ManualResetEvent表示线程同步事件,可以对所有进行等待的线程进行统一管理(收到信号时必须手动重置该事件)
其构造函数为:
public ManualResetEvent (bool initialState);
参数 initialState 表示是否初始化,如果为 true,则将初始状态设置为终止(不阻塞);如果为 false,则将初始状态设置为非终止(阻塞)。
注意:如果其参数设置为true,则ManualResetEvent等待的线程不会阻塞。 如果初始状态为false, 则在Set调用方法之前, 将阻止线程。
它只有两个方法
//将事件状态设置为终止状态,从而允许继续执行一个或多个等待线程。 public bool Set (); //将事件状态设置为非终止,从而导致线程受阻。 public bool Reset (); //返回值:操作成功返回true,否则false
讲了这么多,看个例子理解一下
using System; using System.Threading; public class Example { // mre is used to block and release threads manually. It is // created in the unsignaled state. private static ManualResetEvent mre = new ManualResetEvent(false); static void Main() { Console.WriteLine(" Start 3 named threads that block on a ManualResetEvent: "); for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++) { Thread t = new Thread(ThreadProc); t.Name = "Thread_" + i; t.Start(); //开始线程 } Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine(" When all three threads have started, press Enter to call Set()" + " to release all the threads. "); Console.ReadLine(); mre.Set(); Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine(" When a ManualResetEvent is signaled, threads that call WaitOne()" + " do not block. Press Enter to show this. "); Console.ReadLine(); for (int i = 3; i <= 4; i++) { Thread t = new Thread(ThreadProc); t.Name = "Thread_" + i; t.Start(); } Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine(" Press Enter to call Reset(), so that threads once again block" + " when they call WaitOne(). "); Console.ReadLine(); mre.Reset(); // Start a thread that waits on the ManualResetEvent. Thread t5 = new Thread(ThreadProc); t5.Name = "Thread_5"; t5.Start(); Thread.Sleep(500); Console.WriteLine(" Press Enter to call Set() and conclude the demo."); Console.ReadLine(); mre.Set(); // If you run this example in Visual Studio, uncomment the following line: //Console.ReadLine(); } private static void ThreadProc() { string name = Thread.CurrentThread.Name; Console.WriteLine(name + " starts and calls mre.WaitOne()"); mre.WaitOne(); //阻塞线程,直到调用Set方法才能继续执行 Console.WriteLine(name + " ends."); } }
结果如下
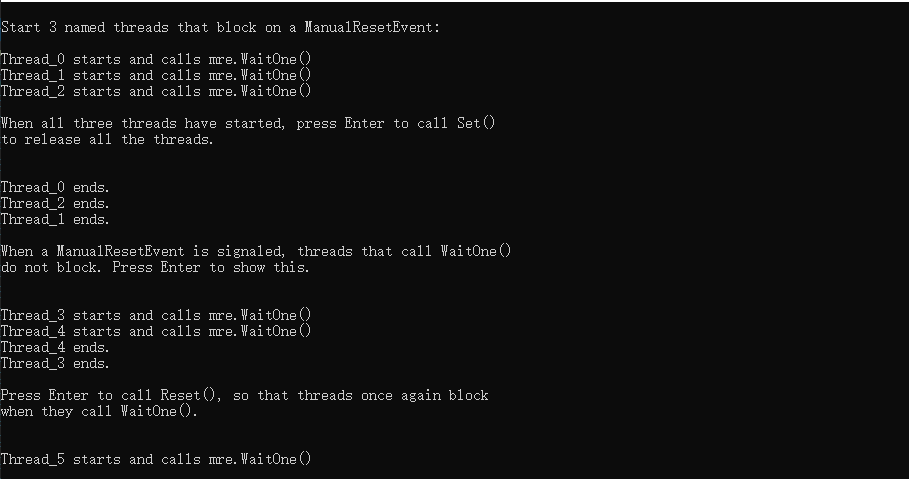
过程:
该示例以信号状态ManualResetEvent( false即传递给构造函数的) 开头。 三个线程, 每个线程在调用其WaitOne方法时被阻止。 当用户按Enter键时, 该示例调用Set方法, 该方法释放所有三个线程,使其继续执行。
再次按 " enter " 键, 此时ManualResetEvent在调用Reset方法之前, 一直保持终止状态,因此这些线程在调用WaitOne方法时不会被阻止, 而是运行到完成。即对应上述(收到信号时必须手动重置该事件)
再次按enter键将导致该示例调用Reset方法, 并启动一个线程, 该线程在调用WaitOne时将被阻止。 按enter键, 最后一次调用Set以释放最后一个线程, 程序结束。
如果还不是很清楚可以复制代码进行单步调试,这样就能明白了!