2019-08-10
此类文章网上很多,偷个懒,转了一篇比较全的文章
1、什么是yum仓库?
yum仓库就是使用yum命令下载软件的镜像地址。
我们通常使用 yum install 命令来在线安装 linux系统的软件, 这种方式可以自动处理依赖性关系,并且一次安装所有依赖的软体包,但是经常会遇到从国外镜像下载速度慢,无法下载的情况。那么此时我们就需要把我们的yum 源改为国内的镜像。
yum的配置文件
yum 的配置文件在 /etc/yum.repos.d 目录下, 其中有多个配置文件,每一个配置文件中都可以配置一个或多个repository, 但是最终会被合并为一个交给系统,所以多个文件只是为了方便管理。
2、yum仓库配置
下面提供了 阿里和 清华大学 两个镜像仓库配置操作说明,=实际使用时,选择其中一个配置即可。
2.1、配置 阿里镜像仓库
进入阿里镜像仓库网站 https://opsx.alibaba.com/mirror

找到centos,点击右边的 帮助 ,看到阿里镜像仓库给出的yum的配置说明。
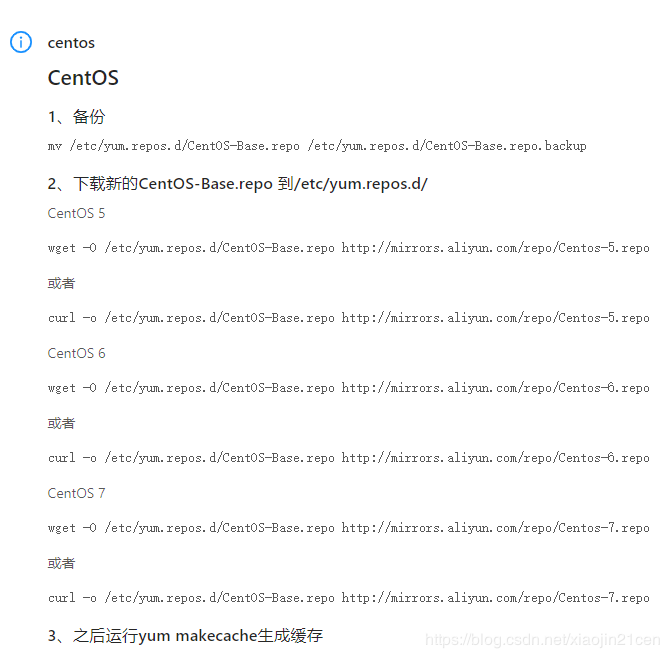
2.1.1、配置步骤
根据官网的说明,我们详细说说每步骤的意思。
(1)、备份,将 CentOS-Base.repo 为CentOS-Base.repo.backup
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.backup
(2)、下载新的 http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo,并命名为CentOS-Base.repo
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo 或者 curl -o /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/Centos-7.repo
(3)、清除缓存
yum clean all # 清除系统所有的yum缓存
yum makecache # 生成yum缓存
yum update
2.1.2、epel源 安装和配置
(1)、查看可用的epel源
[java@localhost yum.repos.d]$ yum list | grep epel-release epel-release.noarch 7-11 extras [java@localhost yum.repos.d]$
(2)、安装 epel
[java@localhost yum.repos.d]$ yum install -y epel-release
......省略.....
(3)、配置阿里镜像提供的epel源
wget -O /etc/yum.repos.d/epel-7.repo http://mirrors.aliyun.com/repo/epel-7.repo
4、清除缓存
yum clean all # 清除系统所有的yum缓存
yum makecache # 生成yum缓存
yum update
2.1.3、查看yum源
查看所有的yum源:
yum repolist all
查看可用的yum源:
yum repolist enabled
2.2、配置 清华大学镜像仓库
地址: https://mirrors.cnnic.cn/
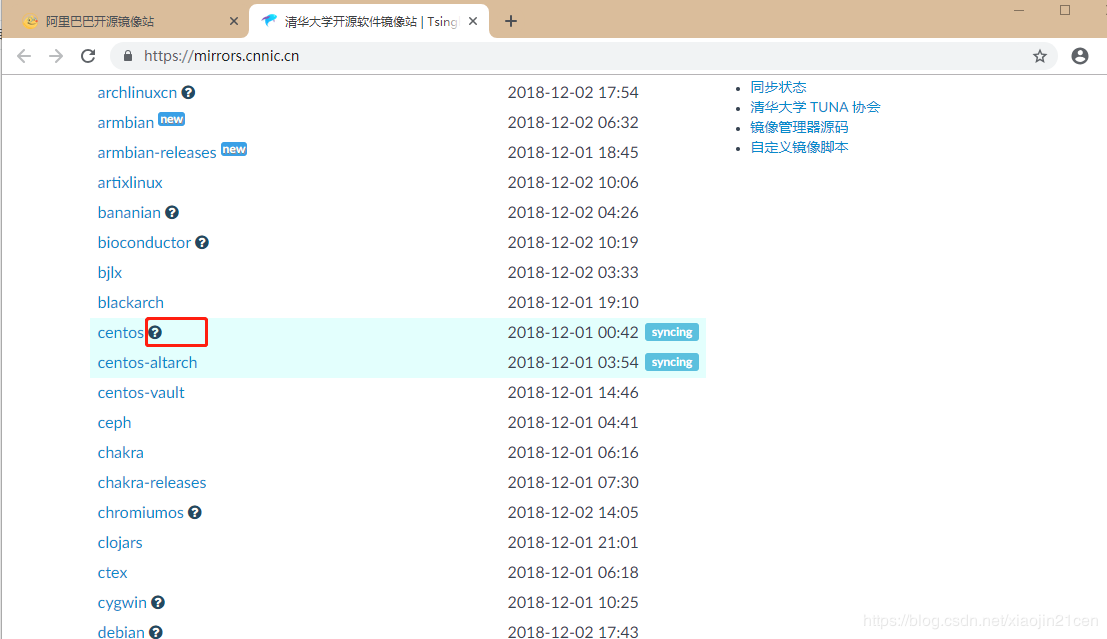
点击 ? 进入帮助说明页面 https://mirrors.cnnic.cn/help/centos/。
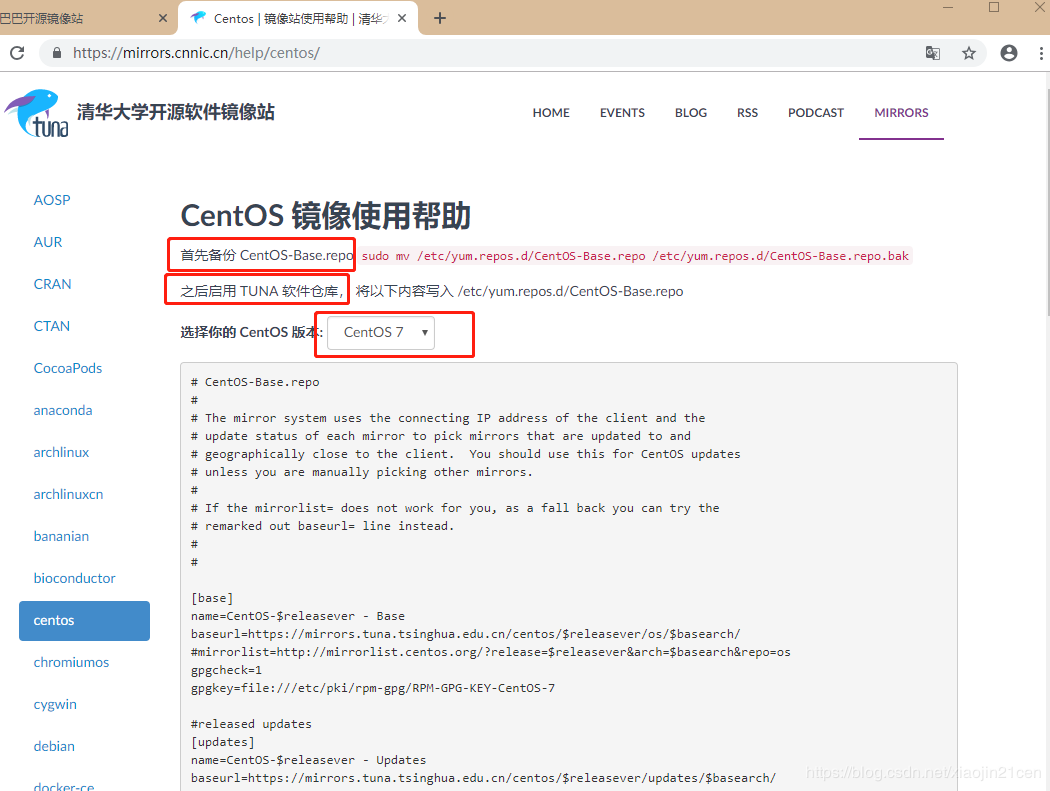
页面提供了 CentOS5,CentOS6、CentOS7 的镜像仓库配置,下面列出的是CentOS7的配置。
(1)、首先备份 CentOS-Base.repo
mv /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo.bak
