以登录,登录成功后进入首页,点击首页的列表按钮进入列表页面