结构中不同成员的存储形式并不是像想像中那样,一个接着一个的分配内存空间。如某些机器的整型变量的长度是4个字节,同时它需要起始存储位置能够被4整除。
如下代码:

#include<stdio.h> #include<stddef.h> struct D { char a; int b; char c; float d; char e; double f; char g; int h[20]; }data1; struct F { double f; float d; int b; int h[20]; char a; char c; char e; char g; }data2; struct E { int a; char b; char c; }; int main() { printf("size of struct D:%d ",sizeof(struct D)); printf("size of struct F:%d ",sizeof(struct F)); printf("size of struct F:%d ",sizeof(struct E)); printf(" struct D: "); printf(" char a: %d ",offsetof(struct D,a)); printf(" int b: %d ",offsetof(struct D,b)); printf(" char c: %d ",offsetof(struct D,c)); printf(" float d: %d ",offsetof(struct D,d)); printf(" char e: %d ",offsetof(struct D,e)); printf(" double f: %d ",offsetof(struct D,f)); printf(" char g: %d ",offsetof(struct D,g)); printf("int h[20]: %d ",offsetof(struct D,h)); printf(" h[0]: %d ",offsetof(struct D,h[0])); printf(" h[1]: %d ",offsetof(struct D,h[1])); printf(" h[19]: %d ",offsetof(struct D,h[19])); printf("% struct F: "); printf(" double f: %d ",offsetof(struct F,f)); printf(" float d: %d ",offsetof(struct F,d)); printf(" int b: %d ",offsetof(struct F,b)); printf("int h[20]: %d ",offsetof(struct F,h)); printf(" h[0]: %d ",offsetof(struct F,h[0])); printf(" h[1]: %d ",offsetof(struct F,h[1])); printf(" h[19]: %d ",offsetof(struct F,h[19])); printf(" char a: %d ",offsetof(struct F,a)); printf(" char c: %d ",offsetof(struct F,c)); printf(" char e: %d ",offsetof(struct F,e)); printf(" char g: %d ",offsetof(struct F,g)); }

size of struct D:120 size of struct F:104 size of struct F:8 struct D: char a: 0 int b: 4 char c: 8 float d: 12 char e: 16 double f: 24 char g: 32 int h[20]: 36 h[0]: 36 h[1]: 40 h[19]: 112 struct F: double f: 0 float d: 8 int b: 12 int h[20]: 16 h[0]: 16 h[1]: 20 h[19]: 92 char a: 96 char c: 97 char e: 98 char g: 99 -------------------------------- Process exited after 0.03223 seconds with return value 14 请按任意键继续. . .
struct D 的内存分配形式(假定初始位置为100这里用0代替以此类推)
(黑色填充的代表被占用,白色的代表是空闲的)
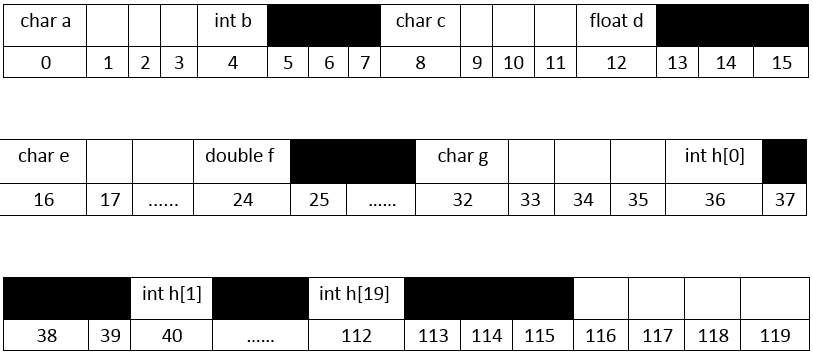
通过这个代码可以看出结构成员如何分配内存的。
它们在结果所分配的时候从初始位置为零算起,必须能被它们在内存中所占的字节数整除,如 int 在占字节数是4的机器中就要求必须能够被4整除,double 所占字节为8位的话,那么就要能被8整除,如果前一个成员的紧接着的内存不满足这个条件,那么就把不符合的位置空出来,起到对齐的效果。同时从整个结构来看,如果整个结构中只有 char 类型那么结构所占的字节数就和成员个数相同,如果在结构中有 double 那么结构的最后必须能够被 double 所占的字节数整除(这里认为它是8),如果没有 只有 int ,float 等4字节的类型,那么结构所占字节就必须能够被4整数。
#include<stdio.h> #include<stddef.h> struct E { double a; int b; char c; char d; char e; char f; char g; }; int main() { printf("size of struct E:%d ",sizeof(struct E)); printf("%d",offsetof(struct E,g)); }
size of struct E:24 16 -------------------------------- Process exited after 0.03793 seconds with return value 2 请按任意键继续. . .
#include<stdio.h> #include<stddef.h> struct E { char e; char f; char g; }; int main() { printf("size of struct E:%d ",sizeof(struct E)); }
size of struct E:3 -------------------------------- Process exited after 0.01826 seconds with return value 19 请按任意键继续. . .
#include<stdio.h> #include<stddef.h> struct E { int a; char b; char c; char d; char e; char f; }; int main() { printf("size of struct E:%d ",sizeof(struct E)); }
size of struct E:12 -------------------------------- Process exited after 0.01588 seconds with return value 20 请按任意键继续. . .
结构的存储所占字节数,必须能够被它成员类型中所占字节最大的数值整除,不满足的内存位置都会被空出来。
在代码中我们用到了 offsetof 这个宏 ,它是在 stddef.h 头文件中定义的 #define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ,TYPE 是结构类型 MEMBER 是成员名,这个表达式的结构是一个 size_t 值,表示这个成员起始存储位置距离结构开始存储的位置的偏移的字节数。
如果一个程序中结构中的成员数量很少,或者结果的数量很少,并且你希望结构中的成员按照某种有意义的顺序进行存储,那么你可以有充分的理由不对结构中的成员按照最节省空间的方式进行排序。但是如果程序中的结构很多那么最紧迫需要的解决的就是空间浪费的问题。