(2)、之后启用 TUNA 软件仓库, 将清华大学镜像仓库信息写入 /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/CentOS-Base.repo 将 CentOS-Base.repo 中的内容 更新为 下面的内容: # CentOS-Base.repo # # The mirror system uses the connecting IP address of the client and the # update status of each mirror to pick mirrors that are updated to and # geographically close to the client. You should use this for CentOS updates # unless you are manually picking other mirrors. # # If the mirrorlist= does not work for you, as a fall back you can try the # remarked out baseurl= line instead. # # [base] name=CentOS-$releasever - Base baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/os/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=os gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #released updates [updates] name=CentOS-$releasever - Updates baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/updates/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=updates gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #additional packages that may be useful [extras] name=CentOS-$releasever - Extras baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/extras/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=extras gpgcheck=1 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7 #additional packages that extend functionality of existing packages [centosplus] name=CentOS-$releasever - Plus baseurl=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/centos/$releasever/centosplus/$basearch/ #mirrorlist=http://mirrorlist.centos.org/?release=$releasever&arch=$basearch&repo=centosplus gpgcheck=1 enabled=0 gpgkey=file:///etc/pki/rpm-gpg/RPM-GPG-KEY-CentOS-7
(3)、清除缓存
yum clean all # 清除系统所有的yum缓存
yum makecache # 生成yum缓存
yum update
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xiaojin21cen/article/details/84726193